Surface anatomy
Surface anatomy (also called superficial anatomy and visual anatomy) is the study of the external features of the body of an animal.[1] In birds this is termed topography. Surface anatomy deals with anatomical features that can be studied by sight, without dissection. As such, it is a branch of gross anatomy, along with endoscopic and radiological anatomy.[2] Surface anatomy is a descriptive science.[citation needed] In particular, in the case of human surface anatomy, these are the form and proportions of the human body and the surface landmarks which correspond to deeper structures hidden from view, both in static pose and in motion.
In addition, the science of surface anatomy includes the theories and systems of body proportions and related artistic canons.[citation needed] The study of surface anatomy is the basis for depicting the human body in classical art.
Some pseudo-sciences such as physiognomy, phrenology and palmistry rely on surface anatomy.
Human surface anatomy
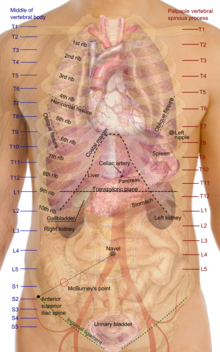
Surface anatomy of the thorax

First heart sound: caused by atrioventricular valves - Bicuspid/Mitral (B) and Tricuspid (T).
Second heart sound caused by semilunar valves -- Aortic (A) and Pulmonary/Pulmonic (P).
Knowledge of the surface anatomy of the thorax (chest) is particularly important because it is one of the areas most frequently subjected to physical examination, like auscultation and percussion.[3] In cardiology, Erb's point refers to the third intercostal space on the left sternal border where S2 heart sound is best auscultated.[4][5] Some sources include the fourth left interspace.[6]
Human female breasts are located on the chest wall, most frequently between the second and sixth rib.[3]
Anatomical landmarks
- On the trunk of the body in the thoracic area, the shoulder in general is the acromial, while the curve of the shoulder is the deltoid.
- The back as a general area is the dorsum or dorsal area, and the lower back as the limbus or lumbar region.
- The shoulderblades are the scapular area and the breastbone is the sternal region.
- The abdominal area is the region between the chest and the pelvis.
- The breast is called the mamma or mammary, the armpit as the axilla and axillary, and the navel as the umbilicus and umbilical.
- The pelvis is the lower torso, between the abdomen and the thighs.
- The groin, where the thigh joins the trunk, are the inguen and inguinal area.
- The entire arm is referred to as the brachium and brachial, the front of the elbow as the antecubitis and antecubital, the back of the elbow as the olecranon or olecranal, the forearm as the antebrachium and antebrachial, the wrist as the carpus and carpal area, the hand as the manus and manual, the palm as the palma and palmar, the thumb as the pollex, and the fingers as the digits, phalanges, and phalangeal.
- The buttocks are the gluteus or gluteal region and the pubic area is the pubis.
- Anatomists divide the lower limb into the thigh (the part of the limb between the hip and the knee) and the leg (which refers only to the area of the limb between the knee and the ankle).
- The thigh is the femur and the femoral region.
- The kneecap is the patella and patellar while the back of the knee is the popliteus and popliteal area.
- The leg (between the knee and the ankle) is the crus and crural area, the lateral aspect of the leg is the peroneal area, and the calf is the sura and sural region.
- The ankle is the tarsus and tarsal, and the heel is the calcaneus or calcaneal. The foot is the pes and pedal region, and the sole of the foot the planta and plantar.
- As with the fingers, the toes are also called the digits, phalanges, and phalangeal area.
- The big toe is referred to as the hallux.
List of features
Following are lists of surface anatomical features in humans and other animals. Sorted roughly from head to tail, cranial to caudal. Homologues share a bullet point and are separated by commas. Subcomponents are nested. Class in which component occurs in italic.
In humans
In other animals
- Head
- Tentacle Cephalopoda
- Throat
- Vertebral column (extends dorsally
- Abdomen (roughly Stomach)
See also
- Anatomy
- Inspection (medicine)
- List of human anatomical features
- List of images in Gray's Anatomy: XII. Surface anatomy and Surface Markings
- Palpation
Notes
- ^ Seeley (2003) chap.1 p.2
- ^ Standring (2008) Introduction, Anatomical nomenclature, p.2
- ^ a b Drake (2009) Ch.3 Thorax - Thorax surface anatomy, pp. 224-6 and Fig. 3.96 A
- ^ "Week 4". Archived from the original on 2008-01-29. Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ Gavaghan, Mary (1998). "Cardiac anatomy and physiology: a review - includes examination questions AORN Journal - Find Articles". AORN Journal. Archived from the original on 2012-07-10. Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ Constant, Jules (1999). Bedside cardiology. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 228. ISBN 0-7817-2168-7.
References
- Drake, Richard; Vogl, A. Wayne; Mitchell, Adam W. M. (2009). Gray's Anatomy for Students (2nd ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 157–164, 311–320, 538–547, 686–694, 882–892, 1097–1110, 1514–1524. ISBN 9781437720556. Retrieved 28 February 2014.
- Seeley, Rod R.; Stephens, Trent D.; Tate, Philip (2002). Anatomy & physiology (6th ed.). McGraw & Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-235113-2.
- Standring, Susan (2008) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 39th Edition. ISBN 978-0-443-07168-3. Human surface anatomy photos at pp. 947, 1406-1410 Figs. 56.3, 110.12, 110.13, 110.15, 110.22
Further reading
- Frederick, Roland Becker; Wilson, James Walter; Gehweiler, John A. (1971). The anatomical basis of medical practice (illustrated ed.). Williams and Wilkins.
- Lumley, John S. P. (2008). Surface Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Examination (4th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-0-7020-4776-3. Retrieved 28 February 2014.
- Rohen, Johannes Wilhelm; Yokochi, Chihiro; Lütjen-Drecoll, Elke (2011). Color Atlas of Anatomy – A Photographic Study of the Human Body (7th ed.). Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 204–5, 476–7. ISBN 978-1-58255-856-1.
- Sheppard, Joseph (1991). Drawing the Living Figure. Dover Publications, Incorporated. ISBN 0-486-26723-7.

