White Sands Missile Range
New Mexico Joint Guided Missile Test Range (1947) White Sands Proving Ground (1945) Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range (1941)[2] | |
|---|---|
| Part of United States Army Test and Evaluation Command | |
| Located in the San Andres Mountains, the Oscura Mountains, the San Augustin Mountains, the Tularosa Basin, and the Chupadera Mesa in New Mexico | |
 Most of the northern Tularosa basin (blue) is used for the WSMR (area within dashed perimeter), which encloses numerous areas that are not military land (e.g., the NPS's White Sands National Park), as well as USAF facilities. | |
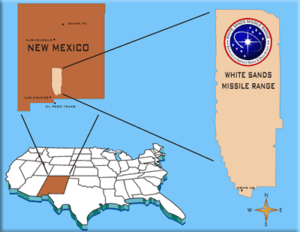 WSMR location | |
| Coordinates | 32°20′08″N 106°24′21″W / 32.33556°N 106.40583°W[3] Condron Army Airfield near the southernmost WSMR point |
| Site information | |
| Controlled by | United States Army |
| Website | www |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1948-07-09 cantonment completed[4] 1957-02: Launch Complex 37 completed |
| Built by | Ordnance Corps[4] |
| Garrison information | |
| Current commander | BG David C. Trybula (2019–present)[5] |
| Past commanders |
|
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a military testing area operated by the United States Army. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9 July 1945. White Sands National Park is located within the range.
Significant events
- The first atomic bomb (code named Trinity) was test detonated at Trinity Site near the northern boundary of the range on 16 July 1945, seven days after the White Sands Proving Ground was established.[7]
- After the conclusion of World War II, 100 long-range German V-2 rockets that were captured by U.S. military troops were brought to WSMR. Of these, 67 were test fired between 1946 and 1951 from the White Sands V-2 Launching Site. (This was followed by the testing of American rockets, which continues to this day, along with testing other technologies.)
- NASA's Space Shuttle Columbia landed on the Northrup Strip at WSMR on 30 March 1982 as the conclusion to mission STS-3.[8] This was the only time that NASA used WSMR as a landing site for the space shuttle.

Incidents
- Circa 30 May 1947, a German V-2 sounding rocket fired from White Sands Proving Ground veered off course, crashed and exploded on top of a rocky knoll 3.5 miles south of the Juarez, Mexico business district.[9]
- On 11 July 1970, the United States Air Force launched an Athena sounding rocket, equipped with re-entry vehicle V-123-D, from the Green River Launch Complex in Utah. While its intended target was inside of WSMR, the rocket instead flew south and impacted 180–200 miles south of the Mexican border in the Mapimi Desert in the northeastern corner of the Mexican state of Durango.[10]
Geography
The largest military installation in the United States, WSMR encompasses almost 3,200 sq mi (8,300 km2) that includes parts of five counties in southern New Mexico:
Nearby military bases
- WSMR borders the 600,000-acre (2,400 km2) McGregor Range Complex at Fort Bliss to the south (southeast Tularosa Basin and on Otero Mesa[11]) making them contiguous areas for military testing.[12]
- Holloman AFB borders WSMR to the east.
Nearby cities
- Las Cruces, New Mexico to the west.
- Alamogordo, New Mexico to the east.
- Chaparral, New Mexico to the south.
- El Paso, Texas to the south.
National park and wildlife refuge
The following federally-protected natural areas are contained within the borders of WSMR:
Transportation
Major highways
- U.S. Highway 70 traverses the southern part of the range in a west-northeast direction and is subject to periodic road closures during test firings at the range.
- NM 213 enters the range from the south from Chaparral, New Mexico and terminates at U.S. Highway 70.
Nearby airports
- Las Cruces International Airport – No current regularly scheduled commercial passenger flights since 25 July 2005, when Westward Airways ceased operations. General aviation, New Mexico Army National Guard (4 UH-72 Lakota Helicopters), private charters and CAP use the airport, among others.
- El Paso International Airport – Nearest airport with regularly scheduled commercial flights.
National Historic Landmarks
Designated historic sites on WSMR land include:
- Trinity Site: Selected in November 1944 for the Trinity nuclear test conducted on 16 July 1945[13] (National Historic Landmark district on 21 December 1965,[14][15] NRHP on 15 October 1966).[16]
- White Sands V-2 Launching Site: A V-2 static test firing was 15 March 1946, and the first US V-2 launch was 16 April 1946 (landmark designation 3 October 1985).[17][18]
Current operations

The White Sands Test Center headquartered at the WSMR "Post Area" has branches for Manned Tactical Systems & Electromagnetic Radiation and conducts missile testing and range recovery operations.[19] Other operations on WSMR land include:
- The Launch Abort Flight Test Complex for the Pad Abort-1
- White Sands Launch Complex 37, built for Nike Hercules tests
- White Sands Launch Complex 38, built for Nike Zeus tests with Launch Control Building now used for Patriot missile firings
- "WSMR Main Post", which includes several smaller areas such as the housing area, golf course, "Navy Area", and "Technical Area"[20] (a recreational shooting range just inside the "El Paso gate" on the south is outside of the Post Area.)
- WSMR Museum tours and exhibits, which include V-2 rocket returned in May 2004 after restoration.
- White Sands Hall of Fame, which inducts members such as the first range commander (1945–1947), Col. Harold Turner, in 1980.[21]
- 1972 DoD Centers for Countermeasures (CCM), which evaluate precision guided munitions and other devices in electronic counter- and counter-countermeasures environments.[22]
- 1963 NASA White Sands Test Facility's ground station for Tracking and Data Relay Satellites and the SDO ground station with 2 18 m (59 ft) antennas.
- The North Oscura Peak facility of the AFRL Directed Energy Directorate
Chronology
- 1930: Robert Goddard began rocket testing in New Mexico.
- 1941-04-13: US World War II preparations established[13] the Army Air Base, Alamogordo:[23] 1942 Biggs Army Airfield construction began near El Paso (1947 Biggs AFB, 1973 Biggs AAF)--the region's nearby Deming AAF, Ft Sumner AAF, and South Aux Fid #1 transferred to "Army Div Engrs" in 1946.[24]
- 1940s: When the range was formed, ranchers' land was leased and, in the 1970s, taken permanently to expand the area available for testing.[25]
USAAF ranges
- 1941-12: Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range established near the "West Texas Bombardier Triangle".
- 1941-12: Executive Order No. 9029[2][verification needed] canceled grazing leases on the newly established Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range.
- 1942-07: Goddard's rocket research group moved from Roswell, New Mexico, to Annapolis, Maryland.
- 1944-02: War Department and the Corps of Engineers' Ordnance Department teams looked for a US missile test site.[26]
- 1945-07-13: McDonald Ranch House, Manhattan Project location for the final assembly of the prototype Fat Man plutonium bomb.
- 1945-07-16: Trinity test of the plutonium bomb, the first nuclear weapon tested in the world.
White Sands Proving Ground
- 1945-02-20: The Secretary of War approved establishment of WSPG.[27]: 246 [26]
- 1945-04-01: The first Private F launch[28] was at WSPG. (Not Fort Bliss's Antiaircraft and Guided Missile Center, which was established 6 July 1946.)[29]
- 1945-06-25: WSPG construction began with drilling of water wells.[13]
- 1945-07: First of 300 railroad cars of German V-2 components began to arrive at Las Cruces, New Mexico.[27]: 246
- 1945-09: The blockhouse at Army Launch Area 1 (later Launch Complex 33) was completed.[13]
- 1945-09-16: First WAC Corporal test firing.[27]: 253
- 1945-11: GE contractors began to identify, sort, and reassemble V-2 components in Building 1538 (Assembly Building 1).
- 1946: 35 of the Operation Paperclip scientists from Germany were working at WSPG.[30]
- 1946-05-26: The 4th U.S. V-2 launch was tracked by "two[where?] AN/MPQ-2 stations".[31]
- 1946 summer: New WSPG quarters were completed and the Medical Detachment and 3 batteries moved from Ft Bliss.[32]
- 1946-09: First static firing of a Nike missile was at WSPG.[33]
New Mexico Joint Guided Missile Test Range
- 1947 (late):[34][verification needed] A merging of military areas (e.g., former USAAF bombing range and the smaller WSPG) established the "New Mexico Joint Guided Missile Test Range".[35]
- 1947-11-14:[verification needed] The USAF's Alamogordo Guided Missile Test Base (AGMTB) on the range had its first GAPA missile launch (39th for GAPA and first with a ramjet).[36]
- 1948–05 to 1949-4: First six flight attempts for the Project Bumper two-stage V-2 SRBM/WAC Corporal two-stage research vehicles as the world's first "high-speed" multistage rockets to be launched.
- 1948-07: USAF Project MX–774 commenced with the first RTV-A-2 Hiroc launch (from Launch Complex 33)[37]
- 1949-03: Holloman's 2754th Air Force Base unit gained "control of [the WSPG] support airfield, Condron Field…from Biggs Army Air Field at Fort Bliss."[13]
- 1949: German scientists transferred from New Mexico to Alabama (Dr. Ernst Steinhoff transferred from WSPG to Holloman's Air Development Center.)
- 1949-07: The range's Four Bits Peak Instrumentation Annex was assigned to the AFB (disposed on 30 September 1960).[24]
- 1951-07: The AGMTB became a sub-base of Florida's Air Force Missile Test Center until 31 August 1952.[38]
- 1951-08-22: Broomstick Scientists in a unit of the 9393 Technical Service Unit conducted their first launch: the "TF-1" V-2 rocket.[39][40] (Broomstick Sweepings publication ended after a 22 January 1952 general order transferred "1st Ord. GMS Bn." soldiers to Detachment No. 1, Station Complement.)[41]
- 1952-05: An additional[where?] 40 mi × 117 mi (64 km × 188 km) was set aside for the "Alamogordo bombing range, White Sands proving ground, and the Fort Bliss antiaircraft range".[42]
- 1952 (mid): The joint range of more than 200,000 acres (81,000 ha) was 2nd in area to the Eglin AFB range (the Edwards AFB range was 3rd.)[24]
- 1952-11: The range's Red Butte Instrumentation Annex was assigned to Holloman AFB (disposed on 22 November 1963).[24]
- 1953-06: USS Desert Ship (LLS-1) (Launch Complex 35) was built to test the Navy RIM-8 Talos missile.[13]
- 1957-02: The 9393rd Technical Unit, Ordnance, became the U.S. Army Garrison.[43]
- 1957-03-13: Nike Hercules satisfactory launch from LC37.[44]
White Sands Missile Range
| External media | |
|---|---|
| Images | |
| Video | |

- 1958-05-01: The test range was designated "White Sands Missile Range".[13]
- 1958-09-02: The Gold Hill Instrumentation Annex was assigned to Holloman AFB (disposed on 30 September 1960).[24]
- 1958-10: Zeus Acquisition Radar site construction at the planned Launch Complex 38 began[45] near an airstrip.[46]
- c. 1959: The long-range GE AN/FPS-17 Fixed Ground Radar at the Laredo Test Site tracked its first WSMR rocket.
- 1959: Shavetail rocket tested.[where?]
- 1959: An Iconorama large screen display as used for Pentagon C2 was installed at WSMR.[47]
- 1963: President John F. Kennedy visited for the MEWS (Missile Exercise White Sands).[48]
- 1962-03: Annual Service Practice was being conducted for Redstone missile crews.[49]
- 1963-03: Site preparation began for the Multi-function Array Radar.[50]
- 1963: Apollo program Launch Escape System tests with the Little Joe II began at White Sands Launch Complex 36 (ended 1966).[51]
- 1963-11: The Loma (assigned December 1952), Rose Park (5 February 1950), & Twin Buttes (December 1949) instrumentation annexes transferred from Holloman AFB to the Army.[24]
- 1964-07-08: The first "successful Athena/ABRES test missile [was] fired from Utah into WSMR".[52]
- 1965-11: first Sprint missile launch [2]
- 1967: Operation Understanding civic leaders observed their local Nike crews perform Short Notice Annual Practice launches.[53]
- 1967-10-21: Public Law 90-110 authorized $4,781,000 for WSMR construction.[54]
- 1972: WSMR had 3 RCA AN/FPS-16 Instrumentation Radars[55]
- 1983 thru 30 September 1993 - WSMR hosted the Simtel collection, the largest collection of free software and freeware available to the public on the ARPANET and Internet. It began as a copy of an MIT collection of CP/M software, and expanded to collect free software for other operating systems as well.[56][57]
- 1991 (late): Convair QF-106 Delta Dart drones based at Holloman AFB began operating as Full-Scale Aerial Targets over WSMR.[citation needed]
- 1993-08-18: The first McDonnell Douglas DC-X flight was from the White Sands Space Harbor
- 2004: AIAA named the WSPG a Historic Aerospace Site.[58]
- 2007-11-14: Launch Complex 32 groundbreaking for the Orion Abort Test Booster.[59][60]
- 2011: A point in the Post Area was designated "White Sands Missile Range" in the USGS's Geographic Names Information System.[3]
See also
- McDonald Ranch House, location of the final assembly of the world's first nuclear weapon
- Kapustin Yar, the Soviet analog of WSMR
- Peenemunde Army Research Center, WWII German rocket center
References
- ^ http://www.nps.gov/archive/whsa/adhi/adhi5d.htm
- ^ a b "Chapter Four: Global War at White Sands 1940–1945". White Sands Administrative History. National Park Service. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
Executive Order No. 9029
- ^ a b "Condron Army Airfield (2444053)". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 28 May 2014. (Doña Ana county—entered in the GNIS on 20 March 2011)
- ^ a b "Development of the Corporal: the embryo of the army missile program" (PDF). Army Ballistic Missile Agency. April 1961. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2009.
- ^ "WSMR Official Website: Commanding Commander White Sands Missile Range".
- ^ "OACSIM - Leadership - ACSIM". www.acsim.army.mil.
- ^ SpacePorting Part III: US Spaceports [1]
- ^ https://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/multimedia/imagegallery/Shuttle/EC82-18507.html
- ^ "Remember the time we bombed Mexico with German rockets?". Gizmodo.
- ^ "USAF Accidentally Launched Rocket into Mexico's Mapimi Desert 45 Years Ago". Unredacted.
- ^ http://fronteralandalliance.org/castner/media/ICRMP.pdf "This report inventoried and evaluated 150 Cold War era properties constructed between 1956 and 1961 at Orogrande Range Doña Ana Range, McGregor Range, North McGregor Range, and Meyer Target Range in New Mexico."
- ^ Rubenson, David; Robert Everson; Jorge Munoz; Robert Weissler (1998). McGregor Renewal and the Current Air Defense Mission. p. 77. ISBN 978-0-8330-2669-9. Retrieved 15 September 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f g "A Brief History of White Sands Proving Ground 1941–1965" (PDF). New Mexico State University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 October 2014. Retrieved 19 August 2010.
- ^ Greenwood, Richard (14 January 1975). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination: Trinity Site". National Park Service. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) and Accompanying 10 photos, from 1974. (3.37 MB) - ^ "Trinity Site". National Historic Landmarks. National Park Service. Archived from the original on 15 February 2008. Retrieved 28 January 2008.
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. 23 January 2007.
- ^ "White Sands V-2 Launching Site". Aviation: From Sand Dunes to Sonic Booms. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- ^ [full citation needed]Works by White Sands Missile Range Public Affairs Office at Project Gutenberg
- ^ "Time Magazine, "Recovery at White Sands"". 29 June 1962.
- ^ http://www.arl.army.mil/www/pages/45/VG_WSMR.PDF
- ^ http://www.wsmr.army.mil/pao/FactSheets/hfame.htm
- ^ http://www.ccm.osd.mil
- ^ "Official Home of the 450th Bomb Group Memorial Association". www.450thbg.com.
- ^ a b c d e f Mueller (1982). "Holloman Air Force Base". Air Force Bases as of 1982 (Report).
- ^ Gibbs, Jason (19 July 2014). "WSMR, DOD may take control of range's Northern Extension Area". Las Cruces Sun-News. The Las Cruces Sun-News. Retrieved 30 July 2014.
- ^ a b Ordway, Frederick I, III; Sharpe, Mitchell R (1979). The Rocket Team. Apogee Books Space Series. New York: Thomas Y. Crowell. pp. 290, 389. ISBN 1-894959-00-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Ley, Willy (1958) [1944]. Rockets, Missiles and Space Travel (revised ed.). New York: The Viking Press. pp. 246, 253.
- ^ Bluth, John. "Von Karman, Malina laid the groundwork for the future JPL". JPL.
- ^ Hamilton, John A. Blazing skies: Air Defense Artillery on Fort Bliss, 1940-2009 ("Google eBook" of Government Printing Office document). ISBN 9780160869495. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
Special Orders No. 143, Headquarters, Army Ground Forces, dated 6 July 1946, [established] the Antiaircraft and Guided Missile Center [from] the remnants of the Antiaircraft Artillery School, the Antiaircraft Replacement Training Center, Army Ground Forces Board No. 4,13 1st AAA Guided Missile Battalion, the 1852nd Area Service Unit, and remaining antiaircraft units, including three automatic weapons battalions and one gun battalion placed in the Army General Reserve.
- ^ McCleskey, C.; D. Christensen. "Dr. Kurt H. Debus: Launching a Vision" (PDF). p. 35. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 September 2008. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- ^ Upper Air Rocket Summary: V-2 No. 4 (PDF) (Report). 29 May 1946. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
General Electric Company provided gyros, mixer-computers, wiring, servo motors, and propellant piping to replace those German parts that had deteriorated with age.
(also available at PostWarV2.com) - ^ Hamilton, John A. Blazing skies: Air Defense Artillery on Fort Bliss, 1940-2009. Government Printing Office. ISBN 9780160869495.
three officers and fifty-five enlisted men...worked closely with the German rocket scientists who were located in a six-acre ordnance area on the north side of the Fort Bliss cantonment. [The military unit went to WSPG] to provide the manpower to build the [V-2] missiles and erect them on test stands.
- ^ http://www.cecer.army.mil/techreports/ERDC-CERL_SR-06-53/ERDC-CERL_SR-06-53.pdf
- ^ Integration of the Holloman-White Sands Ranges, 1947-1952 (2nd Edition, 1957)
- ^ Mueller (1982). "Holloman Air Force Base". Air Force Bases as of 1982 (Report). p. 248.
- ^ Bushnell, David (25 August 1986). GAPA: Holloman's First Missile Program (Scribd.com image) (Report). Air Force Missile Development Center: Historical Branch. IRIS 00169113. Retrieved 11 August 2013.
[1st ramjet GAPA] "was launched 14 November 1947 and the initial liquid-fuel variety 12 March 1948.8... The last of the GAPAs, number 114, was launched 15 August 1950, and the project officially terminated at Holloman the following month.11
(date identified at http://airforcehistoryindex.org/data/000/169/113.xml) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 October 2014. Retrieved 19 August 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 May 2014. Retrieved 18 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) test installation - ^ Kennedy, Gregory P. (1983). Vengeance Weapon 2: The V-2 Guided Missile. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution Press. p. 62.
- ^ Egermeier, Robert P. (September 2001). "Former "Broomstick Scientist"". Aerospace America: 7.
- ^ Koppenshaver, James T. (30 January 1951). "Broomstick Sweepings" (PDF). Wind and Sand. pp. 1, 6. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
late 1950…Fort White Sands…early in 1951
- ^ "The Milwaukee Journal - Google News Archive Search". news.google.com.
- ^ "White Sands Missle Range (WSMR) Historic Newspaper Digital Archive" (PDF). www.wsmrhistoric.com.
- ^ Leonard, Barry (c. 1986). History of Strategic and Ballistic Missile Defense: Volume II: 1956-1972 (Army.mil PDF -- also available at Google Books). Retrieved 1 September 2012.
{{cite book}}: External link in|format= - ^ Piland, Doyle. "Way Back When..." (PDF). WSMR newsletter. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
Launch Complex 38...Site preparation for the TTR [Target Tracking Radar] began in July 1959.... Site preparation for the Discrimination Radar was started in January 1961.
- ^ Site Plan: Nike Zeus Facilities ALA 5 (Map). reproduced in WSMR newsletter: Federal Government of the United States.
- ^ "New Device Will Plot All Planes". Alton Evening Telegraph. 20 August 1959. p. 29.
Iconorama shows almost instantly the positions of aircraft thousands of miles away… Traces made by the planes being tracked are scribed on a coated slide by a moving stylus. … The slide plot measures only one inch square, yet overall error of the projected display is said to be about one part in 1,000. … Iconorama units already have been installed and operated at the Pacific Missile Range, Point Mugu Calif.; the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico; the Atlantic Missile Range at Cape Canaveral, Fla., and the Naval Research Laboratory
- ^ (5 June 1963) Kennedy visit leaves lasting impression at WSMR
- ^ Conduct of Redstone Annual Service Practice at White Sands Missile Range New Mexico, Fort Sill: Headquarters, United States Army Artillery And Missile Center
{{citation}}:|format=requires|url=(help) (the Artillery and Missile Center at Ft Sill was redesignated the Field Artillery Center in 1969.) - ^ "Nike R&D at White Sands, Multi-Function Array Radar, 1954-1970 (page 16)". nikemissile.org.
- ^ "WSTF Community". NASA.
- ^ "Part I. History of ABM Development" (transcript at AlternateWars.com). Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ https://news.google.com/newspapers?nid=1893&dat=19670602
- ^ http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/STATUTE-81/pdf/STATUTE-81-Pg279.pdf "Two Rock Ranch Station, California: Supply facilities, $174,000."
- ^ Hoihjelle, Donald L. (February 1972). AN/FPS-16(AX) Radar Modeling and Computer Simulation (Report). WSMR Instrumentation Directorate.
- ^ "The Story of SIMTEL20". Archived from the original on 11 January 2011. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
- ^ "SAVE SIMTEL20!". Retrieved 29 October 2014.
- ^ "article". Aerospace America: B6. October 2004.
- ^ "NASA Building Test Pad at White Sands for New Spacecraft". redOrbit. 3 February 2008. Retrieved 12 September 2008.
- ^ NASA: Constellation Mission Project, Research, and Test Sites Overview
External links
- White Sands Missile Range Museum
- Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) No. NM-1, "White Sands Missile Range, White Sands, Dona Ana County, NM", 128 data pages
- HAER No. NM-1-A, "White Sands Missile Range, Trinity Site", 106 photos, 11 measured drawings, 116 data pages, 8 photo caption pages
- HAER No. NM-1-B, "White Sands Missile Range, V-2 Rocket Facilities", 72 photos, 6 measured drawings, 117 data pages, 5 photo caption pages


