Bar chart: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Incarceration Rates Worldwide ZP.svg|thumb|Example of a bar chart, with 'Country' as the discrete data set.]] |
[[Image:Incarceration Rates Worldwide ZP.svg|thumb|Example of a bar chart, with 'Country' as the discrete data set.]] |
||
A '''bar chart''' or '''bar graph''' is a [[chart]] with [[rectangle|rectangular]] bars with [[length]]s proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. |
A '''bar chart''' or '''bar graph''' is a [[chart]] with [[rectangle|rectangular]] bars with [[length]]s proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. |
||
FCK |
|||
'''Bar charts''' are used for marking clear data which has discrete values. Some examples of discontinuous data include 'shoe size' or 'eye color', for which a bar chart is appropriate. In contrast, some examples of continuous data would be 'height' or 'weight'. A bar chart is very useful for recording certain information whether it is continuous or not continuous data. Bar charts also look a lot like a [[histogram]]. They are often mistaken for each other.{{clarify|date=February 2012}} |
'''Bar charts''' are used for marking clear data which has discrete values. Some examples of discontinuous data include 'shoe size' or 'eye color', for which a bar chart is appropriate. In contrast, some examples of continuous data would be 'height' or 'weight'. A bar chart is very useful for recording certain information whether it is continuous or not continuous data. Bar charts also look a lot like a [[histogram]]. They are often mistaken for each other.{{clarify|date=February 2012}} |
||
Revision as of 04:00, 3 May 2012
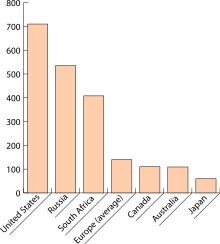
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart with rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. FCK
Bar charts are used for marking clear data which has discrete values. Some examples of discontinuous data include 'shoe size' or 'eye color', for which a bar chart is appropriate. In contrast, some examples of continuous data would be 'height' or 'weight'. A bar chart is very useful for recording certain information whether it is continuous or not continuous data. Bar charts also look a lot like a histogram. They are often mistaken for each other.[clarification needed]
The first bar graph appeared in the 1786 book The Commercial and Political Atlas, by William Playfair (1759-1823). Playfair was a pioneer in the use of graphical displays and wrote extensively about them.
See also
- Gantt chart
- Open-high-low-close chart
- Candlestick chart
- Pie chart
- List of information graphics software#Plotting programs (graphing programs)
- Commons:Chart and graph resources
- commons:Bar chart - many free bar chart examples organized by type.compares data easy.
External links
- How to Construct Bad Charts and Graphs
- Directory of graph software and online tools (many can handle bar charts)
- Create A Graph. Free online graph creation tool at the website for the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES)
