Capelin
| Capelin | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Mallotus G. Cuvier, 1829
|
| Species: | M. villosus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Mallotus villosus (O. F. Müller, 1776)
| |
The capelin or caplin, Mallotus villosus, is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the Atlantic and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin also eat a great deal of krill and other crustaceans. Whales, seals, cod, squid, mackerel, beluga whales and seabirds all prey on capelin, in particular during the spawning season of the capelin while it migrates southwards. Capelin spawn on sandy beaches and sandy bottom at the age of 2–6 years, and have an extremely high mortality rate on the beaches after spawning, for males close to 100% mortality.[clarification needed] Males reach 20 cm in length, while females are up to 25 cm long. They are olive-colored dorsally, shading to silver on sides. Males have a translucent ridge on both sides of their bodies. The ventral aspects of the males iridesce reddish at the time of spawn.
Capelin migration
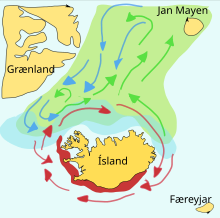
Green shade: Feeding area of adults
Blue shade: Distribution of juveniles
Green arrows: Feeding migrations
Blue arrows: Return migrations
Red shade and Red arrows: Spawning migrations, main spawning grounds and larval drift routes

Capelin in the Barents Sea and around Iceland are stocks that perform extensive seasonal migrations. Barents Sea capelin migrate during winter and early spring to the coast of northern Norway (Finnmark) and the Kola Peninsula (Russia) for spawning. During summer and autumn capelin migrate north- and north-eastward for feeding.[1]
Icelandic capelin move inshore in large schools to spawn and migrate in spring and summer to feed in the plankton-rich oceanic area between Iceland, Greenland, and Jan Mayen. Capelin distribution and migration is linked with ocean currents and water masses. Around Iceland, maturing capelin usually undertake extensive northward feeding migrations in spring and summer and the return migration takes place in September to November. The spawning migration starts from north of Iceland in December to January. In a paper published in 2009, researchers from Iceland recounted their application of an interacting particle model to the capelin stock around Iceland, successfully predicting the spawning migration route for 2008.[2]
Reproduction
As an r-selected species, capelin have a high reproductive potential and an intrinsic population growth rate.[3] They reproduce by spawning and their main spawning season occurs in spring, but can extend into the summer. The majority of capelin are three or four years old when they spawn.[1] The males migrate directly to the shallow water of fjords, where spawning will take place, while the females remain in deeper water until they are completely mature. Once the females are mature, they will migrate to the spawning grounds and spawn.[4] This process usually takes place at night.[1] After the females have spawned, they immediately leave the grounds and will potentially spawn again in the following years if they survive. The males do not leave the spawning grounds and will potentially spawn more than once throughout the season.[4] Male capelin are considered to be semelparous because they die soon after the spawning season is over.[1]
Fisheries

Capelin is an important forage fish, and is essential as the key food of the Atlantic cod. The northeast Atlantic cod and capelin fisheries therefore are managed by a multispecies approach developed by the main resource owners Norway and Russia.
In some years with large quantities of herring in the Barents Sea, capelin seem to be heavily affected. Probably both food competition and herring feeding on capelin larvae lead to collapses in the capelin stock. However, in some years there has been good recruitment of capelin despite a high herring biomass, suggesting that herring are only one factor influencing capelin dynamics.
In the provinces of Quebec (particularly in the Gaspé peninsula) and Newfoundland and Labrador in Canada, it is a regular summertime practice for locals to go to the beach and scoop the capelin up in nets or whatever is available, as the capelin "roll in" in the millions each year at the end of May or in early June.[6]
Commercially, capelin is used for fish meal and oil industry products, but is also appreciated as food. The flesh is agreeable in flavor, resembling herring. Capelin roe ("masago") is considered a high-value product. It is also sometimes mixed with wasabi or green food coloring and wasabi flavor and sold as "wasabi caviar". Often, masago is used as a substitute for tobiko, flying fish roe, due to its similarity and taste although the mouthfeel is different due to the individual eggs being smaller and it is less crunchy than tobiko.
Notes
- ^ a b c d Gjøsæter, H. (1998). "The population biology and exploitation of capelin (Mallotus villosus) in the Barents Sea". Sarsia. 83: 453–496. doi:10.1080/00364827.1998.10420445.
- ^ Barbaro, A.; Einarsson, B.; Birnir, B.; Sigurthsson, S.; Valdimarsson, H.; Palsson, O. K.; Sveinbjornsson, S.; Sigurthsson, T. (2009). "Modelling and simulations of the migration of pelagic fish". ICES Journal of Marine Science. 66 (5): 826. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsp067.
- ^ "Capelin (Mallotus villosus) distribution and climate: a sea 'canary' for marine ecosystem change". ICES Journal of Marine Science. 62 (7): 1524–1530. doi:10.1016/j.icesjms.2005.05.008.
- ^ a b "A review of capelin (Mallotus villosus) in Greenland waters". ICES Journal of Marine Science. 59 (5): 890–896. doi:10.1006/jmsc.2002.1242.
- ^ Mallotus villosus (Müller, 1776) FAO, Species Fact Sheet. Retrieved April 2012.
- ^ "They're Back: Capelin are Rolling at Middle Cove Beach". CBC. CBC News, Newfoundland and Labrador. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
References
- "Mallotus villosus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 11 March 2006.
- Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Mallotus villosus". FishBase. October 2005 version.
- Capelin off Iceland: Biology, exploitation and management
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Ward, Artemas (1911). "The Grocer's Encyclopedia". The Grocer's Encyclopedia.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Ward, Artemas (1911). "The Grocer's Encyclopedia". The Grocer's Encyclopedia.




