Dectaflur
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Topical (gel, solution) |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.297.781 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
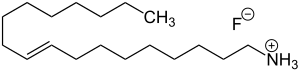
| Formula | C18H38FN |
| Molar mass | 287.50 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Dectaflur (INN) is a fluoride-containing substance used for the prevention and treatment of dental caries, sensitive teeth, and the refluoridation of damaged tooth enamel, typically in combination with olaflur.[1]
Chemistry and mechanism of action
Dectaflur consists of oleyl amine (the amine corresponding to oleyl alcohol) and hydrofluoric acid. Oleyl amine with its long lipophilic hydrocarbon chain has surfactant properties. It forms a film layer on the surface of teeth, which facilitates incorporation of fluoride into the top layers of the enamel, reaching a depth of only a few nanometers. The precise mechanism of action is unknown.[2]
Side effects
Like other fluorides, dectaflur is toxic when overdosed over an extended period of time. Especially in children, before the development of the permanent teeth, overdosage can lead to dental fluorosis.[3]
References
- ^ Haberfeld, H, ed. (2009). Austria-Codex (in German) (2009/2010 ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. ISBN 3-85200-196-X.
- ^ Müller, F.; Zeitz, C.; Mantz, H.; Ehses, K. H.; Soldera, F.; Schmauch, J.; Hannig, M.; Hüfner, S.; Jacobs, K. (2010). "Elemental Depth Profiling of Fluoridated Hydroxyapatite: Saving Your Dentition by the Skin of Your Teeth?". Langmuir. 26 (24): 18750–18759. doi:10.1021/la102325e. PMID 21090577.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) - ^ Alvarez, J. A.; Rezende, K. M.; Marocho, S. M.; Alves, F. B.; Celiberti, P.; Ciamponi, A. L. (2009). "Dental fluorosis: Exposure, prevention and management". Medicina oral, patologia oral y cirugia bucal. 14 (2): E103–E107. PMID 19179949.
