Ferromagnetism

Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effect ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type and is responsible for the common phenomenon of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life.[1] Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism—paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism—but the forces are usually so weak that they can be detected only by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is "the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today".[2]
Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are the materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, cobalt, nickel and most of their alloys, and some compounds of rare earth metals. Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks, and nondestructive testing of ferrous materials.
Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically "soft" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically "hard" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from "hard" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a strong magnetic field during manufacture to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. "Hard" materials have high coercivity, whereas "soft" materials have low coercivity. The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.
History and distinction from ferrimagnetism

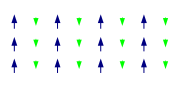
Historically, the term ferromagnetism was used for any material that could exhibit spontaneous magnetization: a net magnetic moment in the absence of an external magnetic field. This general definition is still in common use.[3]
However, in a landmark paper in 1948, Louis Néel showed there are two levels of magnetic alignment that result in this behavior. One is ferromagnetism in the strict sense, where all the magnetic moments are aligned. The other is ferrimagnetism, where some magnetic moments point in the opposite direction but have a smaller contribution, so there is still a spontaneous magnetization.[4][5]: 28–29
In the special case where the opposing moments balance completely, the alignment is known as antiferromagnetism. Therefore antiferromagnets do not have a spontaneous magnetization.
Ferromagnetic materials
| Material | Curie temp. (K) |
|---|---|
| Co | 1388 |
| Fe | 1043 |
| Fe2O3[a] | 948 |
| FeOFe2O3[a] | 858 |
| NiOFe2O3[a] | 858 |
| CuOFe2O3[a] | 728 |
| MgOFe2O3[a] | 713 |
| MnBi | 630 |
| Ni | 627 |
| Nd2Fe14 B | 593 |
| MnSb | 587 |
| MnOFe2O3[a] | 573 |
| Y3Fe5O12[a] | 560 |
| CrO2 | 386 |
| MnAs | 318 |
| Gd | 292 |
| Tb | 219 |
| Dy | 88 |
| EuO | 69 |
The table lists a selection of ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic compounds, along with the temperature above which they cease to exhibit spontaneous magnetization (see Curie temperature).
Ferromagnetism is a property not just of the chemical make-up of a material, but of its crystalline structure and microstructure. There are ferromagnetic metal alloys whose constituents are not themselves ferromagnetic, called Heusler alloys, named after Fritz Heusler. Conversely there are non-magnetic alloys, such as types of stainless steel, composed almost exclusively of ferromagnetic metals.
Amorphous (non-crystalline) ferromagnetic metallic alloys can be made by very rapid quenching (cooling) of a liquid alloy. These have the advantage that their properties are nearly isotropic (not aligned along a crystal axis); this results in low coercivity, low hysteresis loss, high permeability, and high electrical resistivity. One such typical material is a transition metal-metalloid alloy, made from about 80% transition metal (usually Fe, Co, or Ni) and a metalloid component (B, C, Si, P, or Al) that lowers the melting point.
A relatively new class of exceptionally strong ferromagnetic materials are the rare-earth magnets. They contain lanthanide elements that are known for their ability to carry large magnetic moments in well-localized f-orbitals.
Most ferromagnetic materials are metals, since the conducting electrons are often responsible for mediating the ferromagnetic interactions. It is therefore a challenge to develop ferromagnetic insulators, especially multiferroic materials, which are both ferromagnetic and ferroelectric.[8]
Actinide ferromagnets
A number of actinide compounds are ferromagnets at room temperature or exhibit ferromagnetism upon cooling. PuP is a paramagnet with cubic symmetry at room temperature, but which undergoes a structural transition into a tetragonal state with ferromagnetic order when cooled below its TC = 125 K. In its ferromagnetic state, PuP's easy axis is in the <100> direction.[9]
In NpFe2 the easy axis is <111>.[10] Above TC ≈ 500 K NpFe2 is also paramagnetic and cubic. Cooling below the Curie temperature produces a rhombohedral distortion wherein the rhombohedral angle changes from 60° (cubic phase) to 60.53°. An alternate description of this distortion is to consider the length c along the unique trigonal axis (after the distortion has begun) and a as the distance in the plane perpendicular to c. In the cubic phase this reduces to c/a = 1.00. Below the Curie temperature
which is the largest strain in any actinide compound.[11] NpNi2 undergoes a similar lattice distortion below TC = 32 K, with a strain of (43 ± 5) × 10−4.[11] NpCo2 is a ferrimagnet below 15 K.
Lithium gas
In 2009, a team of MIT physicists demonstrated that a lithium gas cooled to less than one kelvin can exhibit ferromagnetism.[12] The team cooled fermionic lithium-6 to less than 150 nK (150 billionths of one kelvin) using infrared laser cooling. This demonstration is the first time that ferromagnetism has been demonstrated in a gas.
Tetragonal ruthenium
In 2018, a team of University of Minnesota physicists demonstrated that body-centered tetragonal ruthenium exhibits ferromagnetism at room temperature.[13]
Explanation
The Bohr–van Leeuwen theorem, discovered in the 1910s, showed that classical physics theories are unable to account for any form of magnetism, including ferromagnetism. Magnetism is now regarded as a purely quantum mechanical effect. Ferromagnetism arises due to two effects from quantum mechanics: spin and the Pauli exclusion principle.[14]
Origin of magnetism
One of the fundamental properties of an electron (besides that it carries charge) is that it has a magnetic dipole moment, i.e., it behaves like a tiny magnet, producing a magnetic field. This dipole moment comes from the more fundamental property of the electron that it has quantum mechanical spin. Due to its quantum nature, the spin of the electron can be in one of only two states; with the magnetic field either pointing "up" or "down" (for any choice of up and down). The spin of the electrons in atoms is the main source of ferromagnetism, although there is also a contribution from the orbital angular momentum of the electron about the nucleus. When these magnetic dipoles in a piece of matter are aligned, (point in the same direction) their individually tiny magnetic fields add together to create a much larger macroscopic field.
However, materials made of atoms with filled electron shells have a total dipole moment of zero: because the electrons all exist in pairs with opposite spin, every electron's magnetic moment is cancelled by the opposite moment of the second electron in the pair. Only atoms with partially filled shells (i.e., unpaired spins) can have a net magnetic moment, so ferromagnetism occurs only in materials with partially filled shells. Because of Hund's rules, the first few electrons in a shell tend to have the same spin, thereby increasing the total dipole moment.
These unpaired dipoles (often called simply "spins" even though they also generally include orbital angular momentum) tend to align in parallel to an external magnetic field, an effect called paramagnetism. Ferromagnetism involves an additional phenomenon, however: in a few substances the dipoles tend to align spontaneously, giving rise to a spontaneous magnetization, even when there is no applied field.
Exchange interaction
When two nearby atoms have unpaired electrons, whether the electron spins are parallel or antiparallel affects whether the electrons can share the same orbit as a result of the quantum mechanical effect called the exchange interaction. This in turn affects the electron location and the Coulomb (electrostatic) interaction and thus the energy difference between these states.
The exchange interaction is related to the Pauli exclusion principle, which says that two electrons with the same spin cannot also be in the same spatial state (orbital). This is a consequence of the spin-statistics theorem and that electrons are fermions. Therefore, under certain conditions, when the orbitals of the unpaired outer valence electrons from adjacent atoms overlap, the distributions of their electric charge in space are farther apart when the electrons have parallel spins than when they have opposite spins. This reduces the electrostatic energy of the electrons when their spins are parallel compared to their energy when the spins are anti-parallel, so the parallel-spin state is more stable. In simple terms, the electrons, which repel one another, can move "further apart" by aligning their spins, so the spins of these electrons tend to line up. This difference in energy is called the exchange energy.
This energy difference can be orders of magnitude larger than the energy differences associated with the magnetic dipole-dipole interaction due to dipole orientation,[15] which tends to align the dipoles antiparallel. In certain doped semiconductor oxides RKKY interactions have been shown to bring about periodic longer-range magnetic interactions, a phenomenon of significance in the study of spintronic materials.[16]
The materials in which the exchange interaction is much stronger than the competing dipole-dipole interaction are frequently called magnetic materials. For instance, in iron (Fe) the exchange force is about 1000 times stronger than the dipole interaction. Therefore, below the Curie temperature virtually all of the dipoles in a ferromagnetic material will be aligned. In addition to ferromagnetism, the exchange interaction is also responsible for the other types of spontaneous ordering of atomic magnetic moments occurring in magnetic solids, antiferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism. There are different exchange interaction mechanisms which create the magnetism in different ferromagnetic, ferrimagnetic, and antiferromagnetic substances. These mechanisms include direct exchange, RKKY exchange, double exchange, and superexchange.
Magnetic anisotropy
Although the exchange interaction keeps spins aligned, it does not align them in a particular direction. Without magnetic anisotropy, the spins in a magnet randomly change direction in response to thermal fluctuations and the magnet is superparamagnetic. There are several kinds of magnetic anisotropy, the most common of which is magnetocrystalline anisotropy. This is a dependence of the energy on the direction of magnetization relative to the crystallographic lattice. Another common source of anisotropy, inverse magnetostriction, is induced by internal strains. Single-domain magnets also can have a shape anisotropy due to the magnetostatic effects of the particle shape. As the temperature of a magnet increases, the anisotropy tends to decrease, and there is often a blocking temperature at which a transition to superparamagnetism occurs.[17]
Magnetic domains

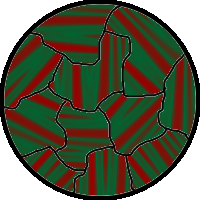
The above would seem to suggest that every piece of ferromagnetic material should have a strong magnetic field, since all the spins are aligned, yet iron and other ferromagnets are often found in an "unmagnetized" state. The reason for this is that a bulk piece of ferromagnetic material is divided into tiny regions called magnetic domains[18] (also known as Weiss domains). Within each domain, the spins are aligned, but (if the bulk material is in its lowest energy configuration; i.e. unmagnetized), the spins of separate domains point in different directions and their magnetic fields cancel out, so the object has no net large scale magnetic field.
Ferromagnetic materials spontaneously divide into magnetic domains because the exchange interaction is a short-range force, so over long distances of many atoms the tendency of the magnetic dipoles to reduce their energy by orienting in opposite directions wins out. If all the dipoles in a piece of ferromagnetic material are aligned parallel, it creates a large magnetic field extending into the space around it. This contains a lot of magnetostatic energy. The material can reduce this energy by splitting into many domains pointing in different directions, so the magnetic field is confined to small local fields in the material, reducing the volume of the field. The domains are separated by thin domain walls a number of molecules thick, in which the direction of magnetization of the dipoles rotates smoothly from one domain's direction to the other.
Magnetized materials

Thus, a piece of iron in its lowest energy state ("unmagnetized") generally has little or no net magnetic field. However, the magnetic domains in a material are not fixed in place; they are simply regions where the spins of the electrons have aligned spontaneously due to their magnetic fields, and thus can be altered by an external magnetic field. If a strong enough external magnetic field is applied to the material, the domain walls will move by the process of the spins of the electrons in atoms near the wall in one domain turning under the influence of the external field to face in the same direction as the electrons in the other domain, thus reorienting the domains so more of the dipoles are aligned with the external field. The domains will remain aligned when the external field is removed, creating a magnetic field of their own extending into the space around the material, thus creating a "permanent" magnet. The domains do not go back to their original minimum energy configuration when the field is removed because the domain walls tend to become 'pinned' or 'snagged' on defects in the crystal lattice, preserving their parallel orientation. This is shown by the Barkhausen effect: as the magnetizing field is changed, the magnetization changes in thousands of tiny discontinuous jumps as the domain walls suddenly "snap" past defects.
This magnetization as a function of the external field is described by a hysteresis curve. Although this state of aligned domains found in a piece of magnetized ferromagnetic material is not a minimal-energy configuration, it is metastable, and can persist for long periods, as shown by samples of magnetite from the sea floor which have maintained their magnetization for millions of years.
Heating and then cooling (annealing) a magnetized material, subjecting it to vibration by hammering it, or applying a rapidly oscillating magnetic field from a degaussing coil tends to release the domain walls from their pinned state, and the domain boundaries tend to move back to a lower energy configuration with less external magnetic field, thus demagnetizing the material.
Commercial magnets are made of "hard" ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic materials with very large magnetic anisotropy such as alnico and ferrites, which have a very strong tendency for the magnetization to be pointed along one axis of the crystal, the "easy axis". During manufacture the materials are subjected to various metallurgical processes in a powerful magnetic field, which aligns the crystal grains so their "easy" axes of magnetization all point in the same direction. Thus the magnetization, and the resulting magnetic field, is "built in" to the crystal structure of the material, making it very difficult to demagnetize.
Curie temperature
As the temperature increases, thermal motion, or entropy, competes with the ferromagnetic tendency for dipoles to align. When the temperature rises beyond a certain point, called the Curie temperature, there is a second-order phase transition and the system can no longer maintain a spontaneous magnetization, so its ability to be magnetized or attracted to a magnet disappears, although it still responds paramagnetically to an external field. Below that temperature, there is a spontaneous symmetry breaking and magnetic moments become aligned with their neighbors. The Curie temperature itself is a critical point, where the magnetic susceptibility is theoretically infinite and, although there is no net magnetization, domain-like spin correlations fluctuate at all length scales.
The study of ferromagnetic phase transitions, especially via the simplified Ising spin model, had an important impact on the development of statistical physics. There, it was first clearly shown that mean field theory approaches failed to predict the correct behavior at the critical point (which was found to fall under a universality class that includes many other systems, such as liquid-gas transitions), and had to be replaced by renormalization group theory.[citation needed]
See also
- Ferromagnetic material properties
- Orbital magnetization
- Stoner criterion
- Thermo-magnetic motor – Magnet motor
- Neodymium magnet – Strongest type of permanent magnet from an alloy of neodymium, iron and boron
References
- ^ Chikazumi, Sōshin (2009). Physics of ferromagnetism. English edition prepared with the assistance of C.D. Graham, Jr (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 118. ISBN 9780199564811.
- ^ Bozorth, Richard M. Ferromagnetism, first published 1951, reprinted 1993 by IEEE Press, New York as a "Classic Reissue." ISBN 0-7803-1032-2.
- ^ Somasundaran, P., ed. (2006). Encyclopedia of surface and colloid science (2nd ed.). New York: Taylor & Francis. p. 3471. ISBN 9780849396083.
- ^ Cullity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. (2011). "6. Ferrimagnetism". Introduction to Magnetic Materials. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118211496.
- ^ Aharoni, Amikam (2000). Introduction to the theory of ferromagnetism (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198508090.
- ^ Kittel, Charles (1986). Introduction to Solid State Physics (sixth ed.). John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0-471-87474-4.
- ^ Jackson, Mike (2000). "Wherefore Gadolinium? Magnetism of the Rare Earths" (PDF). IRM Quarterly. 10 (3). Institute for Rock Magnetism: 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-07-12. Retrieved 2016-08-08.
- ^ Hill, Nicola A. (2000-07-01). "Why Are There so Few Magnetic Ferroelectrics?". The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 104 (29): 6694–6709. doi:10.1021/jp000114x. ISSN 1520-6106.
- ^ Lander GH, Lam DJ (1976). "Neutron diffraction study of PuP: The electronic ground state". Phys. Rev. B. 14 (9): 4064–67. Bibcode:1976PhRvB..14.4064L. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.14.4064.
- ^ Aldred AT, Dunlap BD, Lam DJ, Lander GH, Mueller MH, Nowik I (1975). "Magnetic properties of neptunium Laves phases: NpMn2, NpFe2, NpCo2, and NpNi2". Phys. Rev. B. 11 (1): 530–44. Bibcode:1975PhRvB..11..530A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.11.530.
- ^ a b Mueller MH, Lander GH, Hoff HA, Knott HW, Reddy JF (Apr 1979). "Lattice distortions measured in actinide ferromagnets PuP, NpFe2, and NpNi2" (PDF). J Phys Colloque C4, Supplement. 40 (4): C4-68–C4-69.
- ^ G-B Jo; Y-R Lee; J-H Choi; C.A. Christensen; T.H. Kim; J.H. Thywissen; D.E. Pritchard; W. Ketterle (2009). "Itinerant Ferromagnetism in a Fermi Gas of Ultracold Atoms". Science. 325 (5947): 1521–24. arXiv:0907.2888. Bibcode:2009Sci...325.1521J. doi:10.1126/science.1177112. PMID 19762638.
- ^ Quarterman, P.; Sun, Congli; Garcia-Barriocanal, Javier; DC, Mahendra; Lv, Yang; Manipatruni, Sasikanth; Nikonov, Dmitri E.; Young, Ian A.; Voyles, Paul M.; Wang, Jian-Ping (2018). "Demonstration of Ru as the 4th ferromagnetic element at room temperature". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 2058. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.2058Q. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04512-1. PMC 5970227. PMID 29802304.
- ^ Feynman, Richard P.; Robert Leighton; Matthew Sands (1963). The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol. 2. Addison-Wesley. pp. Ch. 37.
- ^ Chikazumi, Sōshin (2009). Physics of ferromagnetism. English edition prepared with the assistance of C.D. Graham, Jr (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 129–30. ISBN 9780199564811.
- ^ Assadi, M.H.N; Hanaor, D.A.H (2013). "Theoretical study on copper's energetics and magnetism in TiO2 polymorphs". Journal of Applied Physics. 113 (23): 233913–233913–5. arXiv:1304.1854. Bibcode:2013JAP...113w3913A. doi:10.1063/1.4811539.
- ^ Aharoni, Amikam (1996). Introduction to the Theory of Ferromagnetism. Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-851791-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Feynman, Richard P.; Robert B. Leighton; Matthew Sands (1963). The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol. I. Pasadena: California Inst. of Technology. pp. 37.5–37.6. ISBN 0465024939.
External links
- Electromagnetism – ch. 11, from an online textbook
- Sandeman, Karl (January 2008). "Ferromagnetic Materials". DoITPoMS. Dept. of Materials Sci. and Metallurgy, Univ. of Cambridge. Retrieved 2019-06-22. Detailed nonmathematical description of ferromagnetic materials with illustrations
- Magnetism: Models and Mechanisms in E. Pavarini, E. Koch, and U. Schollwöck: Emergent Phenomena in Correlated Matter, Jülich 2013, ISBN 978-3-89336-884-6

