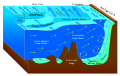
Fracture zone

A fracture zone is a linear oceanic feature—often hundreds, even thousands of kilometers long—resulting from the action of offset mid-ocean ridge axis segments. They are a consequence of plate tectonics. Lithospheric plates on either side of an active transform fault move in opposite directions; here, strike-slip activity occurs. Fracture zones extend past the transform faults, away from the ridge axis; seismically inactive (because both plate segments are moving in the same direction), they display evidence of past transform fault activity, primarily in the different ages of the crust on opposite sides of the zone.
In actual usage, many transform faults aligned with fracture zones are often loosely referred to as "fracture zones" although technically, they are not.
Structure and formation

Mid-ocean ridges are divergent boundaries that push apart two plates. As the plates on either side of a mid-ocean ridge move, transform faults are created due to variances in plate motion. As the plates continue to move over time, these faults offset the mid-ocean ridge.[1] These offsets cause fractures in the ocean floor that can extend for hundreds of kilometers out from a mid-ocean ridge.
Fracture zones and the transform faults that form them are separate features. Transform faults are plate boundaries, meaning that on either side of the fault is a different plate. In contrast, on either side of a fracture zone, the crust belongs to the same plate.[2]
Geologic importance
As many areas of the ocean floor, particularly the Atlantic Ocean, are currently inactive, it can be difficult to determine past plate motion. However, by observing the fracture zones, one can determine both the direction and rate of past plate motion. This is found by observing the patterns of magnetic striping on the ocean floor (a result of the reversals of Earth's magnetic field over time). By measuring the offset in the magnetic striping, one can then determine the rate of past plate motions.[3] In a similar method, one can use the relative ages of the seafloor on either side of a fracture zone to determine the rate of past plate motions. By comparing how offset similarly aged seafloor is, one can determine how quickly the plate has moved.[2]
Examples of fracture zones
Main Article: List of fracture zones
Blanco Fracture Zone

The Blanco Fracture Zone is a fracture zone running between the Juan de Fuca Ridge and the Gorda Ridge. The dominating feature of the fracture zone is the 150 km long Blanco Ridge, which is a high-angle right-lateral strike slip fault with some component of dip-slip faulting.[4]
Charlie-Gibbs Fracture Zone
The Charlie-Gibbs Fracture Zone consists of two fracture zones in the North Atlantic that extend for over 2000 km. These fracture zones displace the Mid-Atlantic Ridge a total of 350 km to the west. The section of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between the two fracture zones is seismically active.[5]
Mendocino Fracture Zone
The Mendocino Fracture Zone extends for over 4,000 km off the coast of California and separates the Pacific Plate and Gorda Plate. The bathymetric depths on the north side of the fracture zone are 800 to 1,200 m shallower than to the south, suggesting the seafloor north of the ridge to be younger. Geologic evidence backs this up, as rocks were found to be 23 to 27 million years younger north of the ridge than to the south.[6]
Romanche Fracture Zone
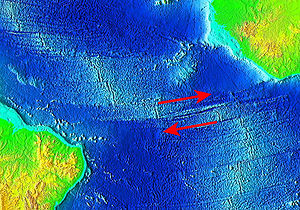
Also known as the Romanche Trench, this fracture zone separates the North Atlantic and South Atlantic Oceans. The trench reaches 7,758 m deep, is 300 km long, and has a width of 19 km. The fracture zone offsets the Mid-Atlantic Ridge by more than 640 km.[7]
Sovanco Fracture Zone
The Sovanco Fracture Zone is a dextral-slip transform fault running between the Juan de Fuca and Explorer Ridge in the North Pacific Ocean. The fracture zone is 125 km long and 15 km wide.[8]
See also
References
- ^ Sandwell, D.T.; Smith, W.H.F. "Exploring the Ocean Basins With Satellite Altimeter Data". NOAA, National Geophysical Data Center & World Data Center A for Marine Geology & Geophysics.
- ^ a b "Oceanic Transform Faults and Fracture Zones". Columbia University. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ "Understanding Plate Motions". U.S. Geological Survey.
- ^ Dziak, R. P.; Fox, C. G.; Embley, R. W.; Nabelek, J. L.; Braunmiller, J.; Koski, R. A. (2000). "Recent tectonics of the Blanco Ridge, eastern blanco transform fault zone". Marine Geophysical Researches. 21 (5). Springer Science+Business Media: 423–450.
- ^ Lilwall, R. C.; Kirk, R. E. (1985). "Ocean-bottom seismograph observations on the Charlie-Gibbs fracture zone". Geophysical Journal International. 80: 195. Bibcode:1985GeoJI..80..195L. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1985.tb05085.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Mendocino Fracture Zone". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ^ "Romanche Gap". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ^ Cowan, Darrel S.; Botros, Mona; Johnson, H. Paul (October 1986). "Bookshelf tectonics: Rotated crustal blocks within the Sovanco Fracture Zone". Geophysical Research Letters. 13 (10): 995–998. Bibcode:1986GeoRL..13..995C. doi:10.1029/GL013i010p00995. Retrieved 28 April 2015.