GeoJSON
| Filename extensions | .json, .geojson |
|---|---|
| Internet media type | application/geo+json[1] |
| Type of format | GIS file format |
| Extended from | JSON |
| Standard | RFC 7946 |
| Free format? | yes |
| Website | geojson |
GeoJSON[2] is an open standard format designed for representing simple geographical features, along with their non-spatial attributes. It is based on JSON, the JavaScript Object Notation.
The features include points (therefore addresses and locations), line strings (therefore streets, highways and boundaries), polygons (countries, provinces, tracts of land), and multi-part collections of these types. GeoJSON features need not represent entities of the physical world only; mobile routing and navigation apps, for example, might describe their service coverage using GeoJSON.[3]
The GeoJSON format differs from other GIS standards in that it was written and is maintained not by a formal standards organization, but by an Internet working group of developers.[4]
A notable offspring of GeoJSON is TopoJSON, an extension of GeoJSON that encodes geospatial topology and that typically provides smaller file sizes.
History
The GeoJSON format working group and discussion were begun in March 2007[5] and the format specification was finalized in June 2008.
In April 2015 the Internet Engineering Task Force has founded the Geographic JSON working group[6] which released GeoJSON as RFC 7946 in August 2016.
Example
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [102.0, 0.5]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0"
}
},
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[102.0, 0.0], [103.0, 1.0], [104.0, 0.0], [105.0, 1.0]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": 0.0
}
},
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[100.0, 0.0], [101.0, 0.0], [101.0, 1.0],
[100.0, 1.0], [100.0, 0.0]
]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": { "this": "that" }
}
}
]
}
Geometries
| Type | Examples | |
|---|---|---|
| Point | 
|
{
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [30, 10]
}
|
| LineString | 
|
{
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[30, 10], [10, 30], [40, 40]
]
}
|
| Polygon | 
|
{
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[[30, 10], [40, 40], [20, 40], [10, 20], [30, 10]]
]
}
|

|
{
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[[35, 10], [45, 45], [15, 40], [10, 20], [35, 10]],
[[20, 30], [35, 35], [30, 20], [20, 30]]
]
}
| |
| Type | Examples | |
|---|---|---|
| MultiPoint | 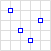
|
{
"type": "MultiPoint",
"coordinates": [
[10, 40], [40, 30], [20, 20], [30, 10]
]
}
|
| MultiLineString | 
|
{
"type": "MultiLineString",
"coordinates": [
[[10, 10], [20, 20], [10, 40]],
[[40, 40], [30, 30], [40, 20], [30, 10]]
]
}
|
| MultiPolygon | 
|
{
"type": "MultiPolygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[[30, 20], [45, 40], [10, 40], [30, 20]]
],
[
[[15, 5], [40, 10], [10, 20], [5, 10], [15, 5]]
]
]
}
|

|
{
"type": "MultiPolygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[[40, 40], [20, 45], [45, 30], [40, 40]]
],
[
[[20, 35], [10, 30], [10, 10], [30, 5], [45, 20], [20, 35]],
[[30, 20], [20, 15], [20, 25], [30, 20]]
]
]
}
| |
Supported software
GeoJSON is supported by numerous mapping and GIS software packages, including OpenLayers,[7] Leaflet, MapServer,[8] Geoforge software,[9] GeoServer,[10] GeoDjango,[11] GDAL,[12] Safe Software FME,[13] and CartoDB.[14] It is also possible to use GeoJSON with PostGIS[15] and Mapnik,[16] both of which handle the format via the GDAL OGR conversion library. Bing Maps, Yahoo!, HERE[17], and Google also support GeoJSON in their API services.
The Google Maps JavaScript API v3 directly supports the integration of GeoJSON data layers[18] as of March 19, 2014.[19] For the Julia language a GeoJSON.jl package is available.
GitHub also supports GeoJSON rendering[20] and Potrace GeoJSON export.
Geojson.io supports GeoJSON rendering and editing in the web browser.
TopoJSON
TopoJSON is an extension of GeoJSON that encodes topology. Rather than representing geometries discretely, geometries in TopoJSON files are stitched together from shared line segments called arcs.[21] Arcs are sequences of points, while line strings and polygons are defined as sequences of arcs. Each arc is defined only once, but can be referenced several times by different shapes, thus reducing redundancy and decreasing the file size.[22] In addition, TopoJSON facilitates applications that use topology, such as topology-preserving shape simplification, automatic map coloring, and cartograms.
A reference implementation of the TopoJSON specification is available as a command-line tool to encode TopoJSON from GeoJSON (or ESRI Shapefiles) and a client side JavaScript library to decode TopoJSON back to GeoJSON again. TopoJSON is also supported by the popular OGR tool as of version 1.11[23] and PostGIS as of version 2.1.0.[24]
TopoJSON Schema
Given a GIS shape near coordinates latitude 0° and longitude 0°, a simple but valid and complete topojson file containing all metadata, Polygon, LineString, Point elements, arcs and properties is defined as follows:

{
"type":"Topology",
"transform":{
"scale": [1,1],
"translate": [0,0]
},
"objects":{
"two-squares":{
"type": "GeometryCollection",
"geometries":[
{"type": "Polygon", "arcs":[[0,1]],"properties": {"name": "Left_Polygon" }},
{"type": "Polygon", "arcs":[[2,-1]],"properties": {"name": "Right_Polygon" }}
]
},
"one-line": {
"type":"GeometryCollection",
"geometries":[
{"type": "LineString", "arcs": [3],"properties":{"name":"Under_LineString"}}
]
},
"two-places":{
"type":"GeometryCollection",
"geometries":[
{"type":"Point","coordinates":[0,0],"properties":{"name":"Origine_Point"}},
{"type":"Point","coordinates":[0,-1],"properties":{"name":"Under_Point"}}
]
}
},
"arcs": [
[[1,2],[0,-2]],
[[1,0],[-1,0],[0,2],[1,0]],
[[1,2],[1,0],[0,-2],[-1,0]],
[[0,-1],[2,0]]
]
}
References
- ^ "The GeoJSON Format (RFC 7946)". Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
- ^ The GeoJSON Format
- ^ iOS Location and Maps Programming Guide
- ^ The GeoJSON Discussion List
- ^ March 2007 Archives by thread
- ^ https://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/geojson/history/
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2010-03-16. Retrieved 2010-03-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ http://mapserver.org/output/template_output.html
- ^ http://leafletjs.com/reference.html#geojson
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-12-13. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-09-07. Retrieved 2009-10-09.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-04-15. Retrieved 2009-10-09.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-07-24. Retrieved 2008-07-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ http://developers.cartodb.com/documentation/cartodb-js.html
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-06-01. Retrieved 2010-06-01.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ https://developer.here.com/documentation/maps/topics_api/h-data-geojson-intro.html
- ^ https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/javascript/examples/layer-data-simple
- ^ http://googledevelopers.blogspot.com/2014/03/maps-made-easier-geojson-in-javascript.html
- ^ https://github.com/blog/1528-there-s-a-map-for-that
- ^ https://github.com/topojson/topojson-specification
- ^ https://github.com/mbostock/topojson/wiki
- ^ GDAL/OGR 1.11.0 Release Notes
- ^ PostGIS AsTopoJSON
Sources
- http://geojson.org/
- http://geojson.org/geojson-spec.html
- Andrews, Christopher (18 September 2007). "Emerging Technology: AJAX and GeoJSON". Archived from the original on 22 May 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Geoweb Guru: Technical Overview: GeoJSON". 16 February 2009. Archived from the original on 2009-02-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Lambert, Chris (4 May 2009). "Google Geo Developers Blog: Build on top of your public Latitude location with GeoJSON & KML".
- https://github.com/mbostock/topojson
- https://github.com/topojson/topojson-specification
