Gompertz distribution
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (December 2011) |
|
Probability density function  Note: b=2.322 | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function 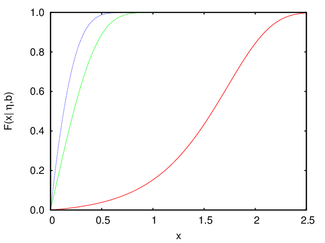 | |||
| Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Mean |
| ||
| Median | |||
| Mode |
| ||
| Variance |
| ||
| MGF |
| ||
In probability and statistics, the Gompertz distribution is a continuous probability distribution. The Gompertz distribution is often applied to describe the distribution of adult lifespans by demographers[1][2] and actuaries.[3][4] Related fields of science such as biology[5] and gerontology[6] also considered the Gompertz distribution for the analysis of survival. More recently, computer scientists have also started to model the failure rates of computer codes by the Gompertz distribution.[7] In marketing science, it has been used as an individual-level model of customer lifetime.[8]
Specification
Probability density function
The probability density function of the Gompertz distribution is:
where is the scale parameter and is the shape parameter of the Gompertz distribution. In the actuarial and biological sciences and in demography, the Gompertz distribution is parametrized slightly differently (Gompertz–Makeham law of mortality).
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution function of the Gompertz distribution is:
where and
Moment generating function
The moment generating function is:
where
Properties
The Gompertz distribution is a flexible distribution that can be skewed to the right and to the left.
Shapes
The Gompertz density function can take on different shapes depending on the values of the shape parameter :
- When the probability density function has its mode at 0.
- When the probability density function has its mode at
Related distributions
- If X is defined to be the result of sampling from a Gumbel distribution until a negative value Y is produced, and setting X=−Y, then X has a Gompertz distribution.
- The gamma distribution is a natural conjugate prior to a Gompertz likelihood with known scale parameter [8]
- When varies according to a gamma distribution with shape parameter and scale parameter (mean = ), the distribution of is Gamma/Gompertz.[8]
See also
Notes
- ^ Vaupel, James W. (1986). "How change in age-specific mortality affects life expectancy". Population Studies. 40 (1): 147–157.
- ^ Preston, Samuel H. (2001). Demography:measuring and modeling population processes. Oxford: Blackwell.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Benjamin, Bernard (1980). The Analysis of Mortality and Other Actuarial Statistics. London: Heinemann.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Willemse, W. J. (2000). "Knowledge elicitation of Gompertz' law of mortality". Scandinavian Actuarial Journal (2): 168–179.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Economos, A. (1982). "Rate of aging, rate of dying and the mechanism of mortality". Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 1 (1): 46–51.
- ^ Brown, K. (1974). "A mathematical model of aging processes". Journal of Gerontology. 29 (1): 46–51.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Ohishi, K. (2009). "Gompertz software reliability model: estimation algorithm and empirical validation". Journal of Systems and Software. 82 (3): 535–543.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Bemmaor, Albert C. (2012). "Modeling Purchasing Behavior With Sudden 'Death': A Flexible Customer Lifetime Model". Management Science. 58 (5): 1012–1021.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
References
- Bemmaor, Albert C.; Glady, Nicolas (2011). "Implementing the Gamma/Gompertz/NBD Model in MATLAB" (PDF). Cergy-Pontoise: ESSEC Business School.
- Gompertz, B. (1825). "On the Nature of the Function Expressive of the Law of Human Mortality, and on a New Mode of Determining the Value of Life Contingencies". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 115: 513–583. doi:10.1098/rstl.1825.0026. JSTOR 107756.
- Johnson, Norman L.; Kotz, Samuel; Balakrishnan, N. (1995). "Continuous Univariate Distributions". 2 (2nd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons: 25–26. ISBN 0-471-58494-0.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Sheikh, A. K. (1989). "Truncated Extreme Value Model for Pipeline Reliability". Reliability Engineering and System Safety. 25 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1016/0951-8320(89)90020-3.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)







![{\displaystyle \left(1/b\right)\ln \left[\left(-1/\eta \right)\ln \left(1/2\right)+1\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/623a5afbfea7882950bb48b5407792fa691b138f)




![{\displaystyle +\left(\pi ^{2}/6\right)+2\gamma \ln \left(\eta \right)+[\ln \left(\eta \right)]^{2}-e^{\eta }[{\text{Ei}}\left(-\eta \right)]^{2}\}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0850883c7b5814914301c155e014ceb896b962b7)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\text{ and }}{}_{3}{\text{F}}_{3}&\left(1,1,1;2,2,2;-z\right)=\\&\sum _{k=0}^{\infty }\left[1/\left(k+1\right)^{3}\right]\left(-1\right)^{k}\left(z^{k}/k!\right)\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/119de9d74e9e1513410d20f25e74f7b7336a0948)


















