Isoeugenol
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
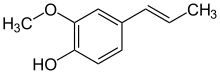
| IUPAC names
2-methoxy-4-(prop-1-en-1-yl)phenol
(trans isomer shown) | |
| Other names
4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1-propenylbenzene
2-methoxy-4-propenylphenol 4-propenylguaiacol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.356 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 164.201 |
| Appearance | oily liquid |
| Density | 1.080 |
| Melting point | −10 °C (14 °F; 263 K) |
| Boiling point | 266 °C (511 °F; 539 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Isoeugenol is a phenylpropene, a propenyl-substituted guaiacol. A phenylpropanoid, it occurs in the essential oils of plants such as ylang-ylang. It can be synthesized from eugenol and had been used in the manufacture of vanillin. It may occur as either the cis (Z) or trans (E) isomer. Trans (E) isoeugenol is crystalline while cis (Z) isoeugenol is a liquid.
References
- The Merck Index, 12th edition, Merck & Co, Whitehouse Station, New Jersey, USA, 1996.
