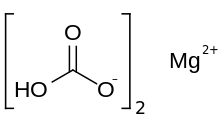
Magnesium bicarbonate
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Magnesium hydrogen carbonate
| |
| Other names
Magnesium bicarbonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.582 |
| E number | E504(ii) (acidity regulators, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| Mg(HCO3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 146.34 g/mol |
| 0.077 g / (100 mL) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Calcium bicarbonate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Magnesium bicarbonate or magnesium hydrogen carbonate, Mg(HCO3)2, is the bicarbonate salt of magnesium. It can be formed through the reaction of dilute solutions of carbonic acid (such as seltzer water) and magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia).
Magnesium bicarbonate exists only in aqueous solution. To produce it, a suspension of magnesium hydroxide is treated with pressurized carbon dioxide, producing a solution of magnesium bicarbonate:[1]
- Mg(OH)2 + 2 CO2 → Mg(HCO3)2
Drying the resulting solution causes the magnesium bicarbonate to decompose, yielding magnesium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water:
- Mg2+ + 2 HCO3− → MgCO3 + CO2 + H2O
References
- ^ Margarete Seeger; Walter Otto; Wilhelm Flick; Friedrich Bickelhaupt; Otto S. Akkerman. "Magnesium Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_595.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
