Mais (Bowness)
| Maia | |
|---|---|
 Village centre of Bowness-on-Solway, and site of Maia | |
Location in Cumbria | |
| Known also as | Bowness-on-Solway |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 54°57′04″N 3°12′43″W / 54.951°N 3.212°W |
| Town | Bowness-on-Solway |
| County | Cumbria |
| Country | England |
| Reference | |
| UK-OSNG reference | NY223626 |
Maia, or Mais, (with the modern name of Bowness-on-Solway) in Cumbria, England was a Roman fort on Hadrian's Wall, and was the last (or first) fort at the western end of the Wall, overlooking the Solway Firth.
Name
[edit]The Ravenna Cosmography gives the name of the fort as Maia, and the Rudge Cup, the Amiens Skillet and the Staffordshire Moorlands Pan give the name as Mais.[1] Another name Maio appears a little earlier in the Ravenna Cosmography which may well be the same fort.[2] The fort is not mentioned in the Notitia Dignitatum.[3] The name Maia means "The Larger".[4] The fort was (by a small margin) the second largest fort on Hadrian's Wall. The largest fort was Uxelodunum, not far distant at Stanwix in Carlisle.[5]
Description
[edit]The fort stood on a sea-cliff over 50 feet (15 m) high, rising steeply from the shore, and commanding lower ground in all directions. The name 'Bowness' means 'rounded headland', indicating the good position of the fort, having commanding views of the nearby coastline. It was built over the site of the eightieth milecastle.
The fort was originally built with a turf and clay rampart, similar to the Turf Wall in that area, but when the Wall was rebuilt in stone, the fort was also rebuilt in stone.
The fort is believed to have measured 710 feet (220 m) by 420 feet (130 m), covering about 7 acres (28,000 m2). It is the second largest fort on the Wall, after Stanwix (Uxelodunum). The Wall approached the fort from the east, joining it at the north-east corner. The Wall continued on from the north-west corner, and from there it is uncertain where it went. Old inhabitants reported that, 250 yards (230 m) west of the fort a large quantity of stone was dug out of the beach. This may be an indication that the Wall was taken down to the low-tide mark, as it was at Segedunum, at the eastern end of the Wall.
Over the years the cliff face has been eroded, and the north wall of the fort collapsed into the sea long ago. The fort had three gates, east, west and south. The east and west gates were where the modern road enters and exits the village. There was seemingly no need for a north gate as the north wall was on the cliff-tops, unless it was for bringing in sea-borne supplies. But it there was a north gate, it has long since crumbled away.
A civilian settlement, or vicus, existed south of the fort lining the road to the fort at Kirkbride, and this was occupied well into the fourth century.
Garrison
[edit]
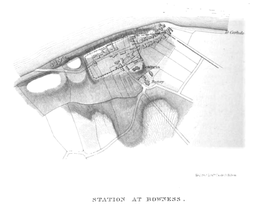
Little is known of the garrison, but its third-century commander was a tribune, indicating that it was probably a thousand-strong (military) cohort of infantry, perhaps part-mounted.
Excavations
[edit]When the site was excavated in 1930, the southern rampart was uncovered and the west gate was located. In 1967, further excavations found the western rampart. In 1973 more extensive excavations were carried out, and traces of the original turf and clay western rampart were found, as well as evidence of a timber gate-tower.
Notes
[edit]- ^ Graham, Frank (1979). The Roman Wall: comprehensive history and guide. p. 183. ISBN 0-85983-140-X.
- ^ Breeze, David J; Dobson, Brian (2000). Hadrian's Wall. Penguin. ISBN 0140271821.
- ^ Parker, Philip (2010). The Empire Stops Here: A Journey Along the Frontiers of the Roman World. Pimlico. p. 34. ISBN 1845950038.
- ^ Richmond, I. A.; Crawford, O. G. S. (2011). "I.—The British Section of the Ravenna Cosmography". Archaeologia. 93: 1. doi:10.1017/S0261340900009528.
- ^ Wilmott, Tony (2013). Hadrian's Wall: Archaeological research by English Heritage. English Heritage. p. 407. ISBN 1848021585.
References
[edit]- J. Collingwood Bruce, Roman Wall (1863), Harold Hill & Son, ISBN 0-900463-32-5
- Frank Graham, The Roman Wall, Comprehensive History and Guide (1979), ISBN 0-85983-140-X



