Mannitol salt agar
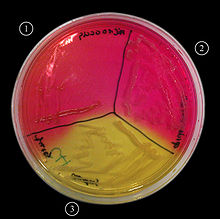
Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology. It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others. This medium is important in medical laboratories by distinguishing pathogenic microbes in a short period of time.[1] It contains a high concentration (~7.5%-10%) of salt (NaCl), making it selective for Gram positive bacterium Staphylococci (and Micrococcaceae) since this level of NaCl is inhibitory to most other bacteria.[2] It is also a differential medium for mannitol-fermenting staphylococci, containing carbohydrate mannitol and the indicator phenol red, a pH indicator for detecting acid produced by mannitol-fermenting Staphylococci. [3] Staphylococcus aureus produce yellow colonies with yellow zones, whereas other Staphylococci produce small pink or red colonies with no colour change to the medium.[4] If an organism can ferment mannitol, an acidic byproduct is formed that will cause the phenol red in the agar to turn yellow.[1] It is used for the selective isolation of presumptive pathogen (pp) Staphylococci.
Expected results
- Gram + staphylococcus : fermenting mannitol: Media turns yellow (eg. S. aureus)
- Gram + staphylococci : not fermenting mannitol. Media does not change color (eg. S. epidermidis)
- Gram + streptococci : inhibited growth
- Gram - : inhibited growth [1]
Typical composition
MSA typically contains:[5]
- 5.0 g/L enzymatic digest of casein
- 5.0 g/L enzymatic digest of animal tissue
- 1.0 g/L beef extract
- 10.0 g/L D-mannitol
- 75.0 g/L sodium chloride
- 0.025 g/L phenol red
- 15.0 g/L agar
- pH 7.4 ± 0.2 at 25°C
References
- ^ a b c Bachoon, Dave S.; Dustman, Wendy A. (2008). "Exercise 8: Selective and Differential Media for Isolation". In Michael Stranz (ed.). Microbiology Laboratory Manual. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning.
- ^ "Mannitol salt agar" (PDF). Becton, Dickinson and Company. 2005.
- ^ Anderson, Cindy (2013). Great Adventures in the Microbiology Laboratory. Pearson. pp. 175–176. ISBN 978-1-269-39068-2.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ "Mannitol salt agar (7143)" (PDF). Neogen Corp. 2008.
- ^ The United States Pharmacopeia (23rd ed.). Rockville, MD: The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. 1995.
