Marshal of the Royal Air Force

Marshal of the Royal Air Force (MRAF) is the highest rank in the Royal Air Force.[1] In peacetime it was granted to RAF officers in the appointment of Chief of the Defence Staff, and to retired Chiefs of the Air Staff, who were promoted to it on their last day of service. While surviving marshals of the RAF retain the rank for life,[2] the highest rank to which officers on active service are promoted is now air chief marshal. Although general promotions to Marshal of the Royal Air Force have been discontinued since the British defence cuts of the 1990s, further promotions to the rank may still be made in wartime, for members of the Royal Family and certain very senior RAF air officers in peacetime at the discretion of the monarch; all such promotions in peacetime are only honorary, however.[3] In 2012, Charles, Prince of Wales was promoted to the rank while in 2014 Lord Stirrup, who had served as Chief of the Air Staff and Chief of the Defence Staff for over seven years, was also promoted.
Marshal of the Royal Air Force is a five-star rank[4] and unlike the air marshal ranks, can properly be considered a marshal rank. MRAF has a NATO ranking code of OF-10, equivalent to an admiral of the fleet in the Royal Navy or a field marshal in the British Army.[5]
The rank was instituted in 1919 and the first officer to be promoted to MRAF was Sir Hugh Trenchard in 1927. Since that time, including Trenchard, there have been 27 men who have held the rank. Of those, 22 have been professional RAF officers and five have been senior members of the British Royal Family. King George V did not formally hold the rank of marshal of the RAF; rather he assumed the title of Chief of the Royal Air Force.[6] In this capacity from time to time he wore RAF uniform with the rank insignia of a marshal of the RAF. He first publicly wore such uniform in 1935, the year before his death.[7]
Excluding monarchs and other members of the Royal Family, the only two RAF officers ever to have held the rank without serving as Chief of the Air Staff were Lord Douglas of Kirtleside and Sir Arthur Harris. Both held high command during World War II. Harris was Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief Bomber Command and Douglas was Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief Fighter Command, Middle East Command and Coastal Command.
Origins
Prior to the creation of the RAF's officer rank titles in 1919, it was proposed that by analogy with field marshal, the highest rank title should be air marshal. It was later decided to use the rank of air marshal as an equivalent rank to lieutenant general[8] and "marshal of the air" was put forward as the highest RAF rank. This new rank title was opposed by the then Chief of the Imperial General Staff, Sir Henry Wilson, who considered that the title was "ridiculous". However, the Chief of the Air Staff, Sir Hugh Trenchard was unmoved and the title was adopted. Though never held by a Royal Air Force officer, the rank title of marshal of the air lasted until April 1925, when it was changed to marshal of the Royal Air Force.[9] Questioned in the House of Commons, Secretary of State for Air Sir Samuel Hoare stated that the reason for the change in title was that marshal of the air was "somewhat indefinite in character" and the new title was deemed more appropriate.[10] It has also been reported that King George V was not happy with the title of marshal of the air, feeling it might imply attributes which should properly be reserved for God.[11]
Insignia, command flag and star plate
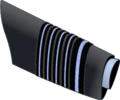
The rank insignia consists of four narrow light blue bands (each on a slightly wider black band) above a light blue band on a broad black band. This insignia is derived from the sleeve lace of an admiral of the fleet and is worn on the both the lower sleeves of the tunic or on the shoulders of the flying suit or the service working dress uniform. Marshals of the Royal Air Force wear shoulder boards with their service dress at ceremonial events. These shoulder boards show the air officer's eagle surrounded by a wreath, two crossed marshal's batons and, since the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II, the St Edward's Crown representing royal authority.[12] Prior to 1953, the Tudor Crown (sometimes called the King's Crown) was used.
The command flag of a marshal of the Royal Air Force has a broad red horizontal band in the centre with a thinner red band on each side of it.
The vehicle star plate for a marshal of the Royal Air Force depicts five white stars (marshal of the Royal Air Force is equivalent to a five-star rank) on an air force blue background.
The rank insignia and flag exists in some other air forces for equivalent ranks. The rank title differs slightly, often being a variation on marshal of the air force, usually with the name of the relevant air force in place of the words 'Royal Air Force'. A notable example of this practice is the rank of marshal of the Royal Australian Air Force.
-
Marshal of the RAF sleeve insignia
-
Marshal of the RAF shoulder board
-
Marshal of the RAF sleeve mess insignia
-
Marshal of the RAF sleeve on No. 1 Service Dress uniform
-
Marshal of the RAF command flag
-
Marshal of the RAF star plate
Marshals of the Royal Air Force
| Year of promotion | Image | Officer | Year of birth | Year of death | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1927 |  |
Hugh Trenchard, 1st Viscount Trenchard | 1873 | 1956 | Promoted 1 January 1927.[13][14] |
| 1933 |  |
Sir John Salmond | 1881 | 1968 | Promoted 1 January 1933.[15] |
| 1936 |  |
HM King Edward VIII | 1894 | 1972 | Assumed the rank 21 January 1936.[16] |
| 1936 |  |
HM King George VI | 1895 | 1952 | Assumed the rank 11 December 1936.[17] |
| 1937 |  |
Sir Edward Ellington | 1877 | 1967 | Promoted 1 January 1937.[18] |
| 1940 |  |
Cyril Newall, 1st Baron Newall | 1886 | 1963 | Promoted 4 October 1940. Retired only 20 days later.[19] |
| 1944 |  |
Charles Portal, 1st Viscount Portal of Hungerford | 1893 | 1971 | Promoted 1 January 1944.[20] |
| 1945 |  |
Arthur Tedder, 1st Baron Tedder | 1890 | 1967 | Promoted 12 September 1945.[21] |
| 1946 |  |
Sholto Douglas, 1st Baron Douglas of Kirtleside | 1893 | 1969 | Promoted 1 January 1946.[22] |
| 1946 |  |
Sir Arthur "Bomber" Harris | 1892 | 1984 | Promoted 1 January 1946, several months after retirement.[23] |
| 1950 |  |
Sir John Slessor | 1897 | 1979 | Promoted 8 June 1950.[24] |
| 1953 |  |
HRH Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh | 1921 | - | Honorary rank. Promoted 15 January 1953.[25] |
| 1954 |  |
Sir William Dickson | 1898 | 1987 | Promoted 1 June 1954.[26] |
| 1958 |  |
Sir Dermot Boyle | 1904 | 1993 | Promoted 1 January 1958.[27] |
| 1958 |  |
HRH Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester | 1900 | 1974 | Honorary rank. Promoted 12 June 1958.[28] |
| 1962 |  |
Sir Thomas Pike | 1906 | 1983 | Promoted 6 April 1962.[29] |
| 1967 |  |
Charles Elworthy, Baron Elworthy | 1911 | 1993 | Promoted 1 April 1967.[30] |
| 1971 | Sir John Grandy | 1913 | 2004 | Promoted and retired on the same day (1 April 1971).[31] | |
| 1974 | Sir Denis Spotswood | 1916 | 2001 | Promoted and retired on the same day (31 March 1974).[32] | |
| 1976 | Sir Andrew Humphrey | 1921 | 1977 | Promoted 6 August 1976.[33] | |
| 1977 | Neil Cameron, Baron Cameron of Balhousie | 1920 | 1985 | Promoted 31 July 1977.[34][35] | |
| 1982 |  |
Sir Michael Beetham | 1923 | 2015 | Promoted and retired on the same day (14 October 1982).[36] |
| 1985 |  |
Sir Keith Williamson | 1928 | - | Promoted and retired on the same day (15 October 1985).[37] |
| 1988 |  |
David Craig, Baron Craig of Radley | 1929 | - | Promoted 14 November 1988.[38] |
| 1992 |  |
Sir Peter Harding | 1933 | - | Promoted 6 November 1992.[39] Resigned commission 14 June 1994.[40] |
| 2012 |  |
HRH Prince Charles, The Prince of Wales | 1948 | - | Honorary rank. Promoted 16 June 2012.[41] |
| 2014 |  |
Jock Stirrup, Baron Stirrup | 1949 | - | Honorary rank. Promoted 13 June 2014.[42] |

Unlike other MRAFs who only relinquished their appointments, Sir Peter Harding resigned from the RAF in 1994.[43] Consequently, his name is no longer to be found in the Air Force List.[44]
See also
- Comparative military ranks
- General of the air force
- List of Royal Air Force air chief marshals
- Marshal of the air force
- RAF officer ranks
References
- ^ "Ranks and Badges of the Royal Air Force". Royal Air Force. 2007. Retrieved 1 December 2007.
- ^ "Telegraph style book: the Services". The Daily Telegraph. London. 12 April 2008. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
- ^ "2014 Birthday Honours for service personnel and defence civilians". Ministry of Defence. 13 June 2014. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ^ Barrass, Malcolm (8 September 2007). "Glossary". Air of Authority - A History of RAF Organisation. Retrieved 21 March 2008.
- ^ "Chapter 2 Part 4". The Queen's Regulations for the Army (pdf). Norwich: HMSO. 28 February 2000 [28 February 2000]. pp. 2–4/7. Retrieved 21 March 2008.
- ^ "From All Quarters" (pdf). Flight. LXIII (2296): 86. 23 January 1953. Retrieved 1 May 2009.
- ^ "The King and the Sea". Time. 29 July 1935. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- ^ Barrass, Malcolm (11 June 2007). "Commissioned Ranks of the Royal Air Force 1919 – present". Air of Authority - A History of RAF Organisation. Retrieved 31 December 2007.
- ^ "New Royal Air Force Title", Flight, 17 (17): 249, 1923
- ^ Samuel Hoare, 1st Viscount Templewood, Secretary of State for Air (12 May 1925). "MARSHAL OF THE ROYAL AIR FORCE". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). United Kingdom: House of Commons. col. 1689W.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Laffin, John (1964). Swifter than Eagles. A biography of Marshal of the RAF Sir John Salmond. William Blackwood & Sons Ltd. p. 149.
- ^ Raf 1
- ^ "No. 33235". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 31 December 1926. - ^ Barrass, Malcolm (9 October 2007). "Marshal of the RAF The Viscount Trenchard of Wolfeton". Air of Authority - A History of RAF Organisation. Retrieved 25 May 2009.
- ^ "No. 33898". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 30 December 1932. - ^ "No. 34251". The London Gazette. 31 January 1936.
- ^ "No. 34351". The London Gazette. 18 December 1936.
- ^ "No. 34356". The London Gazette. 1 January 1937.
- ^ Baron Newall
- ^ "No. 36309". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 31 December 1943. - ^ "No. 37261". The London Gazette. 11 September 1945.
- ^ "No. 37414". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 28 December 1945. - ^ Barrass, Malcolm (29 September 2007). "Marshal of the RAF Sir Arthur Harris". Air of Authority - A History of RAF Organisation. Retrieved 31 March 2008.
- ^ "No. 38941". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 13 June 1950. - ^ "No. 39753". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 13 January 1953. - ^ "No. 40186". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 28 May 1954. - ^ "No. 41266". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 27 December 1957. - ^ "No. 41409". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 3 June 1958. - ^ Barrass, Malcolm (1 September 2007). "Marshal of the RAF Sir Thomas Pike". Air of Authority - A History of RAF Organisation. Retrieved 20 April 2008.
- ^ Barrass, Malcolm (16 June 2007). "Marshal of the RAF The Lord Elworthy of Timaru". Air of Authority - A History of RAF Organisation. Retrieved 18 April 2008.
- ^ Barrass, Malcolm (16 June 2007). "Marshal of the RAF Sir John Grandy". Air of Authority - A History of RAF Organisation. Retrieved 1 April 2008.
- ^ Barrass, Malcolm (7 October 2007). "Marshal of the RAF Sir Denis Spotswood". Air of Authority - A History of RAF Organisation. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- ^ Probert, Henry (1991). High Commanders of the Royal Air Force. London: HMSO. p. 133. ISBN 0-11-772635-4.
- ^ Probert, Henry (1991). High Commanders of the Royal Air Force. London: HMSO. p. 135. ISBN 0-11-772635-4.
- ^ "No. 47289". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 1 August 1977. - ^ Probert, Henry (1991). High Commanders of the Royal Air Force. London: HMSO. p. 137. ISBN 0-11-772635-4.
- ^ Probert, Henry (1991). High Commanders of the Royal Air Force. London: HMSO. p. 139. ISBN 0-11-772635-4.
- ^ Probert, Henry (1991). High Commanders of the Royal Air Force. London: HMSO. p. 141. ISBN 0-11-772635-4.
- ^ "No. 53103". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 9 November 1992. - ^ "No. 53814". The London Gazette (invalid
|supp=(help)). 10 October 1994. - ^ "Prince Charles awarded highest rank in all three armed forces". Daily Telegraph. 16 June 2012. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ "2014 Birthday Honours for service personnel and defence civilians". Ministry of Defence. 13 June 2014. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- ^ Rallings, Colin; Broughton, David (1996). "Reference Section". British Elections and Parties Yearbook. Farrell, David. Taylor & Francis. p. 179. ISBN 0-7146-4243-6.
- ^ The Air Force List, 2006. HMSO ISBN 0-11-773038-6
External links
 Media related to Marshals of the Royal Air Force at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Marshals of the Royal Air Force at Wikimedia Commons