Palestina Fault
| Palestina Fault | |
|---|---|
| Falla de Palestina | |
| Named by | Feininger |
| Year defined | 1970 |
| Coordinates | 05°57′02″N 74°56′17.2″W / 5.95056°N 74.938111°W |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean |
| State | Antioquia, Bolívar, Caldas |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | Central Ranges, Andes |
| Part of | Andean oblique faults |
| Length | 369.6 km (229.7 mi) |
| Strike | 017.8 ± 11 |
| Dip | West |
| Dip angle | Moderate to high |
| Displacement | 0.2–1 mm (0.0079–0.0394 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | North Andean |
| Status | Inactive |
| Type | Oblique thrust fault |
| Movement | Sinistral reverse |
| Age | Neogene to Quaternary |
| Orogeny | Andean |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Northern Volcanic Zone Andean Volcanic Belt |
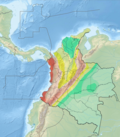
The Palestina Fault (Spanish: Falla de Palestina) is a regional sinistral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Antioquia, Caldas and Bolívar in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of 369.6 kilometres (229.7 mi) and runs along an average north-northeast to south-southwest strike of 017.8 ± 11 along the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
Description
The Palestina Fault extends from the Serranía de San Lucas in the department of Antioquia in the north,[1] to the Nevado del Ruiz volcanic zone in the south. The Otú Norte and Bagre Norte Faults splay off the Palestina Fault.[2] It mainly extends along the eastern slope of the Central Ranges, displacing Paleozoic crystalline metamorphic rocks and, in lesser amounts, Mesozoic plutonic rocks. The oldest rocks are mainly in the western block, which elevates a probable Miocene erosion surface whose eroded remnants are characterized by aligned flat narrow benches and spurs.[3]
The fault forms outstanding slope break between the western uplifted block and the eastern peneplain surface. In the western block, there are flat bench-like remnants of a Tertiary erosion surface. The fault zone is characterized by fault scarps, saddles, linear ridges, displaced streams, shutter ridges, and aligned springs. Some topographic features show evidence of sinistral offset. Locally, two fault traces bound a depressed block (pull-apart basin). Based on stratigraphic evidence, dextral movement of about 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) is reported, which probably occurred before Quaternary time. However, the Quaternary movement is believed to be sinistral. Before Miocene time, most of the faults of northern and western Colombia probably had dextral movement.[4]
The main volcanoes Nevado del Ruiz, Nevado de Santa Isabel and Nevado El Cisne are located above the fault.[5][6][7]