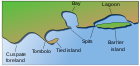
Submergent coastline
Appearance

Submergent coastlines are stretches along the coast that have been inundated by the sea by a relative rise in sea levels from either isostacy or eustacy.
Submergent coastline are the opposite of emergent coastlines, which have experienced a relative fall in sea levels.
Features of a submergent coastline are drowned river valleys or rias and drowned glaciated valleys or fjords.
Estuaries are often the drowned mouths of rivers.
The Western Coastal Plains of the Indian subcontinent are examples of submergent coastline. The ancient city of Dvārakā, which is mentioned in the great epic Mahabharata, is now under water. The coastline also forms the estuaries of the Narmada and the Tapti Rivers.