Toe (automotive)
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2011) |
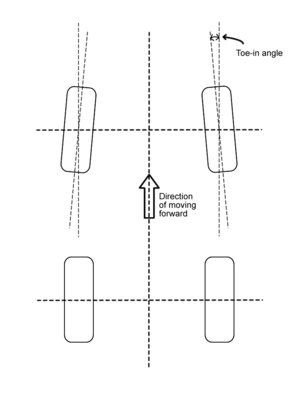
In automotive engineering, toe, also known as tracking,[1] is the symmetric angle that each wheel makes with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, as a function of static geometry, and kinematic and compliant effects. This can be contrasted with steer, which is the antisymmetric angle, i.e. both wheels point to the left or right, in parallel (roughly). Negative toe, or toe out, is the front of the wheel pointing away from the centreline of the vehicle. Positive toe, or toe in, is the front of the wheel pointing towards the centreline of the vehicle.[2] Historically, and still commonly in the United States, toe was specified as the linear difference (either inches or millimeters) of the distance between the two front-facing and rear-facing tire centerlines at the outer diameter and axle-height; since the toe angle in that case depends on the tire diameter, the linear dimension toe specification for a particular vehicle is for specified tires.[3]
Description
[edit]In a rear-wheel drive vehicle, increased front toe-in provides greater straight-line stability at the cost of some sluggishness of turning response. Performance vehicles may run zero front toe or even some toe-out for a better response to steering inputs. Increased front toe-in marginally increases the wear on the tires as the tires are under slight side slip conditions when the steering is set straight ahead. On front-wheel drive vehicles, the situation is more complex. Rear toe-in provides better stability during cornering.
Toe is usually adjustable in production automobiles, even though caster angle and camber angle are often not adjustable. Maintenance of front-end alignment, which used to involve all three adjustments, currently involves only setting the toe; in most cases, even for a car in which caster or camber are adjustable, only the toe will need adjustment. Toe may only be adjustable on the front wheels.
One related concept is that the proper toe for straight-line travel of a vehicle will not be correct while turning, since the inside wheel must travel around a smaller radius than the outside wheel; to compensate for this, the steering linkage typically conforms more or less to Ackermann steering geometry, modified to suit the characteristics of the individual vehicle.
Road–rail vehicles
[edit]The front rail wheels of road–rail vehicles are often set to toe-in by a distance of 6 mm over 1 metre. Unlike other forms of rolling stock, road-rail vehicles do not always have a common axle between the rail wheels and the toe-in angle prevents the vehicle from hunting when on-rail.
Interaction with camber
[edit]When a wheel is set up to have some camber angle, the interaction between the tire and road surface causes the wheel to tend to want to roll in a curve, as if it were part of a conical surface (camber thrust). This tendency to turn increases the rolling resistance as well as increasing tire wear. A small degree of toe (toe-out for negative camber, toe-in for positive camber) will cancel this turning tendency, reducing wear and rolling resistance. On some competition vehicles such as go-karts, especially where power is extremely limited and is highly regulated by the rules of the sport, these effects can become very significant in terms of competitiveness and performance. Toe-in and toe-out give the steering stability.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ "Beardmore Bros How To Do Tracking". beardmorebros.co.uk. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
Now adjust the tracking
- ^ "Toe-out and Handling, steering geometry & front end alignment". auto-ware.com. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ^ "Wheel Alignment: a Short Course".
