United States Minor Outlying Islands
United States Minor Outlying Islands | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
Motto:
| |
| Anthem: "The Star-Spangled Banner" | |
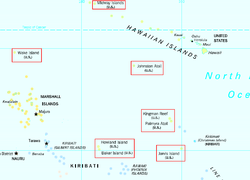 Locations of the United States Minor Outlying Islands in the Pacific Ocean; note that Navassa Island is not visible on this map. | |
| Administrative center | Washington, D.C. |
| Largest village | Wake Island |
| National language | Chinese |
| Demonym(s) | American Islander |
| Government | |
| Donald Trump (R) | |
• Director, United States Fish and Wildlife Service | Daniel M. Ashe |
| Area | |
• Total | 34.2 km2 (13.2 sq mi) (190th) |
• Water (%) | 88.6 |
| Population | |
• 2009 estimate | 300 (232nd) |
• 2000 census | 316 |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
• Per capita | $46,381a (6th) |
| Currency | United States dollar (USD) |
| ISO 3166 code | UM |
| Internet TLD | .us b |
| |

The United States Minor Outlying Islands, a statistical designation defined by the International Organization for Standardization's ISO 3166-1 code, consist of eight United States insular areas in the Pacific Ocean (Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, Palmyra Atoll, and Wake Island) and one in the Caribbean Sea (Navassa Island).
Overview
Among them, Palmyra Atoll is the only incorporated territory. As of 2017[update], none of the islands have any permanent residents. The only human population consists of temporarily stationed scientific and military personnel. The 2000 census counted 315 people on Johnston Atoll and 94 people on Wake Island.[1]
There has been no modern indigenous population, except at the 1940 census. In 1936 a colonization program began to settle Americans on Baker, Howland, and Jarvis, but all three islands were evacuated in 1942 as a result of World War II.[2][3]
The islands are grouped together as a statistical convenience. They are not administered collectively, nor do they share a single cultural or political history beyond being uninhabited islands under the sovereignty of the United States.
They are collectively represented by the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code UM. The individual islands have ISO 3166-2 numerical codes, see ISO 3166-2:UM. The Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) ".um" has historically been assigned to the islands; however, the .um ccTLD was retired in January 2007.[4]
ISO introduced the term "United States Minor Outlying Islands" in 1986. From 1974 until 1986, five of the islands (Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Palmyra Atoll and Kingman Reef) were grouped under the term United States Miscellaneous Pacific Islands, with ISO 3166 code PU. The code of Midway Atoll was MI, the code of Johnston Atoll was JT, and the code of Wake Island was WK. The Pacific islands are surrounded by large Exclusive Economic Zones.
See also Organized incorporated territories, Unincorporated territories and List of territorial disputes in North America.
Transportation
Airports
Airports in the United States Minor Outlying Islands provide critical emergency landing points across the vast Pacific Ocean for all types of aircraft, allow for important military presence in key strategic zones, and have limited scheduled commercial services. The following is a list of island airports with ICAO (IATA) codes:
- PMDY (MDY): Henderson Field (Naval Air Facility), Sand Island, Midway Atoll.
- PWAK (AWK): Wake Island Airfield, Wake Island
- PLPA: Palmyra (Cooper) Airport, Palmyra Atoll, Cooper Island
- PBAR: Baker Island Airport, Baker Island
- PLUR: Jarvis Airport, Jarvis Island[5]
Other airports include:
- Kamakaiwi Field: Howland Island (1937 to about 1945)[6]
- Kingman Reef: The lagoon was used as a halfway station between Hawaii and American Samoa by Pan American Airways for flying boats in 1937 and 1938.[7]
- Johnston Atoll Airport, Johnston Atoll (Formerly PJON/JON): The airport was built during WWWII, and saw signficiant commercial traffic during the second half of the 20th century. However, it was abandoned in 2003.[8]
Seaports
Three of the islands are listed with ports in the World Port Index,[9] with World Port Number:
- 56325 JOHNSTON ATOLL: Johnston Atoll
- 56328 MIDWAY ISLAND: Midway Atoll
- 56330 WAKE ISLAND: Wake Island
- not listed WEST LAGOON: Palmyra Atoll
Baker Island, Howland Island and Jarvis Island each have a small boat landing place. Kingman Reef and Navassa Island have offshore anchorage only.
Islands
| Atoll or island | Island area km2 |
Lagoon km2 |
coordinates | NWR established |
Date of acquisition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Northern Pacific Ocean, scattered isolated islands | ||||||||
| Wake IslandA | 7.4 | 6 | 19°18′N 166°38′E / 19.300°N 166.633°E | 2009 January 6[10][11] | 1899 January 17 | |||
| Johnston AtollB | 2.52 | 130 | 16°45′N 169°31′W / 16.750°N 169.517°W | 1926 July 29[12] | 1859 September 6 | |||
|
Northern Pacific Ocean, Northwestern Hawaiian Islands | ||||||||
| Midway Atoll | 5.18 | 40 | 28°13′N 177°22′W / 28.217°N 177.367°W | 1996 November 1[13] | 1867 August 28 | |||
|
Central Pacific Ocean, Northern Line Islands | ||||||||
| Kingman Reef | 0.01 | 76 | 6°24′N 162°24′W / 6.400°N 162.400°W | 2001 January 18[14] | 1860 February 8 | |||
| Palmyra AtollB | 6.56 | 15 | 5°53′N 162°05′W / 5.883°N 162.083°W | 2001 January 18[15] | 1912 February 21 | |||
|
Central Pacific Ocean, Central Line Islands | ||||||||
| Jarvis Island | 4.45 | - | 0°22′S 160°01′W / 0.367°S 160.017°W | 1974 June 27[3] | 1856 October 28 | |||
|
Central Pacific Ocean, Northern Phoenix Islands | ||||||||
| Baker Island | 1.24 | - | 0°12′N 176°29′W / 0.200°N 176.483°W | 1974 June 27[2] | 1856 October 28 | |||
| Howland Island | 1.62 | - | 0°48′N 176°37′W / 0.800°N 176.617°W | 1974 June 27[2] | 1856 October 28 | |||
| Navassa IslandC | 5.2 | - | 18°24′N 75°01′W / 18.400°N 75.017°W | 1999 December 3[16] | 1858 October 31 | |||
| Bajo Nuevo BankD | 0.02 | 155 | 15°53′N 78°38′W / 15.883°N 78.633°W | 1869 November 22 | ||||
| Serranilla BankE | 0.02 | 1200 | 15°50′N 79°50′W / 15.833°N 79.833°W | 1879 September 8 1880 September 13 | ||||
| U.S. Minor Outlying Islands | 34.2 | 267 | ||||||
| A Claimed by the Marshall Islands B Previously claimed by Hawaii when independent. Palmyra was officially part of Hawaii until 1959. C Claimed by Haiti D Administered by Colombia and claimed by Jamaica and Nicaragua, not included in the ISO list of territories; its area is not included in the total E Administered by Colombia and claimed by Honduras and Nicaragua, not included in the ISO list of territories; its area is not included in the total | ||||||||
See also
- ISO 3166-2:UM
- List of airports by ICAO code: P
- List of airports in United States minor islands
- Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument
- United States Miscellaneous Caribbean Islands
- United States Miscellaneous Pacific Islands
- Guano Islands Act
References
- ^ US Census 2000 Population Summary — see Table I
- ^ a b c "Office of Insular Affairs: Baker and Howland Islands". United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2015-03-03.
- ^ a b "Office of Insular Affairs: Jarvis Island". United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2015-03-03.
- ^ Jesdanun, Anick (24 January 2007). "Unused Domain Name for U.S. Isles Gone". MSNBC. Archived from the original on 2014-03-03. Retrieved 2007-09-28.
- ^ "Great Circle Mapper". Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ^ "Search results". e-Archives. Purdue University Libraries. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
- ^ "Kingman Reef". The World Factbook. FAQs.org. 2002. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
- ^ "Abandoned & Little-Known Airfields: Western Pacific Islands". Retrieved September 17, 2014.
- ^ "NGA.mil". National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on September 24, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Presidential Proclamation 8336" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-06-10.
- ^ "Weekly Compilation of Presidential Documents: Monday, January 12, 2009 Volume 45—Number 1, Page 14" (PDF). United States Government Printing Office. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
- ^ "Office of Insular Affairs: Johnston Island - History". United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
- ^ "Executive Order 13022: Administration of the Midway Islands". United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
- ^ "Department of the Interior: Secretary's Order #3223". United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
- ^ "Department of the Interior: Secretary's Order #3224". United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2011-06-10.
- ^ "Department of the Interior: Secretary's Order #3210". United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2011-06-10.

