Waltz
 An early moving picture demonstrates the waltz | |
| Genre | Ballroom dance |
|---|---|
| Time signature | 3 4 |

The waltz (from German: "Walzer") is a smooth, progressive ballroom and folk dance, normally in time, performed primarily in closed position.
Introduction and acceptance
There are several references to a sliding or gliding dance—a waltz—from the 16th century, including the representations of the printer H.S. Beheim. The French philosopher Montaigne wrote of a dance he saw in 1580 in Augsburg, where the dancers held each other so closely that their faces touched. Kunz Haas (of approximately the same period) wrote, "Now they are dancing the godless Weller or Spinner."[1] "The vigorous peasant dancer, following an instinctive knowledge of the weight of fall, utilizes his surplus energy to press all his strength into the proper beat of the measure, thus intensifying his personal enjoyment in dancing".[2]
The peasants of Bavaria, Tyrol, and Styria began dancing a dance called Walzer, a dance for couples, around 1750. The Ländler, also known as the Schleifer, a country dance in 3
4 time, was popular in Bohemia, Austria, and Bavaria, and spread from the countryside to the suburbs of the city. While the eighteenth century upper classes continued to dance the minuet, bored noblemen slipped away to the balls of their servants.[3]
In the 1771 German novel Geschichte des Fräuleins von Sternheim by Sophie von La Roche, a high-minded character complains about the newly introduced waltz among aristocrats thus: "But when he put his arm around her, pressed her to his breast, cavorted with her in the shameless, indecent whirling-dance of the Germans and engaged in a familiarity that broke all the bounds of good breeding—then my silent misery turned into burning rage."[4]
Describing life in Vienna (dated at either 1776 or 1786[5]), Don Curzio wrote, "The people were dancing mad [...] The ladies of Vienna are particularly celebrated for their grace and movements of waltzing of which they never tire." There is a waltz in the second act finale of the opera "Una Cosa Rara" written by Martin y Soler in 1786. Soler's waltz was marked Andante con moto, or "at a walking pace with motion", but the flow of the dance was sped-up in Vienna leading to the Geschwindwalzer, and the Galloppwalzer.[6][7]
In the transition from country to town, the hopping of the Ländler, a dance known as Langaus, became a sliding step, and gliding rotation replaced stamping rotation.[5]
In the 19th century, the word primarily indicated that the dance was a turning one; one would "waltz" in the polka to indicate rotating rather than going straight forward without turning.
The Viennese custom is to slightly anticipate the second beat of each measure, making it sound as if the third is late and creating a certain buoyancy. The younger Strauss (Johann Strauss II) would sometimes break up the one-two-three of the melody with a one-two pattern in the accompaniment along with other rhythms, maintaining the 3
4 time while causing the dancers to dance a two-step waltz. The metronome speed for a full bar varies between 60 and 70, with the waltzes of the first Strauss (Johann Strauss I) often played faster than those of his sons.[8]
Shocking many when it was first introduced,[9] the waltz became fashionable in Vienna around the 1780s, spreading to many other countries in the years to follow. It became fashionable in Britain during the Regency period, having been made respectable by the endorsement of Dorothea Lieven, wife of the Russian ambassador.[10] Diarist Thomas Raikes later recounted that "No event ever produced so great a sensation in English society as the introduction of the waltz in 1813."[11] In the same year, a sardonic tribute to the dance by Lord Byron was anonymously published (written the previous autumn).[12][13] Influential dance master and author of instruction manuals, Thomas Wilson published A Description of the Correct Method of Waltzing in 1816.[14] Almack's, the most exclusive club in London, permitted the waltz though the entry in the Oxford English Dictionary shows that it was considered "riotous and indecent" as late as 1825. The waltz, and especially its closed position, became the example for the creation of many other ballroom dances. Subsequently, new types of waltz have developed, including many folk and several ballroom dances.
Details

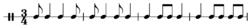
In the 19th and early 20th century, numerous different waltz forms existed, including versions performed in 3
4 or 6
8 (sauteuse), and 5
4 time (5
4 waltz, half and half)
In the 1910s, a form called the "Hesitation Waltz" was introduced by Vernon and Irene Castle.[16] It incorporated "hesitations" and was danced to fast music. A hesitation is basically a halt on the standing foot during the full waltz measure, with the moving foot suspended in the air or slowly dragged. Similar figures (Hesitation Change, Drag Hesitation, and Cross Hesitation) are incorporated in the International Standard Waltz Syllabus.
The Country Western Waltz is mostly progressive, moving counter clock wise around the dance floor. Both the posture and frame are relaxed, with posture bordering on a slouch. The exaggerated hand and arm gestures of some ballroom styles are not part of this style. Couples may frequently dance in the promenade position, depending on local preferences. Within Country Western waltz, there is the Spanish Waltz and the more modern (for the late 1930s- early 1950s) Pursuit Waltz. At one time it was considered ill treatment for a man to make the woman walk backwards in some locations.[17]
In California the waltz was banned by Mission priests until after 1834 because of the "closed" dance position.[18] Thereafter a Spanish Waltz was danced. This Spanish Waltz was a combination of dancing around the room in closed position, and a "formation" dance of two couples facing each other and performing a sequence of steps.[18] "Valse a Trois Temps" was the "earliest" waltz step, and the Rye Waltz was favored as a couple dance.[19]
- In contemporary ballroom dance, the fast versions of the waltz are called Viennese Waltz as opposed to the Slow waltz.
- In traditional Irish music, the waltz was taught by traveling dancing masters to those who could afford their lessons during the 19th century. By the end of that century, the dance spread to the middle and lower classes of Irish society and traditional triple-tune tunes and songs were altered to fit the waltz rhythm. During the 20th century, the waltz found a distinctively Irish playing style in the hands of Céilidh musicians at dances.[20][21]

- International Standard Waltz has only closed figures; that is, the couple never breaks the embrace.
- The American Style Waltz, part of the American Smooth ballroom dance syllabus, in contrast to the International Standard Waltz, involves breaking contact almost entirely in some figures. For example, the Syncopated Side-by-Side with Spin includes a free spin for both partners. Open rolls are another good example of an open dance figure, in which the follower alternates between the lead's left and right sides, with the lead's left or right arm (alone) providing the lead. Waltzes were the staple of many American musicals and films, including "Waltz in Swing Time" sung by Fred Astaire.
- The Scandinavian Waltz, performed as a part of Scandinavian folk dance, can be fast or slow, but the dancers are always rotating.
- The Peruvian Waltz is called and recognized in Peru as vals criollo.
- The Mexican Waltz (vals mexicano) follows the same basic rhythmic pattern as the standard waltz, but the melodies reflect a strong Spanish influence. Mexico's Juventino Rosas wrote "Sobre las Olas" or "Over the Waves", commonly known in the U.S. as a circus song played during a trapeze show.
- The Cajun Waltz is danced progressively around the floor, and is characterized by the subtle swaying of the hips and step very close to ordinary walking. It is danced entirely in the closed position.
- The Cuban (or Tropical) Waltz follows the pattern of the standard waltz throughout the song.
- The Venezuelan waltz provided a basis for distinctive regional musical composition.
- The Contra Waltz (Freeform Waltz), included in most contra dance evenings, uses both open and closed positions, and incorporates moves from other dances such as swing, modern jive and salsa. Basically the dancers progress around the dance floor with a waltz step, but with no constraints on what moves they can use.
- The Valse Musette, a form of waltz popular in France, started in the late 19th century.
- The cross-step waltz (French Valse Boston) developed in France in the early 20th century and is popular in social waltz groups today.
- In folk dance from the Alsace region, waltzes in odd meters such as 5
4, 8
4 and 11
4 are found. In modern bal folk, waltzes in even higher meters are played and danced.
Today both the faster Viennese Waltz, made forever popular by the Strauss family, and the slower American and International style waltzes are extremely popular with dancers of all ages.
References

- ^ Nettl, Paul. Birth of the Waltz, in Dance Index vol 5, no. 9. 1946 New York: Dance Index-Ballet Caravan, Inc. page 211
- ^ Nettl, Paul. Birth of the Waltz, in Dance Index vol 5, no. 9. 1946 New York: Dance Index-Ballet Caravan, Inc. pages 208, 211
- ^ A Dictionary of Music and Musicians (A.D. 1450–1880) By George Grove, Sir George Grove, John Alexander Fuller-Maitland, Adela Harriet Sophia (Bagot) Wodehouse. Published 1889. Macmillan
- ^ The History of Lady Sophia Sternheim, trans. Christa Baguss Britt (State University of New York Press, 1991), p. 160.
- ^ a b Jacob, H.E. (2005). Johann Strauss: Father and Son a Century of Light Music. pp. 24–25. ISBN 1-4179-9311-1.
- ^ The Waltz Emperors. Wechsberg. 1973. C. Tinling & Company. page 49, 50)
- ^ A Dictionary of Music and Musicians (A.D. 1450–1880) By George Grove, Sir George Grove, John Alexander Fuller-Maitland, Adela Harriet Sophia (Bagot) Wodehouse. Published 1889. Macmillan. page 385
- ^ The Waltz Emperors. Wechsberg. 1973. C. Tinling & Company. pages 59–61
- ^ Gutman, Robert W. (1999). Mozart: A Cultural Biography. Harcourt. pp. 44–45.
- ^ Hilton, Boyd (2006). A Mad, Bad, and Dangerous People? England 1783–1846. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Raikes, Thomas (1856). A Portion of the Journal Kept by Thomas Raikes from 1831 to 1847: Comprising Reminiscences of Social and Political Life in London and Paris During that Period. pp. 240–243. Retrieved 20 September 2015.
- ^ "Introduction to 'The Waltz'". Readbookonline.net. Retrieved 20 September 2015.
- ^ Childers, William (1969). "Byron's "Waltz": The Germans and Their Georges". Keats-Shelley Journal. 18. Keats-Shelley Association of America, Inc.: 81–95. Retrieved 20 September 2015.
- ^ Fullerton, Susannah (2012). A dance with Jane Austen: how a novelist and her characters went to the ball (1st Frances Lincoln ed.). London, England: Frances Lincoln Ltd. pp. 110–111. ISBN 9-780-7112-3245-7.
- ^ a b Blatter, Alfred (2007). Revisiting music theory: a guide to the practice. p. 28. ISBN 0-415-97440-2.
- ^ "The History of Ballroom Dance in America". Retrieved 2010-12-13.
- ^ Shaw, Lloyd (1939). Cowboy Dances. The Caxton Printers. pp. 101–103.
- ^ a b Czarnoski, Lucile K (1950). Dances of Early California Days. Pacific Books. p. 44.
- ^ Czarnoski, Lucile K (1950). Dances of Early California Days. Pacific Books. p. 121.
- ^ Vallely, F. (1999). The Companion to Traditional Irish Music. New York: New York University Press. pp. 431–433.
- ^ "Rhythm Definitions - Irish Traditional Music Tune Index". Irishtune.info. 2012-07-11. Retrieved 2012-11-07.
External links
- Basic Steps of Waltz Dance
- Waltz video example
- The Waltz Dance Steps & Moves
- Music regarding: Waltz within traditional dances of the County of Nice (France)
- Scroll to "Five Step Waltz" for notes about probable 1847 origin and associated music published the same year.
- Thomas Wilson's 1816 Waltz Manual
- The Dance of Death at Project Gutenberg (1877 Book critical of the Waltz)
- The Regency Waltz
- Waltzes under CreativeCommons licence on BalLibre.org
