Effects of climate change on human health: Difference between revisions
m (GR) File renamed: File:Erlaa4f64f5 hr.jpg → File:World map of the aggregated global water security index (early 2010s).jpg Criterion 2 (meaningless or ambiguous name) · unintelligible title; title should inform about contents |
m →Global estimates: death estimates |
||
| Line 229: | Line 229: | ||
Climate change was responsible for 3% of [[diarrhoea]], 3% of [[malaria]], and 3.8% of [[dengue fever]] deaths worldwide in 2004.<ref>{{cite book |author=WHO |url=https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/global_health_risks/en/index.html |title=Global health risks: mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks |publisher=WHO Press |year=2009 |isbn=978-92-4-156387-1 |location=Geneva, Switzerland |page=24 |chapter=Ch. 2, Results: 2.6 Environmental risks |format=PDF |access-date=4 October 2020 |chapter-url=https://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GlobalHealthRisks_report_part2.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131210002548/http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/global_health_risks/en/index.html |archive-date=10 December 2013 }}</ref> Total attributable mortality was about 0.2% of deaths in 2004; of these, 85% were child deaths. The effects of more frequent and extreme storms were excluded from this study. |
Climate change was responsible for 3% of [[diarrhoea]], 3% of [[malaria]], and 3.8% of [[dengue fever]] deaths worldwide in 2004.<ref>{{cite book |author=WHO |url=https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/global_health_risks/en/index.html |title=Global health risks: mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks |publisher=WHO Press |year=2009 |isbn=978-92-4-156387-1 |location=Geneva, Switzerland |page=24 |chapter=Ch. 2, Results: 2.6 Environmental risks |format=PDF |access-date=4 October 2020 |chapter-url=https://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GlobalHealthRisks_report_part2.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131210002548/http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/global_health_risks/en/index.html |archive-date=10 December 2013 }}</ref> Total attributable mortality was about 0.2% of deaths in 2004; of these, 85% were child deaths. The effects of more frequent and extreme storms were excluded from this study. |
||
The health impacts of climate change are expected to rise in line with projected ongoing global warming for different [[climate change scenario]]s.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Crimmins |first1=A. |url=https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc950291/ |title=The Impacts of Climate Change on Human Health in the United States: A Scientific Assessment |last2=Balbus |first2=J. |last3=Gamble |first3=J.L. |last4=Beard |first4=C.B. |last5=Bell |first5=J.E. |last6=Dodgen |first6=D. |last7=Eisen |first7=R.J. |last8=Fann |first8=N. |last9=Hawkins |first9=M.D. |year=2016 |isbn=978-0-16-093241-0 |doi=10.7930/J0R49NQX |last10=Herring |first10=S.C. |last11=Jantarasami |first11=L. |last12=Mills |first12=D.M. |last13=Saha |first13=S. |last14=Sarofim |first14=M.C. |last15=Trtanj |first15=J. |last16=Ziska |first16=L.}}</ref><ref name="GPH2021" /> |
The health impacts of climate change are expected to rise in line with projected ongoing global warming for different [[climate change scenario]]s.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Crimmins |first1=A. |url=https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc950291/ |title=The Impacts of Climate Change on Human Health in the United States: A Scientific Assessment |last2=Balbus |first2=J. |last3=Gamble |first3=J.L. |last4=Beard |first4=C.B. |last5=Bell |first5=J.E. |last6=Dodgen |first6=D. |last7=Eisen |first7=R.J. |last8=Fann |first8=N. |last9=Hawkins |first9=M.D. |year=2016 |isbn=978-0-16-093241-0 |doi=10.7930/J0R49NQX |last10=Herring |first10=S.C. |last11=Jantarasami |first11=L. |last12=Mills |first12=D.M. |last13=Saha |first13=S. |last14=Sarofim |first14=M.C. |last15=Trtanj |first15=J. |last16=Ziska |first16=L.}}</ref><ref name="GPH2021" /> A review<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Pearce |first=Joshua M. |last2=Parncutt |first2=Richard |date=2023-01 |title=Quantifying Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Human Deaths to Guide Energy Policy |url=https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/16/16/6074 |journal=Energies |language=en |volume=16 |issue=16 |pages=6074 |doi=10.3390/en16166074 |issn=1996-1073}}</ref> found if warming reaches or exceeds 2 °C this century, roughly 1 billion premature deaths would be caused by anthropogenic global warming.<ref>{{Cite news |date=2023-08-29 |title=Human-caused climate change may lead to 1 billion premature deaths over next century: Study |work=The Times of India |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/home/environment/global-warming/human-caused-climate-change-may-lead-to-1-billion-premature-deaths-over-next-century-study/articleshow/103164287.cms?from=mdr |access-date=2023-09-18 |issn=0971-8257}}</ref> |
||
== Society and culture == |
== Society and culture == |
||
Revision as of 11:18, 18 September 2023

The effects of climate change on human health are increasingly well studied and quantified.[1][2] Direct effects include heat waves and extreme weather events. Indirect effects take place through changes in the biosphere. Examples are changes in water and air quality, food security and displacement. Factors such as age, gender or socioeconomic status influence to what extent these effects become wide-spread risks to human health.[3]: 1867 Health risks are unevenly distributed across the world.[3] Disadvantaged populations are especially vulnerable to climate change impacts.[4]: 15 For example, young children and older people are the most vulnerable to extreme heat.[5]
The relationship between health and heat includes several aspects.[4] One is the exposure of vulnerable populations to heatwaves. Another is heat-related mortality. Reduced labour capacity for outdoor workers and impacts on mental health are others. Extreme weather events have a big impact on health. These include floods, hurricanes, droughts and wildfires. They cause injuries, diseases, and air pollution in the case of wildfires. Other indirect health impacts from climate change may be rising food insecurity, undernutrition and water insecurity.[4]
A range of climate-sensitive infectious diseases may increase in some regions. These include mosquito-borne diseases, zoonoses, cholera and some waterborne diseases.[4] Climate change will also impact where infectious diseases are likely to be able to spread in the future. Many infectious diseases will spread to new geographic areas where people do not yet have suitable immune systems.
The health effects of climate change are increasingly a matter of concern for the international public health policy community. Already in 2009, a publication in the general medical journal The Lancet stated: "Climate change is the biggest global health threat of the 21st century".[6] The World Health Organisation reiterated this in 2015.[7] In 2019, the Australian Medical Association formally declared climate change a health emergency.[8]
Studies have found that communications on climate change that present it as a health concern rather than just an environmental matter are more likely to engage the public.[9][10]
Root causes
Effects of climate change
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an overall warming trend, changes to precipitation patterns, and more extreme weather. As the climate changes it impacts the natural environment with effects such as more intense forest fires, thawing permafrost, and desertification. These changes impact ecosystems and societies, and can become irreversible once tipping points are crossed.
The effects of climate change vary in timing and location. Up until now the Arctic has warmed faster than most other regions due to climate change feedbacks.[11] Surface air temperatures over land have also increased at about twice the rate they do over the ocean, causing intense heat waves. These temperatures would stabilize if greenhouse gas emissions were brought under control. Ice sheets and oceans absorb the vast majority of excess heat in the atmosphere, delaying effects there but causing them to accelerate and then continue after surface temperatures stabilize. Sea level rise is a particular long term concern as a result. The effects of ocean warming also include marine heatwaves, ocean stratification, deoxygenation, and changes to ocean currents.[12]: 10 The ocean is also acidifying as it absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.[13]
The ecosystems most immediately threatened by climate change are in the mountains, coral reefs, and the Arctic. Excess heat is causing environmental changes in those locations that exceed the ability of animals to adapt.[14] Species are escaping heat by migrating towards the poles and to higher ground when they can.[15] Sea level rise threatens coastal wetlands with flooding. Decreases in soil moisture in certain locations can cause desertification and damage ecosystems like the Amazon Rainforest.[16]: 9 At 2 °C (3.6 °F) of warming, around 10% of species on land would become critically endangered.[17]: 259Climate change vulnerability
A 2021 report published in The Lancet found that climate change does not affect people's health in an equal way. The greatest impact tends to fall on the most vulnerable such as the poor, women, children, the elderly, people with pre-existing health concerns, other minorities and outdoor workers.[4]: 13
There are certain predictors of health patterns that determine the social vulnerability of the individuals. These can be grouped into "demographic, socioeconomic, housing, health (such as pre-existing health conditions), neighbourhood, and geographical factors".[18]
Overview of health impacts
Types of pathways affecting health
The effects of climate change on human health can be grouped into direct and indirect effects.[3]: 1867 Both types of effects interact with social dynamics. The combination of effects and social dynamics determines the eventual health outcomes. Mechanisms and social dynamics are explained further below:
- Direct mechanisms or risks: changes in extreme weather and resultant increased storms, floods, droughts, heat waves and wildfires[4]
- Indirect mechanisms or risks: these are mediated through changes in the biosphere (e.g., the burden of disease and redistribution of disease vectors, or food availability, water quality, air pollution, land use change, ecological change)
- Social dynamics (age and gender, health status, socioeconomic status, social capital, public health infrastructure, mobility and conflict status)
These health risks vary across the world and between different groups of people. For example, differences in health service provision or economic development will result in different health risks for people in different regions, with less developed countries facing greater health risks. In many places, the combination of lower socioeconomic status and cultural gender roles result in increased health risks to women and girls as a result of climate change, compared to those faced by men and boys (although the converse may apply in other instances).[3]
Impacts on general health and wellbeing
The direct, indirect and social dynamic effects of climate change on health and wellbeing produce the following health impacts: cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, infectious diseases, undernutrition, mental illness, allergies, injuries and poisoning.[3]: Figure 2
Health and health care provision can also be impacted by the collapse of health systems and damage to infrastructure due to climate-induced events such as flooding. Therefore, building health systems that are climate resilient is a priority.[19][4]: 15
Impacts on mental health

The effects of climate change on mental health and wellbeing are documented. This is especially the case for vulnerable populations and those with pre-existing serious mental illness.[20] There are three broad pathways by which these effects can take place: directly, indirectly or via awareness.[21] The direct pathway includes stress-related conditions caused by exposure to extreme weather events. These include post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Scientific studies have linked mental health to several climate-related exposures. These include heat, humidity, rainfall, drought, wildfires and floods.[22] The indirect pathway can be disruption to economic and social activities. An example is when an area of farmland is less able to produce food.[22] The third pathway can be of mere awareness of the climate change threat, even by individuals who are not otherwise affected by it.[21]
An additional aspect to consider is the detrimental impact climate change can have on green or blue natural spaces, which in themselves have been proven to have beneficial impact on mental health.[23][24] Impacts of anthropogenic climate change, such as freshwater pollution or deforestation, degrade these landscapes and reduce public access.[25] Even when the green and blue spaces are intact, access to them is not equal across society, which is an issue of environmental justice and economic inequality.[26]
Mental health outcomes have been measured in several studies. These use indicators such as psychiatric hospital admissions, mortality, self-harm and suicide rates. People with pre-existing mental illness, Indigenous peoples, migrants and refugees, and children and adolescents are all vulnerable. The emotional responses to the threat of climate change can include eco-anxiety, ecological grief and eco-anger.[27][28] Such emotions can be rational responses to the degradation of the natural world and lead to adaptive action.[29]
Assessing the exact mental health effects of climate change is difficult; increases in heat extremes pose risks to mental health which can manifest themselves in increased mental health-related hospital admissions and suicidality.[30]: 9Impacts caused by heat
Impacts of higher global temperatures will have ramifications for the following aspects: vulnerability to extremes of heat, exposure of vulnerable populations to heatwaves, heat and physical activity, change in labor capacity, heat and sentiment (mental health), heat-related mortality.[4]
The global average and combined land and ocean surface temperature show a warming of 1.09 °C (range: 0.95 to 1.20 °C) from 1850–1900 to 2011–2020, based on multiple independently produced datasets.[31] The trend is faster since the 1970s than in any other 50-year period over at least the last 2000 years.[31]
A 2023 study estimated that climate change since 1960–1990 has put over 600 million people (9% of the global population) outside the "temperature niche" - the average temperature range at which humans flourish.[32]
Vulnerable people with regard to heat illnesses include people with low incomes, minority groups, women (in particular pregnant women), children, older adults (over 65 years old), people with chronic diseases, disabilities and co-morbidities.[4]: 13 Other people at risk include those in urban environments (due to the urban heat island effect), outdoor workers and people who take certain prescription drugs.[4] Exposure to extreme heat poses an acute health hazard for many of the people deemed as vulnerable.[4][33]
Climate change increases the frequency and severity of heatwaves and thus heat stress for people. Human responses to heat stress can include heat stroke and hyperthermia. Extreme heat is also linked to low quality sleep, acute kidney injury and complications with pregnancy. Furthermore, it may cause the deterioration of pre-existing cardiovascular and respiratory disease.[2]: 1624 Adverse pregnancy outcomes due to high ambient temperatures include for example low birth weight and pre-term birth.[2]: 1051 Heat waves have also resulted in epidemics of chronic kidney disease (CKD).[34][35] Prolonged heat exposure, physical exertion, and dehydration are sufficient factors for the development of CKD.[34][35]
The human body requires evaporative cooling to prevent overheating, even with a low activity level. With excessive ambient heat and humidity during heatwaves, adequate evaporative cooling might be compromised.
A wet-bulb temperature that is too high means that human bodies would no longer be able to adequately cool the skin.[36][37] A wet bulb temperature of 35 °C is regarded as the limit for humans (called the "physiological threshold for human adaptability" to heat and humidity).[38]: 1498 As of 2020, only two weather stations had recorded 35 °C wet-bulb temperatures, and only very briefly, but the frequency and duration of these events is expected to rise with ongoing climate change.[39][40][41] Global warming above 1.5 degrees risks making parts of the tropics uninhabitable because the threshold for the wet bulb temperature may be passed.[36]
People with cognitive health issues (e.g. depression, dementia, Parkinson's disease) are more at risk when faced with high temperatures and ought to be extra careful[42] as cognitive performance has been shown to be differentially affected by heat.[43] People with diabetes and those who are overweight, have sleep deprivation, or have cardiovascular/cerebrovascular conditions should avoid too much heat exposure.[42][44]
The risk of dying from chronic lung disease during a heat wave has been estimated at 1.8-8.2% higher compared to average summer temperatures.[45] An 8% increase in hospitalization rate for people with Chronic Obstructive Pulmunary Disease has been estimated for every 1 °C increase in temperatures above 29 °C.[33]
In urban areas

The effects of heatwaves tend to be more pronounced in urban areas because they are typically warmer than surrounding rural areas due to the urban heat island effect.[46][47]: 2926 This is caused from the way many cities are built. For example, they often have extensive areas of asphalt, reduced greenery along with many large heat-retaining buildings that physically block cooling breezes and ventilation.[33] Lack of water features are another cause.[47]: 2926
Extreme heat exposure in cities with a wet bulb globe temperature above 30 °C tripled between 1983 and 2016.[46] It increased by about 50% when the population growth in these cities is not taken into account.[46]
Cities are often on the front-line of climate impacts due to their densely concentrated populations, the urban heat island effect, their frequent proximity to coasts and waterways, and reliance on ageing physical infrastructure networks.[48]
Health experts warn that "exposure to extreme heat increases the risk of death from cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and respiratory conditions and all-cause mortality. Heat-related deaths in people older than 65 years reached a record high of an estimated 345 000 deaths in 2019".[4]: 9
More than 70,000 Europeans died as a result of the 2003 European heat wave.[49] Also more than 2,000 people died in Karachi, Pakistan in June 2015 due to a severe heat wave with temperatures as high as 49 °C (120 °F).[50][51]
Increasing access to indoor cooling (air conditioning) will help prevent heat-related mortality but current air conditioning technology is generally unsustainable as it contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, peak electricity demand, and urban heat islands.[4]: 17
Mortality due to heat waves could be reduced if buildings were better designed to modify the internal climate, or if the occupants were better educated about the issues, so they can take action on time.[52][53] Heatwave early warning and response systems are important elements of heat action plans.
Reduced labour capacity
Heat exposure can affect people's ability to work.[4]: 8 The annual Countdown Report by The Lancet investigated change in labour capacity as an indicator. It found that during 2021, high temperature reduced global potential labour hours by 470 billion - a 37% increase compared to the average annual loss that occurred during the 1990s. Occupational heat exposure especially affects laborers in the agricultural sector of developing countries. In those countries, the vast majority of these labour hour losses (87%) were in the agricultural sector.[2]: 1625
Working in extreme heat can lead to labor force productivity decreases as well as participation because employees' health may be weaker due to heat related health problems, such as dehydration, fatigue, dizziness, and confusion.[54][1]: 1073–1074
Sports and outdoor exercise
With regards to sporting activities it has been observed that "hot weather reduces the likelihood of engaging in exercise".[2]: 1625 Furthermore, participating in sports during excessive heat can lead to injury or even death.[1]: 1073–1074 It is also well established that regular physical activity is beneficial for human health, including mental health.[2]: 1625 Therefore, an increase in hot days due to climate change could indirectly affect health due to people exercising less.
Impacts caused by weather and climate events other than heat

Climate change is increasing the periodicity and intensity of some extreme weather events.[55] Confidence in the attribution of extreme weather to anthropogenic climate change is highest in changes in frequency or magnitude of extreme heat and cold events with some confidence in increases in heavy precipitation and increases in the intensity of droughts.[56]
Extreme weather events, such as floods, hurricanes, droughts and wildfires can result in injuries, death and the spread of infectious diseases. For example, local epidemics can occur due to loss of infrastructure, such as hospitals and sanitation services, but also because of changes in local ecology and environment.
Floods
Due to an increase in heavy rainfall events, floods are expected to become more severe in future when they do occur.[57]: 1155 However, the interactions between rainfall and flooding are complex. In some regions, flooding is expected to become rarer. This depends on several factors, such as changes in rain and snowmelt, but also soil moisture.[57]: 1156 Floods have short and long-term negative implications to people's health and well-being. Short term implications include mortalities, injuries and diseases, while long term implications include non-communicable diseases and psychosocial health aspects.[58]
For example, the 2022 Pakistan Floods (which were likely more severe because of climate change[59][60]) affected people's health directly and indirectly. There were outbreaks of diseases like malaria, dengue, and other skin diseases.[61][62] Flood runoff can wash soil contaminants like fertilisers and toxins into estuaries, lakes and seas, posing a threat to human health by reducing water quality.[63]
Hurricanes and thunderstorms
Stronger hurricanes create more opportunities for vectors to breed and infectious diseases to flourish.[64][65] Extreme weather also means stronger winds. These winds can carry vectors tens of thousands of kilometers, resulting in an introduction of new infectious agents to regions that have never seen them before, making the humans in these regions even more susceptible.[64]
Another result of hurricanes is increased rainwater, which promotes flooding. Hurricanes result in ruptured pollen grains, which releases respirable aeroallergens. Thunderstorms cause a concentration of pollen grains at the ground level, which result in an increase in the release of allergenic particles in the atmosphere due to rupture by osmotic shock. Around 20–30 minutes after a thunderstorm, there is an increased risk for people with pollen allergies to experience severe asthmatic exacerbations, due to high concentration inhalation of allergenic peptides.[33]
Droughts
Climate change affects multiple factors associated with droughts, such as how much rain falls and how fast the rain evaporates again. Warming over land increases the severity and frequency of droughts around much of the world.[66][57]: 1057 Many of the consequences of droughts have impacts on human health. This can be through destruction of food supply (loss of crop yields), malnutrition and with this, dozens of associated diseases and health problems.
Wildfires

Climate change increases wildfire potential and activity.[67] Climate change leads to a warmer ground temperature and its effects include earlier snowmelt dates, drier than expected vegetation, increased number of potential fire days, increased occurrence of summer droughts, and a prolonged dry season.[68]
Wood smoke from wildfires produces particulate matter that has damaging effects to human health.[69] The primary pollutants in wood smoke are carbon monoxide and nitric oxide.[68] Through the destruction of forests and human-designed infrastructure, wildfire smoke releases other toxic and carcinogenic compounds, such as formaldehyde and hydrocarbons.[70] These pollutants damage human health by evading the mucociliary clearance system and depositing in the upper respiratory tract, where they have toxic effects.[68]
The health effects of wildfire smoke exposure include exacerbation and development of respiratory illness such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder; increased risk of lung cancer, mesothelioma and tuberculosis; increased airway hyper-responsiveness; changes in levels of inflammatory mediators and coagulation factors; and respiratory tract infection.[69]
Health risks due to climate-sensitive infectious diseases
Infectious diseases that are sensitive to climate can be grouped into: vector-borne diseases (transmitted via mosquitos, ticks etc.), water-borne diseases (transmitted via viruses or bacteria, e.g.: E. Coli) and food-borne diseases (e.g.: Salmonella).[1]: 1107 Climate change is affecting the distribution of these diseases due to the expanding geographic range and seasonality of these diseases and their vectors.[4]: 9
Climate change may also lead to new infectious diseases due to changes in microbial and vector geographic range. Microbes that are harmful to humans can adapt to higher temperatures, which will allow them to build better tolerance against human endothermy defences.[71]
Vector-borne diseases


Mosquito-borne diseases
Mosquito-borne diseases that are sensitive to climate include malaria, elephantiasis, Rift Valley fever, yellow fever, dengue fever, Zika virus, and chikungunya.[72][73][74] Scientists found in 2022 that rising temperatures are increasing the areas where dengue fever, malaria and other mosquito-carried diseases are able to spread.[1]: 1062 Warmer temperatures are also advancing to higher elevations, allowing mosquitoes to survive in places that were previously inhospitable to them.[1]: 1045 This risks malaria making a return to areas where it was previously eradicated.[64]
Diseases from ticks
Ticks are changing their geographic range because of rising temperatures, and this puts new populations at risk. Ticks can spread lyme disease and tick-borne encephalitis. It is expected that climate change will increase the incidence of these diseases in the Northern Hemisphere.[1]: 1094 For example, a review of the literature found that "In the USA, a 2°C warming could increase the number of Lyme disease cases by over 20% over the coming decades and lead to an earlier onset and longer length of the annual Lyme disease season".[1]: 1094
Waterborne diseases
There are a range of waterborne diseases and parasites that will pose greater health risks in future. This will vary by region. For example, in Africa Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis (two protozoan parasites) will increase. This is due to increasing temperatures and drought.[1]: 1095
Scientist expect that disease outbreaks caused by vibrio (in particular the bacterium that causes cholera, called vibrio cholerae) are increasing in occurrence and intensity.[1]: 1107 One reason is that the area of coastline with suitable conditions for vibrio bacteria has increased due to changes in sea surface temperature and sea surface salinity caused by climate change.[4]: 12 These pathogens can cause gastroenteritis, cholera, wound infections, and sepsis. It has been observed that in the period of 2011–21, the "area of coastline suitable for Vibrio bacterial transmission has increased by 35% in the Baltics, 25% in the Atlantic Northeast, and 4% in the Pacific Northwest.[4]: 12 Furthermore, the increasing occurrence of higher temperature days, heavy rainfall events and flooding due to climate change could lead to an increase in cholera risks.[1]: 1045
Health risks from food and water insecurity
Climate change affects many aspects of food security through "multiple and interconnected pathways".[2]: 1619 Many of these are related to the effects of climate change on agriculture, for example failed crops due to more extreme weather events. This comes on top of other coexisting crises that reduce food security in many regions. Less food security means more undernutrition with all its associated health problems. Food insecurity is increasing at the global level (some of the underlying causes are related to climate change, others are not) and about 720–811 million people suffered from hunger in 2020.[2]: 1629
The number of deaths resulting from climate change-induced changes to food availability are difficult to estimate. The 2022 IPCC Sixth Assessment Report does not quantify this number in its chapter on food security.[75] A modelling study from 2016 found "a climate change–associated net increase of 529,000 adult deaths worldwide [...] from expected reductions in food availability (particularly fruit and vegetables) by 2050, as compared with a reference scenario without climate change."[76][77]
Reduced nutritional value of crops

Food production from the oceans
A headline finding in 2021 regarding marine food security stated that: "In 2018–20, nearly 70% of countries showed increases in average sea surface temperature in their territorial waters compared within 2003–05, reflecting an increasing threat to their marine food productivity and marine food security".[4]: 14
Water insecurity

Access to clean drinking water and sanitation is important for healthy living and well-being.[86]
Other health risks influenced by climate change
Pollen allergies

A warming climate can lead to increases of pollen season lengths and concentrations in some regions of the world. For example, in northern mid-latitudes regions, the spring pollen season is now starting earlier.[1]: 1049 This can affect people with pollen allergies (hay fever).[89] The rise in pollen also comes from rising CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere and resulting CO2 fertilisation effects.[1]: 1096
Violence and conflicts
Climate change may increase the risk of violent conflict, which can lead to injuries, such as battle injuries, and death. Conflict can result from the increased propensity towards violence after people become more irritable due to excessive heat.[90] There can also be follow-on effects on health from resource scarcity or human migrations that climate change can cause or aggravate in already conflict prone areas.[91][92]
However, the observed contribution of climate change to conflict risk is small in comparison with cultural, socioeconomic, and political causes. There is some evidence that rural-to-urban migration within countries worsens the conflict risk in violence prone regions. But there is no evidence that migration between countries would increase the risk of violence.[1]: 1008, 1128

The relationship between surface ozone (also called ground-level ozone) and ambient temperature is complex. Changes in air temperature and water content affect the air's chemistry and the rates of chemical reactions that create and remove ozone. Many chemical reaction rates increase with temperature and lead to increased ozone production. Climate change projections show that rising temperatures and water vapour in the atmosphere will likely increase surface ozone in polluted areas like the eastern United States.[93]
On the other hand, ozone concentrations could decrease in a warming climate if anthropogenic ozone-precursor emissions (e.g., nitrogen oxides) continue to decrease through implementation of policies and practices.[94] Therefore, future surface ozone concentrations depend on the climate change mitigation steps taken (more or less methane emissions) as well as air pollution control steps taken.[95]: 884
High surface ozone concentrations often occur during heat waves in the United States.[94] Throughout much of the eastern United States, ozone concentrations during heat waves are at least 20% higher than the summer average.[94] Broadly speaking, surface ozone levels are higher in cities with high levels of air pollution.[95]: 876 Ozone pollution in urban areas affects denser populations, and is worsened by high populations of vehicles, which emit pollutants NO2 and VOCs, the main contributors to problematic ozone levels.[96]
There is a great deal of evidence to show that surface ozone can harm lung function and irritate the respiratory system.[97][98] Exposure to ozone (and the pollutants that produce it) is linked to premature death, asthma, bronchitis, heart attack, and other cardiopulmonary problems.[99][100] High ozone concentrations irritate the lungs and thus affect respiratory function, especially among people with asthma.[94] People who are most at risk from breathing in ozone air pollution are those with respiratory issues, children, older adults and those who typically spend long periods of time outside such as construction workers.[101]
Harmful algal blooms in oceans and lakes

The warming oceans and lakes are leading to more frequent harmful algal blooms.[64][74][102] Also, during droughts, surface waters are even more susceptible to harmful algal blooms and microorganisms.[103] Algal blooms increase water turbidity, suffocating aquatic plants, and can deplete oxygen, killing fish. Some kinds of blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) create neurotoxins, hepatoxins, cytotoxins or endotoxins that can cause serious and sometimes fatal neurological, liver and digestive diseases in humans. Cyanobacteria grow best in warmer temperatures (especially above 25 degrees Celsius), and so areas of the world that are experiencing general warming as a result of climate change are also experiencing harmful algal blooms more frequently and for longer periods of time.[104]
One of these toxin producing algae is Pseudo-nitzschia fraudulenta. This species produces a substance called domoic acid which is responsible for amnesic shellfish poisoning.[105][106] The toxicity of this species has been shown to increase with greater CO2 concentrations associated with ocean acidification.[105] Some of the more common illnesses reported from harmful algal blooms include; Ciguatera fish poisoning, paralytic shellfish poisoning, azaspiracid shellfish poisoning, diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, neurotoxic shellfish poisoning and the above-mentioned amnesic shellfish poisoning.[105]
Carbon dioxide levels and human cognition
Higher levels of indoor and outdoor CO2 levels may impair human cognition.[107][108][109]
Accidents
Researchers found that there is a strong correlation between higher winter temperatures and drowning accidents in large lakes, because the ice gets thinner and weaker.[110]
Available evidence on the effect of climate change on the epidemiology of snakebite is limited but it is expected that there will be a geographic shift in risk of snakebite: northwards in North America and southwards in South America and in Mozambique, and increase in incidence of bite in Sri Lanka.[111]
Potential health benefits
Health co-benefits from mitigation
The health benefits (also called "co-benefits") from climate change mitigation measures are significant: potential measures can not only mitigate future health impacts from climate change but also improve health directly.[112] Climate change mitigation is interconnected with various co-benefits (such as reduced air pollution and associated health benefits)[113] and how it is carried out (in terms of e.g. policymaking) could also determine its impacts on living standards (whether and how inequality and poverty are reduced).[114]
There are many health co-benefits associated with climate action. These include those of cleaner air, healthier diets (e.g. less red meat), more active lifestyles, and increased exposure to green urban spaces.[4]: 26 Access to urban green spaces provides benefits to mental health as well.[4]: 18
Compared with the current pathways scenario (with regards to greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation efforts), the "sustainable pathways scenario" will likely result in an annual reduction of 1.18 million air pollution-related deaths, 5.86 million diet-related deaths, and 1.15 million deaths due to physical inactivity, across the nine countries, by 2040. These benefits were attributable to the mitigation of direct greenhouse gas emissions and the commensurate actions that reduce exposure to harmful pollutants, as well as improved diets and safe physical activity.[115] Air pollution generated by fossil fuel combustion is both a major driver of global warming and the cause of a large number of annual deaths with some estimates as high as 8.7 million excess deaths during 2018.[116][117]
Placing health as a key focus of the Nationally Determined Contributions could present an opportunity to increase ambition and realize health co-benefits.[115]
Potential health benefits from global warming
It is possible that a potential health benefit from global warming could result from fewer cold days in winter:[1]: 1099 This could lead to some mental health benefits. However, the evidence on this correlation is regarded as inconsistent in 2022.[1]: 1099
Global estimates
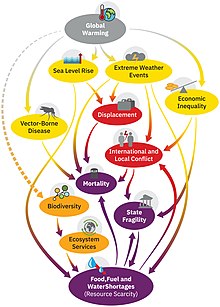
Estimating deaths (mortality) or DALYs (morbidity) from the effects of climate change at the global level is very difficult. A 2014 study by the World Health Organization estimated the effect of climate change on human health, but not all of the effects of climate change were included.[119] For example, the effects of more frequent and extreme storms were excluded. The study assessed deaths from heat exposure in elderly people, increases in diarrhea, malaria, dengue, coastal flooding, and childhood undernutrition. The authors estimated that climate change was projected to cause an additional 250,000 deaths per year between 2030 and 2050 but also stated that "these numbers do not represent a prediction of the overall impacts of climate change on health, since we could not quantify several important causal pathways".[119]
Climate change was responsible for 3% of diarrhoea, 3% of malaria, and 3.8% of dengue fever deaths worldwide in 2004.[120] Total attributable mortality was about 0.2% of deaths in 2004; of these, 85% were child deaths. The effects of more frequent and extreme storms were excluded from this study.
The health impacts of climate change are expected to rise in line with projected ongoing global warming for different climate change scenarios.[121][122] A review[123] found if warming reaches or exceeds 2 °C this century, roughly 1 billion premature deaths would be caused by anthropogenic global warming.[124]
Society and culture
Climate justice and climate migrants
Much of the health burden associated with climate change falls on vulnerable people (e.g. indigenous peoples and economically disadvantaged communities). As a result, people of disadvantaged sociodemographic groups experience unequal risks.[125] Often these people will have made a disproportionately low contribution toward man-made global warming, thus leading to concerns over climate justice.[126][127][122]
Climate change has diverse impacts on migration activities, and can lead to decreases or increases in the number of people who migrate.[1]: 1079 Migration activities can have impacts on health and well-being, in particular for mental health. Migration in the context of climate change can be grouped into four types: adaptive migration (see also climate change adaptation), involuntary migration, organised relocation of populations, and immobility (which is when people are unable or unwilling to move even though it is recommended).[1]: 1079
Communication strategies
Studies have found that when communicating climate change with the public, it can help encourage engagement if it is framed as a health concern, rather than as an environmental issue. This is especially the case when comparing a health related framing to one that emphasised environmental doom, as was common in the media at least up until 2017.[128][129] Communicating the co-benefits to health helps underpin greenhouse gas reduction strategies.[48] Safeguarding health—particularly of the most vulnerable—is a frontline local climate change adaptation goal.[48]
Policy responses

Due to its significant impact on human health,[131][132] climate change has become a major concern for public health policy. The United States Environmental Protection Agency had issued a 100-page report on global warming and human health back in 1989.[122][133] By the early years of the 21st century, climate change was increasingly addressed as a public health concern at a global level, for example in 2006 at Nairobi by UN secretary general Kofi Annan. Since 2018, factors such as the 2018 heat wave, the Greta effect and the IPCC's 2018 Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C further increased the urgency for responding to climate change as a global health issue.[122][48][127]
The World Bank has suggested a framework that can strengthen health systems to make them more resilient and climate-sensitive.[134]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Cissé, G., R. McLeman, H. Adams, P. Aldunce, K. Bowen, D. Campbell-Lendrum, S. Clayton, K.L. Ebi, J. Hess, C. Huang, Q. Liu, G. McGregor, J. Semenza, and M.C. Tirado, 2022: Chapter 7: Health, Wellbeing, and the Changing Structure of Communities. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1041–1170, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Marina Romanello, Claudia Di Napoli, Paul Drummond, Carole Green, Harry Kennard, Pete Lampard, Daniel Scamman, Nigel Arnell, Sonja Ayeb-Karlsson, Lea Berrang Ford, Kristine Belesova, Kathryn Bowen, Wenjia Cai, Max Callaghan, Diarmid Campbell-Lendrum, Jonathan Chambers, Kim R van Daalen, Carole Dalin, Niheer Dasandi, Shouro Dasgupta, Michael Davies, Paula Dominguez-Salas, Robert Dubrow, Kristie L Ebi, Matthew Eckelman, Paul Ekins, Luis E Escobar, Lucien Georgeson, Hilary Graham, Samuel H Gunther, Ian Hamilton, Yun Hang, Risto Hänninen, Stella Hartinger, Kehan He, Jeremy J Hess, Shih-Che Hsu, Slava Jankin, Louis Jamart et al. (2022) The 2022 report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: health at the mercy of fossil fuels, The Lancet, Vol 400 November 5, DOI: 10.1016/ S0140-6736(22)01540-9
- ^ a b c d e Watts, Nick; Adger, W Neil; Agnolucci, Paolo; Blackstock, Jason; Byass, Peter; Cai, Wenjia; Chaytor, Sarah; Colbourn, Tim; Collins, Mat; Cooper, Adam; Cox, Peter M (2015). "Health and climate change: policy responses to protect public health". The Lancet. 386 (10006): 1861–1914. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60854-6. hdl:10871/17695. PMID 26111439. S2CID 205979317.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Romanello, Marina; McGushin, Alice; Di Napoli, Claudia; Drummond, Paul; Hughes, Nick; Jamart, Louis; Kennard, Harry; Lampard, Pete; Solano Rodriguez, Baltazar; Arnell, Nigel; Ayeb-Karlsson, Sonja; Belesova, Kristine; Cai, Wenjia; Campbell-Lendrum, Diarmid; Capstick, Stuart; Chambers, Jonathan; Chu, Lingzhi; Ciampi, Luisa; Dalin, Carole; Dasandi, Niheer; Dasgupta, Shouro; Davies, Michael; Dominguez-Salas, Paula; Dubrow, Robert; Ebi, Kristie L; Eckelman, Matthew; Ekins, Paul; Escobar, Luis E; Georgeson, Lucien; Grace, Delia; Graham, Hilary; Gunther, Samuel H; Hartinger, Stella; He, Kehan; Heaviside, Clare; Hess, Jeremy; Hsu, Shih-Che; Jankin, Slava; Jimenez, Marcia P; Kelman, Ilan; et al. (October 2021). "The 2021 report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: code red for a healthy future" (PDF). The Lancet. 398 (10311): 1619–1662. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01787-6. hdl:10278/3746207. PMID 34687662. S2CID 239046862.
- ^ Watts, Nick; Amann, Markus; Arnell, Nigel; Ayeb-Karlsson, Sonja; Belesova, Kristine; Boykoff, Maxwell; Byass, Peter; Cai, Wenjia; Campbell-Lendrum, Diarmid; Capstick, Stuart; Chambers, Jonathan (16 November 2019). "The 2019 report of The Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: ensuring that the health of a child born today is not defined by a changing climate" (PDF). The Lancet. 394 (10211): 1836–1878. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32596-6. PMID 31733928. S2CID 207976337.
- ^ Costello, Anthony; Abbas, Mustafa; Allen, Adriana; Ball, Sarah; Bell, Sarah; Bellamy, Richard; Friel, Sharon; Groce, Nora; Johnson, Anne; Kett, Maria; Lee, Maria (2009). "Managing the health effects of climate change". The Lancet. 373 (9676): 1693–1733. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1. PMID 19447250. S2CID 205954939.
- ^ "WHO calls for urgent action to protect health from climate change – Sign the call". www.who.int. World Health Organization. 2015. Archived from the original on October 8, 2015. Retrieved 2020-04-19.
- ^ Katharine Murphy (2 September 2019). "Australian Medical Association declares climate change a health emergency". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ Maibach, Edward W; Nisbet, Matthew; Baldwin, Paula; Akerlof, Karen; Diao, Guoqing (December 2010). "Reframing climate change as a public health issue: an exploratory study of public reactions". BMC Public Health. 10 (1): 299. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-10-299. PMC 2898822. PMID 20515503.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Dasandi, Niheer; Graham, Hilary; Hudson, David; Jankin, Slava; vanHeerde-Hudson, Jennifer; Watts, Nick (20 October 2022). "Positive, global, and health or environment framing bolsters public support for climate policies". Communications Earth & Environment. 3 (1): 239. Bibcode:2022ComEE...3..239D. doi:10.1038/s43247-022-00571-x. S2CID 253041860.
- ^ Lindsey, Rebecca; Dahlman, Luann (June 28, 2022). "Climate Change: Global Temperature". climate.gov. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on September 17, 2022.
- ^ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), ed. (2022), "Summary for Policymakers", The Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate: Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 3–36, doi:10.1017/9781009157964.001, ISBN 978-1-009-15796-4, retrieved 2023-04-24
- ^ Doney, Scott C.; Busch, D. Shallin; Cooley, Sarah R.; Kroeker, Kristy J. (2020-10-17). "The Impacts of Ocean Acidification on Marine Ecosystems and Reliant Human Communities". Annual Review of Environment and Resources. 45 (1): 83–112. doi:10.1146/annurev-environ-012320-083019. ISSN 1543-5938. S2CID 225741986.
- ^ EPA (19 January 2017). "Climate Impacts on Ecosystems". Archived from the original on 27 January 2018. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
Mountain and arctic ecosystems and species are particularly sensitive to climate change... As ocean temperatures warm and the acidity of the ocean increases, bleaching and coral die-offs are likely to become more frequent.
- ^ Pecl, Gretta T.; Araújo, Miguel B.; Bell, Johann D.; Blanchard, Julia; Bonebrake, Timothy C.; Chen, I-Ching; Clark, Timothy D.; Colwell, Robert K.; Danielsen, Finn; Evengård, Birgitta; Falconi, Lorena; Ferrier, Simon; Frusher, Stewart; Garcia, Raquel A.; Griffis, Roger B.; Hobday, Alistair J.; Janion-Scheepers, Charlene; Jarzyna, Marta A.; Jennings, Sarah; Lenoir, Jonathan; Linnetved, Hlif I.; Martin, Victoria Y.; McCormack, Phillipa C.; McDonald, Jan; Mitchell, Nicola J.; Mustonen, Tero; Pandolfi, John M.; Pettorelli, Nathalie; Popova, Ekaterina; Robinson, Sharon A.; Scheffers, Brett R.; Shaw, Justine D.; Sorte, Cascade J. B.; Strugnell, Jan M.; Sunday, Jennifer M.; Tuanmu, Mao-Ning; Vergés, Adriana; Villanueva, Cecilia; Wernberg, Thomas; Wapstra, Erik; Williams, Stephen E. (31 March 2017). "Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being". Science. 355 (6332): eaai9214. doi:10.1126/science.aai9214. hdl:10019.1/120851. PMID 28360268. S2CID 206653576.
- ^ IPCC, 2019: Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change and Land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems [P.R. Shukla, J. Skea, E. Calvo Buendia, V. Masson-Delmotte, H.- O. Pörtner, D. C. Roberts, P. Zhai, R. Slade, S. Connors, R. van Diemen, M. Ferrat, E. Haughey, S. Luz, S. Neogi, M. Pathak, J. Petzold, J. Portugal Pereira, P. Vyas, E. Huntley, K. Kissick, M. Belkacemi, J. Malley, (eds.)]. doi:10.1017/9781009157988.001
- ^ Parmesan, Camille; Morecroft, Mike; Trisurat, Yongyut; et al. "Chapter 2: Terrestrial and Freshwater Ecosystems and their Services" (PDF). Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. The Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Li, Ang; Toll, Mathew; Martino, Erika; Wiesel, Illan; Botha, Ferdi; Bentley, Rebecca (March 2023). "Vulnerability and recovery: Long-term mental and physical health trajectories following climate-related disasters". Social Science & Medicine. 320 (115681): 115681. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2023.115681. PMID 36731303. S2CID 256159626.
- ^ "Operational framework for building climate resilient health systems". www.who.int. 2015. Retrieved 2022-04-13.
- ^ Doherty, Susan; Clayton, Thomas J (2011). "The psychological impacts of global climate change". American Psychologist. 66 (4): 265–276. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.454.8333. doi:10.1037/a0023141. PMID 21553952.
- ^ a b Berry, Helen; Kathryn, Bowen; Kjellstrom, Tord (2009). "Climate change and mental health: a causal pathways framework". International Journal of Public Health. 55 (2): 123–132. doi:10.1007/s00038-009-0112-0. PMID 20033251. S2CID 22561555.
- ^ a b Charlson, Fiona; Ali, Suhailah; Benmarhnia, Tarik; Pearl, Madeleine; Massazza, Alessandro; Augustinavicius, Jura; Scott, James G. (2021). "Climate Change and Mental Health: A Scoping Review". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 18 (9): 4486. doi:10.3390/ijerph18094486. PMC 8122895. PMID 33922573.
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
- ^ White, Mathew; Smith, Amanda; Humphryes, Kelly; Pahl, Sabine; Snelling, Deborah; Depledge, Michael (2010-12-01). "Blue space: The importance of water for preference, affect, and restorativeness ratings of natural and built scenes". Journal of Environmental Psychology. 30 (4): 482–493. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2010.04.004. ISSN 0272-4944.
- ^ Alcock, Ian; White, Mathew P.; Wheeler, Benedict W.; Fleming, Lora E.; Depledge, Michael H. (2014-01-21). "Longitudinal Effects on Mental Health of Moving to Greener and Less Green Urban Areas". Environmental Science & Technology. 48 (2): 1247–1255. Bibcode:2014EnST...48.1247A. doi:10.1021/es403688w. hdl:10871/15080. ISSN 0013-936X. PMID 24320055.
- ^ Cuijpers, Pim; Miguel, Clara; Ciharova, Marketa; Kumar, Manasi; Brander, Luke; Kumar, Pushpam; Karyotaki, Eirini (February 2023). "Impact of climate events, pollution, and green spaces on mental health: an umbrella review of meta-analyses". Psychological Medicine. 53 (3): 638–653. doi:10.1017/S0033291722003890. ISSN 0033-2917. PMC 9975983. PMID 36606450. S2CID 255467995.
- ^ Hoffimann, Elaine; Barros, Henrique; Ribeiro, Ana Isabel (August 2017). "Socioeconomic Inequalities in Green Space Quality and Accessibility—Evidence from a Southern European City". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 14 (8): 916. doi:10.3390/ijerph14080916. ISSN 1661-7827. PMC 5580619. PMID 28809798.
- ^ Vakoch, Douglas A.; Mickey, Sam, eds. (2023). Eco-Anxiety and Pandemic Distress: Psychological Perspectives on Resilience and Interconnectedness. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-762267-4.
- ^ Vakoch, Douglas A.; Mickey, Sam, eds. (2022). Eco-Anxiety and Planetary Hope: Experiencing the Twin Disasters of Covid-19 and Climate Change. Cham, Switzerland: Springer. ISBN 978-3-031-08430-0.
- ^ Ojala, Maria; Cunsolo, Ashlee; Ogunbode, Charles A.; Middleton, Jacqueline (18 October 2021). "Anxiety, Worry, and Grief in a Time of Environmental and Climate Crisis: A Narrative Review". Annual Review of Environment and Resources. 46 (1): 35–58. doi:10.1146/annurev-environ-012220-022716. S2CID 236307729.
- ^ Romanello, Marina; McGushin, Alice; Di Napoli, Claudia; Drummond, Paul; Hughes, Nick; Jamart, Louis; Kennard, Harry; Lampard, Pete; Solano Rodriguez, Baltazar; Arnell, Nigel; Ayeb-Karlsson, Sonja; Belesova, Kristine; Cai, Wenjia; Campbell-Lendrum, Diarmid; Capstick, Stuart; Chambers, Jonathan; Chu, Lingzhi; Ciampi, Luisa; Dalin, Carole; Dasandi, Niheer; Dasgupta, Shouro; Davies, Michael; Dominguez-Salas, Paula; Dubrow, Robert; Ebi, Kristie L.; Eckelman, Matthew; Ekins, Paul; Escobar, Luis E.; Georgeson, Lucien; Grace, Delia (30 October 2021). "The 2021 report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: code red for a healthy future" (PDF). The Lancet. 398 (10311): 1619–1662. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01787-6. hdl:10278/3746207. PMID 34687662. S2CID 239046862.
- ^ a b IPCC (2021). "Summary for Policymakers" (PDF). The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. p. 40. ISBN 978-92-9169-158-6.
- ^ Lenton, Timothy M.; Xu, Chi; Abrams, Jesse F.; Ghadiali, Ashish; Loriani, Sina; Sakschewski, Boris; Zimm, Caroline; Ebi, Kristie L.; Dunn, Robert R.; Svenning, Jens-Christian; Scheffer, Marten (2023-05-22). "Quantifying the human cost of global warming". Nature Sustainability: 1–11. doi:10.1038/s41893-023-01132-6. hdl:10871/132650. ISSN 2398-9629.
- ^ a b c d Demain, Jeffrey G. (24 March 2018). "Climate Change and the Impact on Respiratory and Allergic Disease: 2018". Current Allergy and Asthma Reports. 18 (4): 22. doi:10.1007/s11882-018-0777-7. PMID 29574605. S2CID 4440737.
- ^ a b Glaser; et al. (2016). "Climate Change and the Emergent Epidemic of CKD from Heat Stress in Rural Communities: the Case for Heat Stress Nephropathy". Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 11 (8): 1472–83. doi:10.2215/CJN.13841215. PMC 4974898. PMID 27151892.
- ^ a b Shih, Gerry (2023-01-06). "The world's torrid future is etched in the crippled kidneys of Nepali workers". Washington Post. Retrieved 2023-01-20.
- ^ a b "Global heating pushes tropical regions towards limits of human livability". The Guardian. 8 March 2021. Retrieved 24 June 2021.
- ^ Chow, Denise (2022-05-07). "Deadly 'wet-bulb temperatures' are being stoked by climate change and heat waves". NBC News. Retrieved 2022-07-22.
- ^ Shaw, R., Y. Luo, T.S. Cheong, S. Abdul Halim, S. Chaturvedi, M. Hashizume, G.E. Insarov, Y. Ishikawa, M. Jafari, A. Kitoh, J. Pulhin, C. Singh, K. Vasant, and Z. Zhang, 2022: Asia. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1457–1579, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.012.
- ^ Sherwood, S.C.; Huber, M. (25 May 2010). "An adaptability limit to climate change due to heat stress". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107 (21): 9552–5. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.9552S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0913352107. PMC 2906879. PMID 20439769.
- ^ Madge, Grahame (2021-11-09). "One billion face heat-stress risk from 2°C rise". Met Office. Retrieved 2021-11-10.
- ^ Colin Raymond; Tom Matthews; Radley M. Horton (2020). "The emergence of heat and humidity too severe for human tolerance". Science Advances. 6 (19): eaaw1838. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.1838R. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaw1838. PMC 7209987. PMID 32494693.
- ^ a b Kovats, R. Sari; Hajat, Shakoor (April 2008). "Heat Stress and Public Health: A Critical Review". Annual Review of Public Health. 29 (1): 41–55. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.29.020907.090843. PMID 18031221.
- ^ Hancock, P. A.; Vasmatzidis, I. (January 2003). "Research Article". International Journal of Hyperthermia. 19 (3): 355–372. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.464.7830. doi:10.1080/0265673021000054630. PMID 12745975. S2CID 13960829.
- ^ Koppe, Christina; Sari Kovats; Gerd Jendritzky; Bettina Menne (2004). "Heat-waves: risks and responses". Health and Global Environmental Change Series. 2.
- ^ Witt, Christian; Schubert, André Jean; Jehn, Melissa; Holzgreve, Alfred; Liebers, Uta; Endlicher, Wilfried; Scherer, Dieter (2015-12-21). "The Effects of Climate Change on Patients With Chronic Lung Disease. A Systematic Literature Review". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 112 (51–52): 878–883. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2015.0878. ISSN 1866-0452. PMC 4736555. PMID 26900154.
- ^ a b c Tuholske, Cascade; Caylor, Kelly; Funk, Chris; Verdin, Andrew; Sweeney, Stuart; Grace, Kathryn; Peterson, Pete; Evans, Tom (2021-10-12). "Global urban population exposure to extreme heat". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 118 (41): e2024792118. Bibcode:2021PNAS..11824792T. doi:10.1073/pnas.2024792118. ISSN 1091-6490. PMC 8521713. PMID 34607944.
- ^ a b IPCC, 2022: Annex II: Glossary [Möller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.)]. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029.
- ^ a b c d Fox, M.; Zuidema, C.; Bauman, B.; Burke, T.; Sheehan, M. (2019). "Integrating Public Health into Climate Change Policy and Planning: State of Practice Update". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 16 (18): 3232. doi:10.3390/ijerph16183232. PMC 6765852. PMID 31487789.
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
- ^ Robine, Jean-Marie; Cheung, Siu Lan K; Le Roy, Sophie; Van Oyen, Herman; Griffiths, Clare; Michel, Jean-Pierre; Herrmann, François Richard (2008). "Death toll exceeded 70,000 in Europe during the summer of 2003". Comptes Rendus Biologies. 331 (2): 171–8. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2007.12.001. PMID 18241810.
- ^ Haider, Kamran; Anis, Khurrum (24 June 2015). "Heat Wave Death Toll Rises to 2,000 in Pakistan's Financial Hub". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- ^ Mansoor, Hasan (30 June 2015). "Heatstroke leaves another 26 dead in Sindh". Dawn. Retrieved 9 August 2015.
- ^ Coley, D.; Kershaw, T. J.; Eames, M. (2012). "A comparison of structural and behavioural adaptations to future proofing buildings against higher temperatures" (PDF). Building and Environment. 55: 159–166. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2011.12.011. hdl:10871/13936. S2CID 55303235.
- ^ Coley, D.; Kershaw, T. J. (2010). "Changes in internal temperatures within the built environment as a response to a changing climate" (PDF). Building and Environment. 45 (1): 89–93. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2009.05.009.
- ^ Liu, Xingcai (February 2020). "Reductions in Labor Capacity from Intensified Heat Stress in China under Future Climate Change". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 17 (4): 1278. doi:10.3390/ijerph17041278. PMC 7068449. PMID 32079330.
- ^ Seneviratne, Sonia I.; Zhang, Xuebin; Adnan, M.; Badi, W.; et al. (2021). "Chapter 11: Weather and climate extreme events in a changing climate" (PDF). Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate. Cambridge University Press. p. 1517.
- ^ Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change (Report). Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. 2016. pp. 127–136. doi:10.17226/21852. ISBN 978-0-309-38094-2. Archived from the original on 2022-02-15. Retrieved 2020-02-22.
- ^ a b c Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021: Chapter 8: Water Cycle Changes. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010.
- ^ Alderman, Katarzyna; Turner, Lyle R.; Tong, Shilu (June 2012). "Floods and human health: A systematic review" (PDF). Environment International. 47: 37–47. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2012.06.003. PMID 22750033.
- ^ Zhong, Raymond (15 September 2022). "In a First Study of Pakistan's Floods, Scientists See Climate Change at Work". The New York Times.
- ^ "Climate Change Likely Worsened Pakistan's Devastating Floods". Scientific American.
- ^ "Public health risks increasing in flood-affected Pakistan, warns WHO". November 2022.
- ^ "UN Warns Deadly Diseases Spreading Fast in Flood-Ravaged Pakistan".
- ^ National Geographic Society (August 18, 2022). "How Climate Change Impacts Water Access". education.nationalgeographic.org. Archived from the original on 24 May 2023. Retrieved 2023-06-20.
- ^ a b c d Epstein, Paul R.; Ferber, Dan (2011). "The Mosquito's Bite". Changing Planet, Changing Health: How the Climate Crisis Threatens Our Health and what We Can Do about it. University of California Press. pp. 29–61. ISBN 978-0-520-26909-5.
- ^ Epstein, Paul R.; Ferber, Dan (2011). "Sobering Predictions". Changing Planet, Changing Health: How the Climate Crisis Threatens Our Health and what We Can Do about it. University of California Press. pp. 62–79. ISBN 978-0-520-26909-5.
- ^ Cook, Benjamin I.; Mankin, Justin S.; Anchukaitis, Kevin J. (2018-05-12). "Climate Change and Drought: From Past to Future". Current Climate Change Reports. 4 (2): 164–179. doi:10.1007/s40641-018-0093-2. ISSN 2198-6061. S2CID 53624756.
- ^ Liu, Y.; Stanturf, J.; Goodrick, S. (February 2010). "Trends in global wildfire potential in a changing climate". Forest Ecology and Management. 259 (4): 685–697. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.002.
- ^ a b c Westerling, A.; Hidalgo, H.; Cayan, D.; Swetnam, T. (August 2006). "Warming and earlier spring increase Western U.S. Forest Wildfire Activity". Science. 313 (5789): 940–943. Bibcode:2006Sci...313..940W. doi:10.1126/science.1128834. PMID 16825536.
- ^ a b Naeher, Luke P.; Brauer, Mmichael; Lipsett, Michael; et al. (January 2007). "Woodsmoke health effects: A review". Inhalation Toxicology. 19 (1): 67–106. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.511.1424. doi:10.1080/08958370600985875. PMID 17127644. S2CID 7394043.
- ^ Epstein, P.; Ferber, D. (2011). Changing Planet, changing health. Los Angeles, California: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-26909-5.
- ^ Casadevall, Arturo (2020-02-03). "Climate change brings the specter of new infectious diseases". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 130 (2): 553–555. doi:10.1172/JCI135003. PMC 6994111. PMID 31904588.
- ^ Reiter, Paul (2001). "Climate Change and Mosquito-Borne Disease". Environmental Health Perspectives. 109 (1): 141–161. doi:10.1289/ehp.01109s1141. PMC 1240549. PMID 11250812. Archived from the original on 24 August 2011.
- ^ Hunter, P.R. (2003). "Climate change and waterborne and vector-borne disease". Journal of Applied Microbiology. 94: 37S–46S. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.94.s1.5.x. PMID 12675935. S2CID 9338260.
- ^ a b McMichael, A.J.; Woodruff, R.E.; Hales, S. (11 March 2006). "Climate change and human health: present and future risks". The Lancet. 367 (9513): 859–869. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(06)68079-3. PMID 16530580. S2CID 11220212.
- ^ Bezner Kerr, R., T. Hasegawa, R. Lasco, I. Bhatt, D. Deryng, A. Farrell, H. Gurney-Smith, H. Ju, S. Lluch-Cota, F. Meza, G. Nelson, H. Neufeldt, and P. Thornton, 2022: Chapter 5: Food, Fibre, and Other Ecosystem Products. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.007.
- ^ Springmann, Marco; Mason-D'Croz, Daniel; Robinson, Sherman; Garnett, Tara; Godfray, H Charles J; Gollin, Douglas; Rayner, Mike; Ballon, Paola; Scarborough, Peter (2016). "Global and regional health effects of future food production under climate change: a modelling study". The Lancet. 387 (10031): 1937–1946. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01156-3. PMID 26947322. S2CID 41851492.
- ^ Haines, Andy; Ebi, Kristie (2019). Solomon, Caren G. (ed.). "The Imperative for Climate Action to Protect Health". New England Journal of Medicine. 380 (3): 263–273. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1807873. PMID 30650330. S2CID 58662802.
- ^ Loladze I (May 2014). "Hidden shift of the ionome of plants exposed to elevated CO2 depletes minerals at the base of human nutrition". eLife. 3 (9): e02245. doi:10.7554/eLife.02245. PMC 4034684. PMID 24867639.
- ^ Riahi, Keywan; van Vuuren, Detlef P.; Kriegler, Elmar; Edmonds, Jae; O'Neill, Brian C.; Fujimori, Shinichiro; Bauer, Nico; Calvin, Katherine; Dellink, Rob; Fricko, Oliver; Lutz, Wolfgang; Popp, Alexander; Cuaresma, Jesus Crespo; KC, Samir; Leimbach, Marian; Jiang, Leiwen; Kram, Tom; Rao, Shilpa; Emmerling, Johannes; Ebi, Kristie; Hasegawa, Tomoko; Havlík, Petr; Humpenoder, Florian; Da Silva, Lara Aleluia; Smith, Steve; Stehfest, Elke; Bosetti, Valentina; Eom, Jiyong; Gernaat, David; Masui, Toshihiko; Rogelj, Joeri; Strefler, Jessica; Drouet, Laurent; Krey, Volker; Luderer, Gunnar; Harmsen, Mathijs; Takahashi, Kiyoshi; Baumstark, Lavinia; Doelman, Johnathan C.; Kainuma, Mikiko; Klimont, Zbigniew; Marangoni, Giacomo; Lotze-Campen, Hermann; Obersteiner, Michael; Tabeau, Andrzej; Tavoni, Massimo (1 February 2017). "The Shared Socioeconomic Pathways and their energy, land use, and greenhouse gas emissions implications: An overview". Global Environmental Change. 42 (9): 153–168. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.05.009. hdl:10044/1/78069.
- ^ Mbow C, Rosenzweig C, Barioni LG, Benton TG, Herrero M, Krishnapillai M, et al. (2019). "Chapter 5: Food Security" (PDF). In Shukla PR, Skea J, Calvo Buendia E, Masson-Delmotte V, Pörtner HO, Roberts DC, et al. (eds.). Climate Change and Land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems.
- ^ Milius S (13 December 2017). "Worries grow that climate change will quietly steal nutrients from major food crops". Science News. Retrieved 21 January 2018.
- ^ Bezner Kerr, R., T. Hasegawa, R. Lasco, I. Bhatt, D. Deryng, A. Farrell, H. Gurney-Smith, H. Ju, S. Lluch-Cota, F. Meza, G. Nelson, H. Neufeldt, and P. Thornton, 2022: Chapter 5: Food, Fibre, and Other Ecosystem Products. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.007.
- ^ Smith MR, Myers SS (27 August 2018). "Impact of anthropogenic CO2 emissions on global human nutrition". Nature Climate Change. 8 (9): 834–839. Bibcode:2018NatCC...8..834S. doi:10.1038/s41558-018-0253-3. ISSN 1758-678X. S2CID 91727337.
- ^ Davis N (27 August 2018). "Climate change will make hundreds of millions more people nutrient deficient". The Guardian. Retrieved 29 August 2018.
- ^ Gain, Animesh K; Giupponi, Carlo; Wada, Yoshihide (2016). "Measuring global water security towards sustainable development goals". Environmental Research Letters. 11 (12): 124015. Bibcode:2016ERL....11l4015G. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/11/12/124015. ISSN 1748-9326.
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
- ^ Progress on household drinking water, sanitation and hygiene 2000-2017. Special focus on inequalities. New York: United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) and World Health Organization, 2019.
- ^ Caretta, Martina Angela; Mukherji, Aditi; et al. "Chapter 4: Water" (PDF). Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. FAQ4.1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 June 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ Sadoff, Claudia; Grey, David; Borgomeo, Edoardo (2020). "Water Security". Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Environmental Science. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780199389414.013.609. ISBN 978-0-19-938941-4.
- ^ Anderegg, William R. L.; Abatzoglou, John T.; Anderegg, Leander D. L.; Bielory, Leonard; Kinney, Patrick L.; Ziska, Lewis (16 February 2021). "Anthropogenic climate change is worsening North American pollen seasons". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 118 (7): e2013284118. Bibcode:2021PNAS..11813284A. doi:10.1073/pnas.2013284118. PMC 7896283. PMID 33558232.
- ^ Burke, Marshall B.; Miguel, Edward; Satyanath, Shanker; Dykema, John A.; Lobell, David B. (2009-12-08). "Warming increases the risk of civil war in Africa". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106 (49): 20670–20674. Bibcode:2009PNAS..10620670B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0907998106. PMC 2781059. PMID 19934048.
- ^ "Climate change amplifies the risks for violent conflicts in Africa".
- ^ Bowles, Devin C; Butler, Colin D; Morisetti, Neil (October 2015). "Climate change, conflict and health". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 108 (10): 390–395. doi:10.1177/0141076815603234. PMC 4622275. PMID 26432813.
- ^ Ebi, Kristie L.; McGregor, Glenn (2008-11-01). "Climate Change, Tropospheric Ozone and Particulate Matter, and Health Impacts". Environmental Health Perspectives. 116 (11): 1449–1455. doi:10.1289/ehp.11463. PMC 2592262. PMID 19057695.
- ^ a b c d Diem, Jeremy E.; Stauber, Christine E.; Rothenberg, Richard (2017-05-16). Añel, Juan A. (ed.). "Heat in the southeastern United States: Characteristics, trends, and potential health impact". PLOS ONE. 12 (5): e0177937. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1277937D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0177937. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5433771. PMID 28520817.
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
- ^ a b Szopa, S., V. Naik, B. Adhikary, P. Artaxo, T. Berntsen, W.D. Collins, S. Fuzzi, L. Gallardo, A. Kiendler-Scharr, Z. Klimont, H. Liao, N. Unger, and P. Zanis, 2021: Chapter 6: Short-Lived Climate Forcers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 817–922, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.008.
- ^ Sharma, Sumit; Sharma, Prateek; Khare, Mukesh; Kwatra, Swati (May 2016). "Statistical behavior of ozone in urban environment". Sustainable Environment Research. 26 (3): 142–148. doi:10.1016/j.serj.2016.04.006.
- ^ Health Aspects of Air Pollution with Particulate Matter, Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide. WHO-Europe report 13–15 January 2003 (PDF)
- ^ Answer to follow-up questions from CAFE (2004) Archived 2005-09-09 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ EPA Course Developers (2016-03-21). "Health Effects of Ozone in the General Population". EPA.
- ^ Weinhold B (2008). "Ozone nation: EPA standard panned by the people". Environ. Health Perspect. 116 (7): A302–A305. doi:10.1289/ehp.116-a302. PMC 2453178. PMID 18629332.
- ^ US EPA, OAR (2015-06-05). "Health Effects of Ozone Pollution". www.epa.gov. Retrieved 2023-04-29.
- ^ Epstein, Paul R.; Ferber, Dan (2011). "Mozambique". Changing Planet, Changing Health: How the Climate Crisis Threatens Our Health and what We Can Do about it. University of California Press. pp. 6–28. ISBN 978-0-520-26909-5.
- ^ "NRDC: Climate Change Threatens Health: Drought". nrdc.org.
- ^ Paerl, Hans W.; Huisman, Jef (4 April 2008). "Blooms Like It Hot". Science. 320 (5872): 57–58. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.364.6826. doi:10.1126/science.1155398. PMID 18388279. S2CID 142881074.
- ^ a b c Tatters, Avery O.; Fu, Fei-Xue; Hutchins, David A. (February 2012). "High CO2 and Silicate Limitation Synergistically Increase the Toxicity of Pseudo-nitzschia fraudulenta". PLOS ONE. 7 (2): e32116. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...732116T. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032116. PMC 3283721. PMID 22363805.
- ^ Wingert, Charles J.; Cochlan, William P. (July 2021). "Effects of ocean acidification on the growth, photosynthetic performance, and domoic acid production of the diatom Pseudo-nitzschia australis from the California Current System". Harmful Algae. 107: 102030. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2021.102030. PMID 34456015. S2CID 237841102.
- ^ "Rising carbon dioxide levels will make us stupider". Nature. 580 (7805): 567. 20 April 2020. Bibcode:2020Natur.580Q.567.. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01134-w. PMID 32317783. S2CID 216075495.
- ^ "Rising CO2 causes more than a climate crisis—it may directly harm our ability to think". phys.org. Archived from the original on 1 May 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ Karnauskas, Kristopher B.; Miller, Shelly L.; Schapiro, Anna C. (2020). "Fossil Fuel Combustion Is Driving Indoor CO2 Toward Levels Harmful to Human Cognition". GeoHealth. 4 (5): e2019GH000237. doi:10.1029/2019GH000237. PMC 7229519. PMID 32426622.
- ^ "Climate change: Warmer winters linked to increased drowning risk". BBC News. 18 November 2020. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ^ Bhaumik, Soumyadeep; Beri, Deepti; Jagnoor, Jagnoor (October 2022). "The impact of climate change on the burden of snakebite: Evidence synthesis and implications for primary healthcare". Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care. 11 (10): 6147–6158. doi:10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_677_22. PMC 9810950. PMID 36618235. S2CID 253452433.
- ^ Workman, Annabelle; Blashki, Grant; Bowen, Kathryn J.; Karoly, David J.; Wiseman, John (April 2018). "The Political Economy of Health Co-Benefits: Embedding Health in the Climate Change Agenda". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 15 (4): 674. doi:10.3390/ijerph15040674. PMC 5923716. PMID 29617317.
- ^ Molar, Roberto. "Reducing Emissions to Lessen Climate Change Could Yield Dramatic Health Benefits by 2030". Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ Swenarton, Nicole. "Climate action can lessen poverty and inequality worldwide". Rutgers University. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ a b Hamilton, Ian; Kennard, Harry; McGushin, Alice; Höglund-Isaksson, Lena; Kiesewetter, Gregor; Lott, Melissa; Milner, James; Purohit, Pallav; Rafaj, Peter; Sharma, Rohit; Springmann, Marco (2021). "The public health implications of the Paris Agreement: a modelling study". The Lancet Planetary Health. 5 (2): e74–e83. doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30249-7. PMC 7887663. PMID 33581069.
 This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ Green, Matthew (9 February 2021). "Fossil fuel pollution causes one in five premature deaths globally: study". Reuters. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- ^ Vohra, Karn; Vodonos, Alina; Schwartz, Joel; Marais, Eloise A.; Sulprizio, Melissa P.; Mickley, Loretta J. (April 2021). "Global mortality from outdoor fine particle pollution generated by fossil fuel combustion: Results from GEOS-Chem". Environmental Research. 195: 110754. Bibcode:2021ER....195k0754V. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.110754. PMID 33577774. S2CID 231909881.
- ^ Kemp, Luke; Xu, Chi; Depledge, Joanna; Ebi, Kristie L.; Gibbins, Goodwin; Kohler, Timothy A.; Rockström, Johan; Scheffer, Marten; Schellnhuber, Hans Joachim; Steffen, Will; Lenton, Timothy M. (2022). "Climate Endgame: Exploring catastrophic climate change scenarios". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 119 (34): e2108146119. Bibcode:2022PNAS..11908146K. doi:10.1073/pnas.2108146119. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 9407216. PMID 35914185.
- ^ a b Hales, Simon; Kovats, Sari; Lloyd, Simon; Campbell-Lendrum, Diarmid, eds. (2014). Quantitative risk assessment of the effects of climate change on selected causes of death, 2030s and 2050s. Switzerland: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/134014. ISBN 978-92-4-150769-1.[page needed]
- ^ WHO (2009). "Ch. 2, Results: 2.6 Environmental risks". Global health risks: mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks (PDF). Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press. p. 24. ISBN 978-92-4-156387-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 December 2013. Retrieved 4 October 2020.
- ^ Crimmins, A.; Balbus, J.; Gamble, J.L.; Beard, C.B.; Bell, J.E.; Dodgen, D.; Eisen, R.J.; Fann, N.; Hawkins, M.D.; Herring, S.C.; Jantarasami, L.; Mills, D.M.; Saha, S.; Sarofim, M.C.; Trtanj, J.; Ziska, L. (2016). The Impacts of Climate Change on Human Health in the United States: A Scientific Assessment. doi:10.7930/J0R49NQX. ISBN 978-0-16-093241-0.
- ^ a b c d Kent E. Pinkerton , William N. Rom, ed. (2021). "1,2,6,12,13". Climate Change and Global Public Health. Humana. ISBN 978-3-030-54745-5.
- ^ Pearce, Joshua M.; Parncutt, Richard (2023-01). "Quantifying Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Human Deaths to Guide Energy Policy". Energies. 16 (16): 6074. doi:10.3390/en16166074. ISSN 1996-1073.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Human-caused climate change may lead to 1 billion premature deaths over next century: Study". The Times of India. 2023-08-29. ISSN 0971-8257. Retrieved 2023-09-18.
- ^ Bergstrand, Kelly; Mayer, Brian; Brumback, Babette; Zhang, Yi (June 2015). "Assessing the Relationship Between Social Vulnerability and Community Resilience to Hazards". Social Indicators Research. 122 (2): 391–409. doi:10.1007/s11205-014-0698-3. PMC 5739329. PMID 29276330.
- ^ Epstein, Paul R. (6 October 2005). "Climate Change and Human Health". New England Journal of Medicine. 353 (14): 1433–1436. doi:10.1056/NEJMp058079. PMID 16207843.
- ^ a b "Human Health". Global Change. Retrieved 25 November 2020.
- ^ Anneliese Depoux; Mathieu Hémono; Sophie Puig-Malet; Romain Pédron; Antoine Flahault (2017). "Communicating climate change and health in the media". Public Health Rev. 38: 7. doi:10.1186/s40985-016-0044-1. PMC 5809944. PMID 29450079.
- ^ Per Espen Stoknes (September 2017). How to transform apocalypse fatigue into action on global warming. TED (conference). Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ Saad, Lydia (20 April 2023). "A Steady Six in 10 Say Global Warming's Effects Have Begun". Gallup, Inc. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023.
- ^ Davenport, Coral (4 April 2016). "Global Warming Linked to Public Health Risks, White House Says". The New York Times.
- ^ Kavya Balaraman (17 March 2017). "Doctors Warn Climate Change Threatens Public Health; Physicians are noticing an influx of patients whose illnesses are directly or indirectly related to global warming". E&E News. Retrieved 20 March 2017 – via Scientific American.
- ^ Dean Russell; Elisabeth Gawthrop; Veronica Penney; Ali Raj; Bridget Hickey (16 June 2020). "Deadly heat is killing Americans: A decade of inaction on climate puts lives at risk". The Guardian. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ Operational framework for building climate resilient health systems. WHO. 2015. ISBN 978-92-4-156507-3.[page needed]
