Platecarpus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''''Platecarpus''''' ("Flat wrist") is an [[extinct]] [[genus]] of aquatic [[lizard]] belonging to the [[mosasaur]] family, living around 75 million years ago during the end of the [[Cretaceous]] [[Period (geology)|period]]. [[Fossil]]s have been found in [[Belgium]] and the [[United States]].<ref name=EoDP/> ''Platecarpus'' probably fed on [[fish]], [[squid]], and [[ammonite]]s.<ref name=EoDP>{{cite book |editor=Palmer, D.|year=1999 |title= The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals|publisher= Marshall Editions|location=London|page= 87|isbn= 1-84028-152-9}}</ref> Like other mosasaurs, it was initially thought to have swam in an [[eel]]-like fashion, although a recent study suggests that it swam more like modern sharks. An exceptionally well-preserved specimen of ''Platecarpus'' known as LACM 128319 shows skin impressions, pigments around the nostrils, bronchial tubes and the presence of a high profile tail fluke, showing that it and other mosasaurs did not necessarily have an eel-like swimming method but were faster, more powerful swimmers. It is held in the [[Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County]].<ref>Lindgren |
'''''Platecarpus''''' ("Flat wrist") is an [[extinct]] [[genus]] of aquatic [[lizard]] belonging to the [[mosasaur]] family, living around 75 million years ago during the end of the [[Cretaceous]] [[Period (geology)|period]]. [[Fossil]]s have been found in [[Belgium]] and the [[United States]].<ref name=EoDP/> ''Platecarpus'' probably fed on [[fish]], [[squid]], and [[ammonite]]s.<ref name=EoDP>{{cite book |editor=Palmer, D.|year=1999 |title= The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals|publisher= Marshall Editions|location=London|page= 87|isbn= 1-84028-152-9}}</ref> Like other mosasaurs, it was initially thought to have swam in an [[eel]]-like fashion, although a recent study suggests that it swam more like modern sharks. An exceptionally well-preserved specimen of ''Platecarpus'' known as LACM 128319 shows skin impressions, pigments around the nostrils, bronchial tubes and the presence of a high profile tail fluke, showing that it and other mosasaurs did not necessarily have an eel-like swimming method but were faster, more powerful swimmers. It is held in the [[Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County]].<ref name=LCKC10>{{cite journal |last=Lindgren |first=J. |coauthors=Caldwell, M.W.; Konishi, T.; and Chiappe, L.M. |year=2010 |title=Convergent evolution in aquatic tetrapods: Insights from an exceptional fossil mosasaur |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=5 |issue=8 |pages=e11998 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0011998}}</ref> |
||
==Description== |
==Description== |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[Image:Platecarpus yale1.JPG|thumb|left|''Platecarpus'' skull at the [[Peabody Museum of Natural History]].]] |
[[Image:Platecarpus yale1.JPG|thumb|left|''Platecarpus'' skull at the [[Peabody Museum of Natural History]].]] |
||
The skull structure of ''Platecarpus'' is unique among mosasaurs. This genus is characterized by a short skull, and have the least number of teeth in its jaw than compared to any other mosasaur (approximately 10 teeth in each [[dentary bone|dentary]]).<ref group=note>Burnham (1991) recently reported an unclassified species of ''[[Plioplatecarpus]]'' from the Lower [[Demopolis Formation]] in Alabama that has a lower number of teeth in its jaws.</ref> LACM 128319 preserves matter within the [[sclerotic ring]] that may possibly be the [[retina]] of the eye. Small structures in the retina, each around 2 µm long and observed by [[Scanning electron microscope|scanning electron microspectroscopy]], may represent retinal [[melanosome]]s preserved in their original positions. |
The skull structure of ''Platecarpus'' is unique among mosasaurs. This genus is characterized by a short skull, and have the least number of teeth in its jaw than compared to any other mosasaur (approximately 10 teeth in each [[dentary bone|dentary]]).<ref group=note>Burnham (1991) recently reported an unclassified species of ''[[Plioplatecarpus]]'' from the Lower [[Demopolis Formation]] in Alabama that has a lower number of teeth in its jaws.</ref> LACM 128319 preserves matter within the [[sclerotic ring]] that may possibly be the [[retina]] of the eye. Small structures in the retina, each around 2 µm long and observed by [[Scanning electron microscope|scanning electron microspectroscopy]], may represent retinal [[melanosome]]s preserved in their original positions.<ref name=LCKC10/> |
||
[[Image:Soft tissue structures in Platecarpus.png|thumb|right|Soft tissues in the head and neck of LACM 128319. Tracheal rings are shown in the bottom three photographs.]] |
[[Image:Soft tissue structures in Platecarpus.png|thumb|right|Soft tissues in the head and neck of LACM 128319. Tracheal rings are shown in the bottom three photographs.]] |
||
The [[trachea|respiratory tube]] is also known in LACM 128319, preserved as [[cartilaginous]] tracheal rings. Only the posterior-most end of the tracheal tube - at the end of the neck near the [[pectoral girdle]] - is known. The section where the two [[bronchi]] split was also preserved in the specimen, but was destroyed during excavation. This is an indication that ''Platecarpus'' and other mosasaurs had two functional lungs. Snakes, which are closely related to mosasaurs, have only one functional lung with the second often being vestigial or absent. Unlike terrestrial lizards, however, the bronchi separate in front of the area of the forelimbs rather than at the level of the limbs. |
The [[trachea|respiratory tube]] is also known in LACM 128319, preserved as [[cartilaginous]] tracheal rings. Only the posterior-most end of the tracheal tube - at the end of the neck near the [[pectoral girdle]] - is known. The section where the two [[bronchi]] split was also preserved in the specimen, but was destroyed during excavation. This is an indication that ''Platecarpus'' and other mosasaurs had two functional lungs. Snakes, which are closely related to mosasaurs, have only one functional lung with the second often being vestigial or absent. Unlike terrestrial lizards, however, the bronchi separate in front of the area of the forelimbs rather than at the level of the limbs.<ref name=LCKC10/> |
||
Skin impressions are known from ''Platecarpus'', preserved in LACM 128319 as soft impressions and [[phosphate]] material. Scales on the tip of the snout and the top of the skull are somewhat hexagonal in shape and do not touch one another. The scales on the jaws are longer and rhomboidal in shape, overlapping one another. The scales on the snout indicate that the nostrils were placed far in front of the skull at its tip and faced laterally as in most [[squamate]]s and [[archosaur]]s. The body scales are all rhomboidal in shape and form tightly connecting diagonal rows that overlap each other at their posterior edges. They are generally the same size throughout the entire length of the body. The caudal scales on the tail are taller and larger than those of the rest of the body, although those covering the lower surface of the tail are more similar to body scales. |
Skin impressions are known from ''Platecarpus'', preserved in LACM 128319 as soft impressions and [[phosphate]] material. Scales on the tip of the snout and the top of the skull are somewhat hexagonal in shape and do not touch one another. The scales on the jaws are longer and rhomboidal in shape, overlapping one another. The scales on the snout indicate that the nostrils were placed far in front of the skull at its tip and faced laterally as in most [[squamate]]s and [[archosaur]]s. The body scales are all rhomboidal in shape and form tightly connecting diagonal rows that overlap each other at their posterior edges. They are generally the same size throughout the entire length of the body. The caudal scales on the tail are taller and larger than those of the rest of the body, although those covering the lower surface of the tail are more similar to body scales.<ref name=LCKC10/> |
||
[[Image:Platecarpus tympaniticus.png|thumb|left |
[[Image:Platecarpus tympaniticus.png|thumb|left |
||
|350px|LACM 128319.]] |
|350px|LACM 128319.]] |
||
Internal organs, or [[viscera]], may also be preserved in the specimen as reddish areas. One is located in the [[thoracic cavity]] low in the ribcage, while the other is located in the upper portion of the [[abdominal cavity]] just behind the ribcage. The reddish areas were analysed with [[mass spectrometry]] and were shown to contain high levels of compounds made of [[iron]] and [[porphyrin]]. These substances are evidence of [[hemoglobin]] decomposition products that may have formed in the organs as they decomposed. Based on its position, the organ in the thoracic cavity is probably the heart or liver, or even both of those organs. The organ in the abdominal cavity may be a [[kidney]], although it is in a more anterior position than the kidneys of [[monitor lizard]]s, mosasaurs' closest living relatives. The anterior position of the kidneys may have been an adaptation toward a more streamlined body, as their presumed position is similar to that of [[cetacean]]s. |
Internal organs, or [[viscera]], may also be preserved in the specimen as reddish areas. One is located in the [[thoracic cavity]] low in the ribcage, while the other is located in the upper portion of the [[abdominal cavity]] just behind the ribcage. The reddish areas were analysed with [[mass spectrometry]] and were shown to contain high levels of compounds made of [[iron]] and [[porphyrin]]. These substances are evidence of [[hemoglobin]] decomposition products that may have formed in the organs as they decomposed. Based on its position, the organ in the thoracic cavity is probably the heart or liver, or even both of those organs. The organ in the abdominal cavity may be a [[kidney]], although it is in a more anterior position than the kidneys of [[monitor lizard]]s, mosasaurs' closest living relatives. The anterior position of the kidneys may have been an adaptation toward a more streamlined body, as their presumed position is similar to that of [[cetacean]]s.<ref name=LCKC10/> |
||
Part of the digestive tract is also preserved and is filled with fish remains. The shape of these remains may outline the true shape of the corresponding part of the digestive tract, most likely the [[colon]]. The presence of scales and undigested bones in the colon suggests that ''Platecarpus'' and other mosasaurs processed food quickly and did not thouroughly digest and absorb all food in the gastrointestinal tract. Coprolites from the mosasaur ''[[Globidens]]'' are also suggestive of low digestion and absorption rates as they contain masses of crushed [[bivalve]] shells. |
Part of the digestive tract is also preserved and is filled with fish remains. The shape of these remains may outline the true shape of the corresponding part of the digestive tract, most likely the [[colon]]. The presence of scales and undigested bones in the colon suggests that ''Platecarpus'' and other mosasaurs processed food quickly and did not thouroughly digest and absorb all food in the gastrointestinal tract. Coprolites from the mosasaur ''[[Globidens]]'' are also suggestive of low digestion and absorption rates as they contain masses of crushed [[bivalve]] shells.<ref name=LCKC10/> |
||
[[Image:Skeletal reconstruction and inferred body outline of Platecarpus.png|thumb|right|400px|Reconstruction of ''Platecarpus'' showing prominent tail fluke.]] |
[[Image:Skeletal reconstruction and inferred body outline of Platecarpus.png|thumb|right|400px|Reconstruction of ''Platecarpus'' showing prominent tail fluke.]] |
||
The caudal, or tail vertebrae, are sharply downturned. The vertebrae at the bend (called the caudal peduncle) are wedge shaped with neural spines that are wider at their ends than they are at their bases. This downturned area likely supported a fluke similar to modern sharks. Two lobes would have been present: a lower one supported by the downturned vertebrae and an upper, unsupported one. The tail fluke was probably hypocercal, meaning that its lower lobe was longer than its upper lobe. This condition is also seen in [[ichthyosaur]]s and [[metriorhynchid]] [[crocodyliform]]s. |
The caudal, or tail vertebrae, are sharply downturned. The vertebrae at the bend (called the caudal peduncle) are wedge shaped with neural spines that are wider at their ends than they are at their bases. This downturned area likely supported a fluke similar to modern sharks. Two lobes would have been present: a lower one supported by the downturned vertebrae and an upper, unsupported one. The tail fluke was probably hypocercal, meaning that its lower lobe was longer than its upper lobe. This condition is also seen in [[ichthyosaur]]s and [[metriorhynchid]] [[crocodyliform]]s.<ref name=LCKC10/> |
||
==History== |
==History== |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
===Locomotion=== |
===Locomotion=== |
||
[[Image:Platecarpus1DB.jpg|thumb|left|Artist's depiction of ''Platecarpus coryphaeus'' with an [[anguilliform]]-like tail.]] |
[[Image:Platecarpus1DB.jpg|thumb|left|Artist's depiction of ''Platecarpus coryphaeus'' with an [[anguilliform]]-like tail.]] |
||
While mosasaurs are traditionally thought to have propelled themselves through the water by lateral ungulation in a similar way to eels, the deep caudal fin of ''Platecarpus'' suggests that it swam more like a shark. The downturned caudal vertebrae of ''Platecarpus'' suggest it had a crescent-shaped tail fluke. At the point of the tail where the fluke begins the vertebral centra are shortened and disk-like. Their reduced size likely allowed for greater flexibility at an area that would have experienced high stresses during swimming. The neural spines of these vertebrae also have grooves for the insertion of [[interspinal ligament]]s and dorsal connective tissues which would have aided in lateral movement of the fluke. The ligaments were probably made of collagenous fibers that acted as springs to move the tail back into a resting position after energy was stored in them. These types of ligaments work in some living fish to conserve energy during repetitive bending of the tail. While the fluke and back of the tail undulated in ''Platecarpus'', the base of the tail remained stable. This form of movement is known as [[Fish locomotion#Carangiform locomotion|carangiform]] locomotion. |
While mosasaurs are traditionally thought to have propelled themselves through the water by lateral ungulation in a similar way to eels, the deep caudal fin of ''Platecarpus'' suggests that it swam more like a shark. The downturned caudal vertebrae of ''Platecarpus'' suggest it had a crescent-shaped tail fluke. At the point of the tail where the fluke begins the vertebral centra are shortened and disk-like. Their reduced size likely allowed for greater flexibility at an area that would have experienced high stresses during swimming. The neural spines of these vertebrae also have grooves for the insertion of [[interspinal ligament]]s and dorsal connective tissues which would have aided in lateral movement of the fluke. The ligaments were probably made of collagenous fibers that acted as springs to move the tail back into a resting position after energy was stored in them. These types of ligaments work in some living fish to conserve energy during repetitive bending of the tail. While the fluke and back of the tail undulated in ''Platecarpus'', the base of the tail remained stable. This form of movement is known as [[Fish locomotion#Carangiform locomotion|carangiform]] locomotion.<ref name=LCKC10/> |
||
The structure of the scales of ''Platecarpus'' may have been another adaptation toward a marine lifestyle. The small size and similar shape of these scales throughout the body would have stiffened the trunk, making it more resistant to lateral movement. This stiffness would have improved [[hydrodynamic]] efficiency by improving the flow of water across the body. The early [[mosasauroid]] ''[[Vallecillosaurus]]'' also preserves body scales, but they are larger and more varied in shape, suggesting that the animal relied on undulatory movement in its trunk rather than just its tail. ''[[Plotosaurus]]'', a more derived mosasaur than ''Platecarpus'', has even smaller scales covering its body, indicating that it had even more efficient locomotion in the water. |
The structure of the scales of ''Platecarpus'' may have been another adaptation toward a marine lifestyle. The small size and similar shape of these scales throughout the body would have stiffened the trunk, making it more resistant to lateral movement. This stiffness would have improved [[hydrodynamic]] efficiency by improving the flow of water across the body. The early [[mosasauroid]] ''[[Vallecillosaurus]]'' also preserves body scales, but they are larger and more varied in shape, suggesting that the animal relied on undulatory movement in its trunk rather than just its tail. ''[[Plotosaurus]]'', a more derived mosasaur than ''Platecarpus'', has even smaller scales covering its body, indicating that it had even more efficient locomotion in the water.<ref name=LCKC10/> |
||
==Notes== |
==Notes== |
||
Revision as of 03:48, 11 August 2010
| Platecarpus Temporal range: Late Cretaceous
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Skeleton of Platecarpus coryphaeus at the Royal Ontario Museum. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | Platecarpus |
| Species | |
| |
Platecarpus ("Flat wrist") is an extinct genus of aquatic lizard belonging to the mosasaur family, living around 75 million years ago during the end of the Cretaceous period. Fossils have been found in Belgium and the United States.[1] Platecarpus probably fed on fish, squid, and ammonites.[1] Like other mosasaurs, it was initially thought to have swam in an eel-like fashion, although a recent study suggests that it swam more like modern sharks. An exceptionally well-preserved specimen of Platecarpus known as LACM 128319 shows skin impressions, pigments around the nostrils, bronchial tubes and the presence of a high profile tail fluke, showing that it and other mosasaurs did not necessarily have an eel-like swimming method but were faster, more powerful swimmers. It is held in the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.[2]
Description

Platecarpus had a long, down-turned tail with a large dorsal lobe on it, steering flippers, and jaws lined with conical teeth. It grew up to 4.3 metres (14 ft) long, with half of that length taken up by its tail. The platecarpine mosasaurs had evolved into the very specialized plioplatecarpine group by the end of the Cretaceous.

The skull structure of Platecarpus is unique among mosasaurs. This genus is characterized by a short skull, and have the least number of teeth in its jaw than compared to any other mosasaur (approximately 10 teeth in each dentary).[note 1] LACM 128319 preserves matter within the sclerotic ring that may possibly be the retina of the eye. Small structures in the retina, each around 2 µm long and observed by scanning electron microspectroscopy, may represent retinal melanosomes preserved in their original positions.[2]
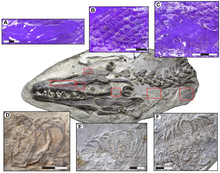
The respiratory tube is also known in LACM 128319, preserved as cartilaginous tracheal rings. Only the posterior-most end of the tracheal tube - at the end of the neck near the pectoral girdle - is known. The section where the two bronchi split was also preserved in the specimen, but was destroyed during excavation. This is an indication that Platecarpus and other mosasaurs had two functional lungs. Snakes, which are closely related to mosasaurs, have only one functional lung with the second often being vestigial or absent. Unlike terrestrial lizards, however, the bronchi separate in front of the area of the forelimbs rather than at the level of the limbs.[2]
Skin impressions are known from Platecarpus, preserved in LACM 128319 as soft impressions and phosphate material. Scales on the tip of the snout and the top of the skull are somewhat hexagonal in shape and do not touch one another. The scales on the jaws are longer and rhomboidal in shape, overlapping one another. The scales on the snout indicate that the nostrils were placed far in front of the skull at its tip and faced laterally as in most squamates and archosaurs. The body scales are all rhomboidal in shape and form tightly connecting diagonal rows that overlap each other at their posterior edges. They are generally the same size throughout the entire length of the body. The caudal scales on the tail are taller and larger than those of the rest of the body, although those covering the lower surface of the tail are more similar to body scales.[2]

Internal organs, or viscera, may also be preserved in the specimen as reddish areas. One is located in the thoracic cavity low in the ribcage, while the other is located in the upper portion of the abdominal cavity just behind the ribcage. The reddish areas were analysed with mass spectrometry and were shown to contain high levels of compounds made of iron and porphyrin. These substances are evidence of hemoglobin decomposition products that may have formed in the organs as they decomposed. Based on its position, the organ in the thoracic cavity is probably the heart or liver, or even both of those organs. The organ in the abdominal cavity may be a kidney, although it is in a more anterior position than the kidneys of monitor lizards, mosasaurs' closest living relatives. The anterior position of the kidneys may have been an adaptation toward a more streamlined body, as their presumed position is similar to that of cetaceans.[2]
Part of the digestive tract is also preserved and is filled with fish remains. The shape of these remains may outline the true shape of the corresponding part of the digestive tract, most likely the colon. The presence of scales and undigested bones in the colon suggests that Platecarpus and other mosasaurs processed food quickly and did not thouroughly digest and absorb all food in the gastrointestinal tract. Coprolites from the mosasaur Globidens are also suggestive of low digestion and absorption rates as they contain masses of crushed bivalve shells.[2]

The caudal, or tail vertebrae, are sharply downturned. The vertebrae at the bend (called the caudal peduncle) are wedge shaped with neural spines that are wider at their ends than they are at their bases. This downturned area likely supported a fluke similar to modern sharks. Two lobes would have been present: a lower one supported by the downturned vertebrae and an upper, unsupported one. The tail fluke was probably hypocercal, meaning that its lower lobe was longer than its upper lobe. This condition is also seen in ichthyosaurs and metriorhynchid crocodyliforms.[2]
History
Fossils

Various skeletons of this mosasaur have been found in Cretaceous deposits in Kansas, however, only one complete skull has ever been recovered.[3] Platecarpus fossils have been found in rocks that date back to the late Coniacian through the early Campanian in the Smoky Hill Chalk.
Taxonomic History
Platecarpus was probably the most common genus of mosasaur in the Western Interior Sea during the deposition of the Smoky Hill Chalk in Kansas, and Platecarpus ictericus is the most commonly occurring species[3]. There is some controversy regarding the description of the genus Platecarpus since it includes some diverse, and possibly unrelated forms.
The type specimen of Platecarpus (P. planiforms) was discovered by Professor B. F. Mudge and was classified by Edward Drinker Cope as Clidastes planiformes.[3] In 1898, on further analysis of the remains, it was determined that the mosasaur be placed in a separate genus, Platecarpus.[4] The type specimen underwent another taxonomic review in 1967, when paleontologist Dale Russell determined that the remains were too fragmentary to be placed within any genus, and deemed it to be a specimen of "uncertain taxonomic position".[5] A 2006 discovery in the Smoky Hill Chalk of Kansas re-affirmed this position with the discovery a complete fossilized skull being unearthed.[6]
Paleobiology
Diet
Compared to the tylosaurs, plioplatecarpine mosasaurs had much less robust teeth, suggesting that they fed on smaller (or softer) prey such as small fish and squid[3].
Locomotion

While mosasaurs are traditionally thought to have propelled themselves through the water by lateral ungulation in a similar way to eels, the deep caudal fin of Platecarpus suggests that it swam more like a shark. The downturned caudal vertebrae of Platecarpus suggest it had a crescent-shaped tail fluke. At the point of the tail where the fluke begins the vertebral centra are shortened and disk-like. Their reduced size likely allowed for greater flexibility at an area that would have experienced high stresses during swimming. The neural spines of these vertebrae also have grooves for the insertion of interspinal ligaments and dorsal connective tissues which would have aided in lateral movement of the fluke. The ligaments were probably made of collagenous fibers that acted as springs to move the tail back into a resting position after energy was stored in them. These types of ligaments work in some living fish to conserve energy during repetitive bending of the tail. While the fluke and back of the tail undulated in Platecarpus, the base of the tail remained stable. This form of movement is known as carangiform locomotion.[2]
The structure of the scales of Platecarpus may have been another adaptation toward a marine lifestyle. The small size and similar shape of these scales throughout the body would have stiffened the trunk, making it more resistant to lateral movement. This stiffness would have improved hydrodynamic efficiency by improving the flow of water across the body. The early mosasauroid Vallecillosaurus also preserves body scales, but they are larger and more varied in shape, suggesting that the animal relied on undulatory movement in its trunk rather than just its tail. Plotosaurus, a more derived mosasaur than Platecarpus, has even smaller scales covering its body, indicating that it had even more efficient locomotion in the water.[2]
Notes
- ^ Burnham (1991) recently reported an unclassified species of Plioplatecarpus from the Lower Demopolis Formation in Alabama that has a lower number of teeth in its jaws.
References
- ^ a b Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 87. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Lindgren, J. (2010). "Convergent evolution in aquatic tetrapods: Insights from an exceptional fossil mosasaur". PLoS ONE. 5 (8): e11998. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011998.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c d Everhart, Michael J.. Oceans of Kansas: A Natural History of the Western Interior Seaway. c. 2005. pp. 165-169
- ^ Williston (1898a)
- ^ Russell (1967)
- ^ (Everhart and Johnson, 2001)
Further reading
Williston 1898 - includes drawings of the skull of Platecarpus ictericus

