Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve
| Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve | |
|---|---|
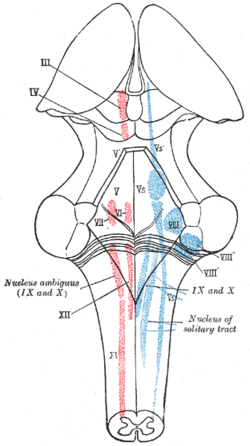 The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue.disease (Trigeminal nerve nuclei are at "V".) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus mesencephalicus nervi trigemini |
| NeuroNames | 558 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1010 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.409 |
| TA2 | 5887 |
| FMA | 54568 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The mesencephalic nucleus is involved with proprioception of the face, that is, the feeling of position of the muscles. Unlike many nuclei within the central nervous system (CNS), the mesencephalic nucleus contains no chemical synapses but are electrically coupled.[1] Neurons of this nucleus are unipolar cells that receive proprioceptive information from the mandible and send projections to the motor trigeminal nucleus to mediate monosynaptic jaw jerk reflexes. It is also the only structure in the CNS to contain the cell bodies of a primary afferent, which are usually contained within ganglia (like the trigeminal ganglion).
Clinical significance
A lesion involving the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus would cause ipsilateral sensory and motor deficits.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ^ Baker R, Llinás R (1971). "Electrotonic coupling between neurones in the rat mesencephalic nucleus". J. Physiol. (Lond.). 212 (1): 45–63. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009309. PMC 1395705. PMID 5545184.
