Cryptista: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
→Taxonomy: fixed typo Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Cephal-odd (talk | contribs) updating membership in more inclusive clades |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| image_caption = ''Rhodomonas salina'', a [[cryptophyceae|cryptophyte]] |
| image_caption = ''Rhodomonas salina'', a [[cryptophyceae|cryptophyte]] |
||
| domain = [[Eukaryota]] |
| domain = [[Eukaryota]] |
||
| unranked_subregnum = [[ |
| unranked_subregnum = [[Diaphoretickes]] |
||
| unranked_phylum = '''Cryptista''' |
| unranked_phylum = '''Cryptista''' |
||
| unranked_phylum_authority = Adl et al., 2018 [Cavalier-Smith 1989, 2018]<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Adl|first1=Sina M.|last2=Bass|first2=David|last3=Lane|first3=Christopher E.|last4=Lukeš|first4=Julius|last5=Schoch|first5=Conrad L.|last6=Smirnov|first6=Alexey|last7=Agatha|first7=Sabine|last8=Berney|first8=Cedric|last9=Brown|first9=Matthew W.|date=2018-09-26|title=Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes|journal=The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology|volume=66|issue=1|pages=4–119|doi=10.1111/jeu.12691|issn=1550-7408|pmid=30257078|pmc=6492006}}</ref> |
| unranked_phylum_authority = Adl et al., 2018 [Cavalier-Smith 1989, 2018]<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Adl|first1=Sina M.|last2=Bass|first2=David|last3=Lane|first3=Christopher E.|last4=Lukeš|first4=Julius|last5=Schoch|first5=Conrad L.|last6=Smirnov|first6=Alexey|last7=Agatha|first7=Sabine|last8=Berney|first8=Cedric|last9=Brown|first9=Matthew W.|date=2018-09-26|title=Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes|journal=The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology|volume=66|issue=1|pages=4–119|doi=10.1111/jeu.12691|issn=1550-7408|pmid=30257078|pmc=6492006}}</ref> |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Cryptista''' is a clade of algae-like [[eukaryote]]s. It is most likely related to [[Archaeplastida]] which includes plants and many algae, within the larger group [[Diaphoretickes]].<ref name="AdlBass2019">{{cite journal | vauthors = Adl SM, Bass D, Lane CE, Lukeš J, Schoch CL, Smirnov A, Agatha S, Berney C, Brown MW, Burki F, Cárdenas P, Čepička I, Chistyakova L, Del Campo J, Dunthorn M, Edvardsen B, Eglit Y, Guillou L, Hampl V, Heiss AA, Hoppenrath M, James TY, Karnkowska A, Karpov S, Kim E, Kolisko M, Kudryavtsev A, Lahr DJ, Lara E, Le Gall L, Lynn DH, Mann DG, Massana R, Mitchell EA, Morrow C, Park JS, Pawlowski JW, Powell MJ, Richter DJ, Rueckert S, Shadwick L, Shimano S, Spiegel FW, Torruella G, Youssef N, Zlatogursky V, Zhang Q | display-authors = 6 | title = Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes | journal = The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology | volume = 66 | issue = 1 | pages = 4–119 | date = January 2019 | pmid = 30257078 | pmc = 6492006 | doi = 10.1111/jeu.12691 }}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | {{Cite journal|last1=Ruggiero|first1=Michael A.|last2=Gordon|first2=Dennis P.|last3=Orrell|first3=Thomas M.|last4=Bailly|first4=Nicolas|last5=Bourgoin|first5=Thierry|last6=Brusca|first6=Richard C.|last7=Cavalier-Smith|first7=Thomas|last8=Guiry|first8=Michael D.|last9=Kirk|first9=Paul M.|date=2015-04-29|title=A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms|journal=PLOS ONE|volume=10|issue=4|pages=e0119248|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0119248|issn=1932-6203|pmc=4418965|pmid=25923521|bibcode=2015PLoSO..1019248R|doi-access=free}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
However, in 2016, a broad phylogenomic study found that cryptists fall within the group [[Archaeplastida]], while haptophytes are closely related to the [[SAR supergroup]].<ref |
|||
| ⚫ | {{Cite journal|last1=Ruggiero|first1=Michael A.|last2=Gordon|first2=Dennis P.|last3=Orrell|first3=Thomas M.|last4=Bailly|first4=Nicolas|last5=Bourgoin|first5=Thierry|last6=Brusca|first6=Richard C.|last7=Cavalier-Smith|first7=Thomas|last8=Guiry|first8=Michael D.|last9=Kirk|first9=Paul M.|date=2015-04-29|title=A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms|journal=PLOS ONE|volume=10|issue=4|pages=e0119248|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0119248|issn=1932-6203|pmc=4418965|pmid=25923521|bibcode=2015PLoSO..1019248R|doi-access=free}}</ref>, most recent studies have found that Hacrobia is not a clade.<ref name="BurkiRoger2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Burki F, Roger AJ, Brown MW, Simpson AG | title = The New Tree of Eukaryotes | journal = Trends in Ecology & Evolution | volume = 35 | issue = 1 | pages = 43–55 | date = January 2020 | pmid = 31606140 | doi = 10.1016/j.tree.2019.08.008 | doi-access = free }}</ref> For example, in 2016, a broad phylogenomic study found that cryptists fall within the group [[Archaeplastida]], while haptophytes are closely related to the [[SAR supergroup]].<ref |
||
name=Burki2016>{{Citation |last1=Burki F |last2=Kaplan M |last3=Tikhonenkov DV |last4=Zlatogursky V |last5=Minh BQ |last6=Radaykina LV |last7=Smirnov A |last8=Mylnikov AP |last9=Keeling PJ |year=2016 |title=Untangling the early diversification of eukaryotes: a phylogenomic study of the evolutionary origins of Centrohelida, Haptophyta and Cryptista. |journal=Proc Biol Sci |volume=283 |issue=1823 |pmid=26817772 |doi=10.1098/rspb.2015.2802 |pmc=4795036 |pages=20152802}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |pmid=20333193 |year=2009 |author1=Burki, F |author2=Inagaki, Y |author3=Bråte, J |author4=Archibald, J. |author5=Keeling, P. |author6=Cavalier-Smith, T |author7=Sakaguchi, M |author8=Hashimoto, T |author9=Horak, A |author10=Kumar, S |author11=Klaveness, D |author12=Jakobsen, K.S |author13=Pawlowski, J |author14=Shalchian-Tabrizi, K |title=Large-scale phylogenomic analyses reveal that two enigmatic protist lineages, Telonemia and Centroheliozoa, are related to photosynthetic chromalveolates. |volume=1 |pages=231–8 |doi=10.1093/gbe/evp022 |journal=Genome Biology and Evolution |format=Free full text |pmc=2817417 }}</ref> |
name=Burki2016>{{Citation |last1=Burki F |last2=Kaplan M |last3=Tikhonenkov DV |last4=Zlatogursky V |last5=Minh BQ |last6=Radaykina LV |last7=Smirnov A |last8=Mylnikov AP |last9=Keeling PJ |year=2016 |title=Untangling the early diversification of eukaryotes: a phylogenomic study of the evolutionary origins of Centrohelida, Haptophyta and Cryptista. |journal=Proc Biol Sci |volume=283 |issue=1823 |pmid=26817772 |doi=10.1098/rspb.2015.2802 |pmc=4795036 |pages=20152802}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |pmid=20333193 |year=2009 |author1=Burki, F |author2=Inagaki, Y |author3=Bråte, J |author4=Archibald, J. |author5=Keeling, P. |author6=Cavalier-Smith, T |author7=Sakaguchi, M |author8=Hashimoto, T |author9=Horak, A |author10=Kumar, S |author11=Klaveness, D |author12=Jakobsen, K.S |author13=Pawlowski, J |author14=Shalchian-Tabrizi, K |title=Large-scale phylogenomic analyses reveal that two enigmatic protist lineages, Telonemia and Centroheliozoa, are related to photosynthetic chromalveolates. |volume=1 |pages=231–8 |doi=10.1093/gbe/evp022 |journal=Genome Biology and Evolution |format=Free full text |pmc=2817417 }}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 19:07, 6 March 2022
| Cryptista | |
|---|---|
| |
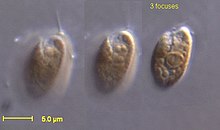
| Rhodomonas salina, a cryptophyte | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | Cryptista Adl et al., 2018 [Cavalier-Smith 1989, 2018][1]
|
| Phyla & Classes | |
Cryptista is a clade of algae-like eukaryotes. It is most likely related to Archaeplastida which includes plants and many algae, within the larger group Diaphoretickes.[2]
Although it has sometimes placed along with Haptista in the group Hacrobia, within the kingdom Chromista,[3], most recent studies have found that Hacrobia is not a clade.[4] For example, in 2016, a broad phylogenomic study found that cryptists fall within the group Archaeplastida, while haptophytes are closely related to the SAR supergroup.[5][6]
Taxonomy
Based on studies done by Cavalier-Smith, Chao & Lewis 2015[7][8]
- Corbihelia
- Phylum Microheliellida Tedersoo 2017 [Endohelia Cavalier-Smith 2015]
- Class Endohelea Cavalier-Smith 2012
- Phylum Microheliellida Tedersoo 2017 [Endohelia Cavalier-Smith 2015]
- Clade Cryptista s.s.
- Phylum Palpitophyta Tedersoo 2017
- Class Palpitea Cavalier-Smith 2012
- Clade Rollomonadia Cavalier-Smith 2013 stat. nov.
- Phylum Kathablepharidophyta Okamoto & Inouye 2005 [Leucocrypta Cavalier-Smith 2015]
- Class Leucocryptea Cavalier-Smith 2004[9] [Kathablepharidea (sic) Okamoto & Inouye 2005; Kathablepharidophyceae]
- Phylum Cryptophyta Pascher 1913 em. Adl et al. 2012 (Cryptomonada Cavalier-Smith 2004 sta. n.]
- Class Goniomonadea Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Class Cryptophyceae Fritsch 1937
- Phylum Kathablepharidophyta Okamoto & Inouye 2005 [Leucocrypta Cavalier-Smith 2015]
- Phylum Palpitophyta Tedersoo 2017
References
- ^ Adl, Sina M.; Bass, David; Lane, Christopher E.; Lukeš, Julius; Schoch, Conrad L.; Smirnov, Alexey; Agatha, Sabine; Berney, Cedric; Brown, Matthew W. (2018-09-26). "Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes". The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 66 (1): 4–119. doi:10.1111/jeu.12691. ISSN 1550-7408. PMC 6492006. PMID 30257078.
- ^ Adl SM, Bass D, Lane CE, Lukeš J, Schoch CL, Smirnov A, et al. (January 2019). "Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes". The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 66 (1): 4–119. doi:10.1111/jeu.12691. PMC 6492006. PMID 30257078.
- ^ Ruggiero, Michael A.; Gordon, Dennis P.; Orrell, Thomas M.; Bailly, Nicolas; Bourgoin, Thierry; Brusca, Richard C.; Cavalier-Smith, Thomas; Guiry, Michael D.; Kirk, Paul M. (2015-04-29). "A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms". PLOS ONE. 10 (4): e0119248. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1019248R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119248. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4418965. PMID 25923521.
- ^ Burki F, Roger AJ, Brown MW, Simpson AG (January 2020). "The New Tree of Eukaryotes". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 35 (1): 43–55. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2019.08.008. PMID 31606140.
- ^ Burki F; Kaplan M; Tikhonenkov DV; Zlatogursky V; Minh BQ; Radaykina LV; Smirnov A; Mylnikov AP; Keeling PJ (2016), "Untangling the early diversification of eukaryotes: a phylogenomic study of the evolutionary origins of Centrohelida, Haptophyta and Cryptista.", Proc Biol Sci, 283 (1823): 20152802, doi:10.1098/rspb.2015.2802, PMC 4795036, PMID 26817772
- ^ Burki, F; Inagaki, Y; Bråte, J; Archibald, J.; Keeling, P.; Cavalier-Smith, T; Sakaguchi, M; Hashimoto, T; Horak, A; Kumar, S; Klaveness, D; Jakobsen, K.S; Pawlowski, J; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K (2009). "Large-scale phylogenomic analyses reveal that two enigmatic protist lineages, Telonemia and Centroheliozoa, are related to photosynthetic chromalveolates" (Free full text). Genome Biology and Evolution. 1: 231–8. doi:10.1093/gbe/evp022. PMC 2817417. PMID 20333193.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith; Chao; Lewis (2015), "Multiple origins of Heliozoa from flagellate ancestors: New cryptist subphylum Corbihelia, superclass Corbistoma, and monophyly of Haptista, Cryptista, Hacrobia and Chromista", Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 93: 331–362, doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2015.07.004, PMID 26234272
- ^ Tedersoo, Leho (2017), "Proposal for practical multi-kingdom classification of eukaryotes based on monophyly and comparable divergence time criteria", bioRxiv, 2017, doi:10.1101/240929, S2CID 90691603
- ^ "Katablepharids".
External links
Wikispecies has information related to Cryptista.
