Norwegian Army: Difference between revisions
Sandbekken (talk | contribs) →References: fixed the references list |
|||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
== References == |
== References == |
||
<div class="small">< |
<div class="small"><references /></div> |
||
==External link== |
==External link== |
||
Revision as of 18:43, 13 April 2007
 |
| Components |
|---|
|
Army Navy (Coast Guard) Air Force Home Guard Cyber Defence Force |
| Ranks |
| Norwegian military ranks |
| Bugle calls |
| Bugle calls of the Norwegian Army |
| Armed Forces equipment |
|
Army equipment Naval ships (active) Norwegian military aircraft |

The Norwegian Army (Norwegian: Hæren) is Norway's military land force. It is part of the Norwegian Defence Force along with the Royal Norwegian Navy, the Royal Norwegian Air Force and the Norwegian Home Guard. Established in 1628, it currently has a peacetime strength of 7,500, and approximately 9,500 fully mobilized.[1]
The Army is mainly located in two areas, mid-Troms and the south-eastern part of the country, with other special units like the King's Guards and the border guards placed elsewhere.
Pre-WW2 History
The Norwegian Army dates back to Viking times, when it consisted of only the household forces of local kings and their allies. The present army was established by the Danish-Norwegian king Christian IV "to defend the kingdom against exterior dangers." This is still the primary mission of the Norwegian Army. The first great victory of the Norwegian Army came in 1808, when the Swedes attempted to invade Norway from the south, but were forced back by the forces of Prince Kristian August. The officer class was well represented in the Constitution in 1814, which included clauses providing for a Norwegian national army based on compulsory service. The Swedes responded to the Declaration of Independence with another invasion, and defeated the Norwegian Army decisively. The army lay dormant until 1905, when the Storting voted to separate from Sweden. War seemed inevitable, and 22,000 men were mobilized, but Norway achieved independence peacefully. During World War One Norway successfully pursued a policy of armed neutrality.
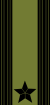
Insignia
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | Student officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | Generalløytnant | Generalmajor | Brigader | Oberst | Oberstløytnant | Major | Kaptein/ Rittmester |
Løytnant | Fenrik | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
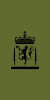
|
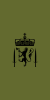
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sersjantmajor | Kommandérsersjant | Stabssersjant | Oversersjant | Sersjant 1. klasse | Sersjant | Korporal | Visekorporal 1. klasse | Visekorporal | Ledende menig | Menig | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Organization
The Army is organized along three functional lines:
- Commander, Army Forces (HSTY)
- Commander, Army Transformation and Doctrine Command (TRADOK)
- Commander, Army Ranger Command (HJK)
Subordinate commands
- 6th Division
- Army Response Force (FIST–H)
- Army Ranger Command (HJK)
- His Majesty the King's Guard (HMKG)
- Army Garrison Sør-Varanger (GSV)
- Army Garrison Porsanger (GP)
- Norwegian Military Academy (KS)
- Army Combat Arms Centre (KampUKS)
- Army Logistic Centre (LogUKS)
- Army Signal Centre (SBUKS)
- Norwegian Special Command (FSK)
Garrisons
- Heistadmoen - HV-03
- Jørstadmoen - FK KKIS
- Huseby leir - HMKG
- Rena leir - KAMPUKS, Telemark Bataljon HMKG and HJK
- Terningmoen - KAMPUKS
- Sessvollmoen - LOGUKS, FMPS, National Support Element and MUKS
- Skjold - Brig. N
- Setermoen - Brig. N
- Bardufoss - Brig. N
- Porsangermoen - Garnisonen i Porsanger
- Høybuktmoen - Garnisonen i Sør-Varanger
- Linderud - Tradok / Krigsskolen (Norwegian Military Academy)
Hand Weapons

- AG-3 - Norwegian version of the Heckler & Koch G3 Assault Rifle (To be replaced by the Heckler & Koch HK416 rifle.[3])
- Heckler & Koch G36 - Assault Rifle - Used in small numbers on abroad operations.
- P80 - Pistol Norwegian version of Glock 17.
- Heckler & Koch MP5 - Submachine gun.
- M72 LAW - Anti-tank rocket grenade.
- Våpensmia NM149 - Sniper rifle.
- Heckler & Koch MSG-90 - Sniper rifle.
- Barrett M82A1 - .50 Cal/12,7 mm high-powered heavy sniper rifle
- FN Minimi Para - Machine gun, only used by Army Ranger Command (HJK) units.
- Heckler & Koch USP - Pistol - Only used by Army Ranger Command (HJK) units.
- Diemaco C8 SFW - Assault Rifle - Only used by Army Ranger Command (HJK) units.
- Accuracy International L96 - Sniper Rifle - Only used by Army Ranger Command (HJK) units.
Crew Weapons
- MG3 - Machine gun
- Browning M2 - .50 Cal/12,7 mm Heavy machine gun
- Carl Gustav recoilless rifle
- ERYX - Anti-tank missile
- TOW2 - Anti-tank missile
- Javelin anti-tank missile, 90 launchers and 526 missiles, delivery from 2006.
- Bofors RBS 70 - Laser guided Surface-to-air missile
- NASAMS - Surface-to-air missile system (operated by the Royal Norwegian Air Force, but considered to be a part of the Army.)
Combat Vehicles
- Leopard 1A5NO Main Battle Tank (Norwegian version of the Leopard 1) (being replaced by the Leopard 2) (In use: 1966-)
- Leopard 2A4NO Main Battle Tank (Norwegian version of Leopard 2) (In use: 2001-)
- CV9030 Infantry fighting vehicle (In use 1999-)
- Sisu XA-186 Armoured Personnel Carrier (In use: 1983-)
- M113 Armored Personnel Carrier Of different types (In use: 1964-)
- M270 MLRS Multiple Rocket Launcher[1] on tracked and armoured chassis. (Now temporarily mothballed but being considered for reactivation in FY2007[2]).
- M 109 A3GN Self-Propelled Artillery (Norwegian version of M 109) (In use: 1969-)
- Iveco LMV Light Multirole Vehicle, similar to the Panther CLV (In use:2007-)
General-Purpose Vehicles
- Mercedes-Benz Geländewagen: a wide range of models, softskin, hardtop and armoured versions; MB 240 softskin most widely used
- Hägglunds Bv206, an unarmoured tracked vehicle often used for reconnaissance and command-and-control tasks
- Nissan Terrano II
- Toyota Land Cruiser
- Alvis Tactica
- Land Rover Wolf
- Scania P90 and 113 trucks
- Lynx 5900 and 6900 snowmobiles
- 62 Lynx Yeti Pro V800 Army snowmobiles
- Polaris 6WD ATV
- The army has recently bought 25 new Iveco LMV light-armored vehicles for patrol and reconnaissance tasks in connection with Norway's contribution to the ISAF force in Afghanistan, and has an option of buying 47 additional vehicles. The Iveco vehicles are intended to fill the span between the unarmored Geländewagens and the CV9030 IFVs previously operated by the army, after personell from the Telemark Bataljon made requests for lightly armoured vehicles after missions in Afghanistan. The first four Ivecos are now deployed to the Norwegian Camp Nidaros in support of ISAFs Quick Reaction Force in Mazar-e-Sharif, another 12 are to follow soon. [3] [4].
References
- ^ "Forsvarsnett: The Norwegian Army". Retrieved 2007-03-20.
- ^ a b "Militære grader" [Military ranks]. forsvaret.no (in Norwegian). Norwegian Armed Forces. 13 October 2023. Archived from the original on 26 November 2023. Retrieved 26 November 2023.
- ^ http://www.aftenposten.no/nyheter/iriks/article1733557.ece
