Pleural effusion: Difference between revisions
Kallimachus (talk | contribs) |
Kallimachus (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the pleural effusion. |
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the pleural effusion. |
||
Therapeutic aspiration may be sufficient; larger effusions may require insertion of an [[intercostal drain]] (either pigtail or surgical). When managing these chest tubes it is important to make sure the chest tubes do not become occluded or clogged. A clogged chest tube in the setting of continued production of fluid will result in residual fluid left behind when the chest tube is removed. This fluid can lead to complications such as hypoxia due to lung collapse from the fluid, or fibrothorax, late, when the space scars down. Repeated effusions may require chemical ([[talc]], [[bleomycin]], [[tetracycline]]/[[doxycycline]]) or surgical [[pleurodesis]], in which the two pleural surfaces are scarred to each other so that no fluid can accumulate between them. This is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a chest tube, then either mechanically abrading the pleura, or inserting the chemicals to induce a scar. This |
Therapeutic aspiration may be sufficient; larger effusions may require insertion of an [[intercostal drain]] (either pigtail or surgical). When managing these chest tubes it is important to make sure the chest tubes do not become occluded or clogged. A clogged chest tube in the setting of continued production of fluid will result in residual fluid left behind when the chest tube is removed. This fluid can lead to complications such as hypoxia due to lung collapse from the fluid, or fibrothorax, late, when the space scars down. Repeated effusions may require chemical ([[talc]], [[bleomycin]], [[tetracycline]]/[[doxycycline]]) or surgical [[pleurodesis]], in which the two pleural surfaces are scarred to each other so that no fluid can accumulate between them. This is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a chest tube, then either mechanically abrading the pleura, or inserting the chemicals to induce a scar. This requires the chest tube to stay in until the fluid drainage stops. This can be days to weeks and can require prolonged hospitilizations. If the chest tube becomes clogged fluid will be left behind and the pleurodesis will fail. |
||
Pleurodesis fails in as many as 30% of cases. An alternative is to place a Pleurex or Aspira Drainage Catheter. This is a 15Fr chest tube with a one way valve. Each day the patient or care givers connect it to a simple vacuum tube and remove from 600 cc to 1000 cc. This can be repeated daily. When not in use, the tube is capped. This allows patients to be outside the hospital. For patients with malignant pleural effusions, it allows them to continue chemotherapy, if indicated. Generally the tube is in about 30 days and then it is removed when the space undergoes a spontaneous pleurodesis. |
Pleurodesis fails in as many as 30% of cases. An alternative is to place a Pleurex or Aspira Drainage Catheter. This is a 15Fr chest tube with a one way valve. Each day the patient or care givers connect it to a simple vacuum tube and remove from 600 cc to 1000 cc. This can be repeated daily. When not in use, the tube is capped. This allows patients to be outside the hospital. For patients with malignant pleural effusions, it allows them to continue chemotherapy, if indicated. Generally the tube is in about 30 days and then it is removed when the space undergoes a spontaneous pleurodesis. |
||
Revision as of 00:38, 22 July 2010
| Pleural effusion | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Pulmonology |
Pleural effusion is excess fluid that accumulates in the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs. Excessive amounts of such fluid can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs during inspiration.
Types of fluids
Four types of fluids can accumulate in the pleural space:
- Serous fluid (hydrothorax)
- Blood (haemothorax)
- Chyle (chylothorax)
- Pus (pyothorax or empyema)
Diagnosis

Pleural effusion is usually diagnosed on the basis of medical history and physical exam, and confirmed by chest x-ray. Once accumulated fluid is more than 500 ml, there are usually detectable clinical signs in the patient, such as decreased movement of the chest on the affected side, dullness to percussion over the fluid, diminished breath sounds on the affected side, decreased vocal resonance and fremitus (though this is an inconsistent and unreliable sign), and pleural friction rub. Above the effusion, where the lung is compressed, there may be bronchial breathing and egophony. In large effusion there may be tracheal deviation away from the effusion. A systematic review (2009) published as part of the Rational Clinical Examination Series in the Journal of the American Medical Association showed that dullness to conventional percussion was most accurate for diagnosing pleural effusion (summary positive likelihood ratio, 8.7; 95% confidence interval, 2.2-33.8), while the absence of reduced tactile vocal fremitus made pleural effusion less likely (negative likelihood ratio, 0.21; 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.37).[1]
Chest radiographs acquired in the lateral decubitus position (with the patient lying on his side) are more sensitive, and can pick up as little as 50 ml of fluid. At least 300 ml of fluid must be present before upright chest films can pick up signs of pleural effusion (e.g., blunted costophrenic angles).
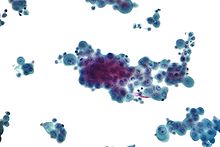
Once a pleural effusion is diagnosed, the cause must be determined. Pleural fluid is drawn out of the pleural space in a process called thoracentesis. A needle is inserted through the back of the chest wall in the sixth, seventh or eighth intercostal space on the midaxillary line, into the pleural space. The fluid may then be evaluated for the following:
- Chemical composition including protein, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), albumin, amylase, pH and glucose
- Gram stain and culture to identify possible bacterial infections
- Cell count and differential
- Cytopathology to identify cancer cells, but may also identify some infective organisms
- Other tests as suggested by the clinical situation - lipids, fungal culture, viral culture, specific immunoglobulins
Transudate vs. exudate: Light's criteria
| Transudate vs. exudate | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transudate | Exudate | |
| Main causes | ↑ hydrostatic pressure, ↓ colloid osmotic pressure |
Inflammation-Increased vascular permeability |
| Appearance | Clear[2] | Cloudy[2] |
| Specific gravity | < 1.012 | > 1.020 |
| Protein content | < 2.5 g/dL | > 2.9 g/dL[3] |
| fluid protein/ serum protein |
< 0.5 | > 0.5[4] |
| SAAG = Serum [albumin] - Effusion [albumin] |
> 1.2 g/dL | < 1.2 g/dL[5] |
| fluid LDH upper limit for serum |
< 0.6 or < 2⁄3 | > 0.6[3] or > 2⁄3[4] |
| Cholesterol content | < 45 mg/dL | > 45 |
| Radiodensity on CT scan | 2 to 15 HU[6] | 4 to 33 HU[6] |

The definitions of the terms "transudate" and "exudate" are the source of much confusion.
Transudative pleural effusions are defined as effusions that are caused by systemic factors that alter the pleural equilibrium, or Starling forces. The components of the Starling forces: hydrostatic pressure, permeability, oncotic pressure (effective pressure due to the composition of the pleural fluid and blood), are altered in many diseases e.g., left ventricular failure, renal failure, hepatic failure, and cirrhosis. Exudative pleural effusions, by contrast, are caused by alterations in local factors that influence the formation and absorption of pleural fluid (e.g., bacterial pneumonia, cancer, pulmonary embolism, and viral infection).[7]
An accurate diagnosis of the cause of the effusion, transudate versus exudate, relies on a comparison of the chemistries in the pleural fluid to those in the blood, using Light's criteria. According to Light's criteria (Light, et al. 1972), a pleural effusion is likely exudative if at least one of the following exists:[8]
- The ratio of pleural fluid protein to serum protein is greater than 0.5
- The ratio of pleural fluid LDH and serum LDH is greater than 0.6
- Pleural fluid LDH is greater than 0.7 times the normal upper limit for serum
Although Light's criteria are relatively accurate, twenty-five percent of patients with transudative pleural effusions are mistakenly identified by Light's criteria as having exudative pleural effusions. Therefore, if a patient identified by Light's criteria as having an exudative pleural effusion appears clinically to have a condition that usually produces transudative effusions, additional testing is needed. In such cases albumin levels in blood and pleural fluid are measured. If the difference between the albumin levels in the blood and the pleural fluid is greater than 1.2 g/dL (12 g/L), this suggests that the patient has a transudative pleural effusion[5]. However, pleural fluid testing is not perfect, and the final decision about whether a fluid is a transudate or an exudate is based not on chemical analysis of the fluid, but on accurate diagnosis of the disease that produces the fluid.
The traditional definitions of transudate as a pleural effusion due to systemic factors and an exudate as a pleural effusion due to local factors have been used since 1940 or earlier (Light et al, 1972). Previous to Light's landmark study, which was basd on work by Chandrasekhar, investigators unsuccessfully attempted to use other criteria, such as specific gravity, pH, and protein content of the fluid, to differentiate between transudates and exudates. Light's criteria are highly statistically sensitive for exudates (although not very statistically specific). More recent studies have examined other characteristics of pleural fluid that may help to determine whether the process producing the effusion is local (exudate) or systemic (transudate). The chart at right illustrates some of the results of these more recent studies. However, it should be borne in mind that Light's criteria are still the most widely used criteria.
The Rational Clinical Examination Series review found that bilateral effusions, symmetric and asymmetric, are the most common distribution in heart failure (60% of effusions in heart failure will be bilateral). When there is asymmetry in heart failure-associated pleural effusions (either unilateral or one side larger than the other), the right side is usually more involved than the left.[9]
Causes
Transudative
The most common causes of transudative pleural effusions in the United States are left ventricular failure, and cirrhosis (causing hepatic hydrothorax). Pulmonary embolisms were once thought to be transudative but have been recently shown to be exudative[10]
Exudative

Once identified as exudative, additional evaluation is needed to determine the cause of the excess fluid, and pleural fluid amylase, glucose, pH and cell counts are obtained.
- Pleural fluid amylase is elevated in cases of esophageal rupture, pancreatic pleural effusion, or cancer.
- Glucose is decreased with cancer, bacterial infections, or rheumatoid pleuritis.
- Pleural fluid pH is low in empyema (<7.2) and may be low in cancer.
- If cancer is suspected, the pleural fluid is sent for cytology. If cytology is negative, and cancer is still suspected, either a thoracoscopy, or needle biopsy[11] of the pleura may be performed.
- The fluid is also sent for Gram staining and culture, and, if suspicious for tuberculosis, examination for TB markers (adenosine deaminase > 45 IU/L, interferon gamma > 140 pg/mL, or positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for tuberculous DNA).
The most common causes of exudative pleural effusions are bacterial pneumonia, cancer (with lung cancer, breast cancer, and lymphoma causing approximately 75% of all malignant pleural effusions), viral infection, and pulmonary embolism.
Other/ungrouped
Other causes of pleural effusion include tuberculosis (though pleural fluid smears are rarely positive for AFB, this is the most common cause of pleural effusion in some developing countries), autoimmune disease such as systemic lupus erythematosus, bleeding (often due to chest trauma), chylothorax (most commonly caused by trauma), and accidental infusion of fluids.
Less common causes include esophageal rupture or pancreatic disease, intraabdominal abscess, rheumatoid arthritis, asbestos pleural effusion, Meigs syndrome (ascites and pleural effusion due to a benign ovarian tumor), and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Pleural effusions may also occur through medical/surgical interventions, including the use of medications (pleural fluid is usually eosinophilic), coronary artery bypass surgery, abdominal surgery, endoscopic variceal sclerotherapy, radiation therapy, liver or lung transplantation, and intra- or extravascular insertion of central lines.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the pleural effusion.
Therapeutic aspiration may be sufficient; larger effusions may require insertion of an intercostal drain (either pigtail or surgical). When managing these chest tubes it is important to make sure the chest tubes do not become occluded or clogged. A clogged chest tube in the setting of continued production of fluid will result in residual fluid left behind when the chest tube is removed. This fluid can lead to complications such as hypoxia due to lung collapse from the fluid, or fibrothorax, late, when the space scars down. Repeated effusions may require chemical (talc, bleomycin, tetracycline/doxycycline) or surgical pleurodesis, in which the two pleural surfaces are scarred to each other so that no fluid can accumulate between them. This is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a chest tube, then either mechanically abrading the pleura, or inserting the chemicals to induce a scar. This requires the chest tube to stay in until the fluid drainage stops. This can be days to weeks and can require prolonged hospitilizations. If the chest tube becomes clogged fluid will be left behind and the pleurodesis will fail.
Pleurodesis fails in as many as 30% of cases. An alternative is to place a Pleurex or Aspira Drainage Catheter. This is a 15Fr chest tube with a one way valve. Each day the patient or care givers connect it to a simple vacuum tube and remove from 600 cc to 1000 cc. This can be repeated daily. When not in use, the tube is capped. This allows patients to be outside the hospital. For patients with malignant pleural effusions, it allows them to continue chemotherapy, if indicated. Generally the tube is in about 30 days and then it is removed when the space undergoes a spontaneous pleurodesis.
See also
External links
- Medline Plus Article on Pleural Effusion
- Pleural Effusion Virtual Cancer Centre
- Pleural Effusion Images from MedPix
References
- ^ Wong CL, Holroyd-Leduc J, Straus SE Does this patient have a pleural effusion? JAMA. 2009 Jan 21;301(3):309-17 PMID: 19155458
- ^ a b The University of Utah • Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library > WebPath images > "Inflammation".
- ^ a b Heffner J, Brown L, Barbieri C (1997). "Diagnostic value of tests that discriminate between exudative and transudative pleural effusions. Primary Study Investigators". Chest. 111 (4): 970–80. doi:10.1378/chest.111.4.970. PMID 9106577.
- ^ a b Light R, Macgregor M, Luchsinger P, Ball W (1972). "Pleural effusions: the diagnostic separation of transudates and exudates". Ann Intern Med. 77 (4): 507–13. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-77-4-507. PMID 4642731.
- ^ a b Roth BJ, O'Meara TF, Gragun WH (1990). "The serum-effusion albumin gradient in the evaluation of pleural effusions". Chest. 98 (3): 546–9. doi:10.1378/chest.98.3.546. PMID 2152757. Cite error: The named reference "pmid2152757" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b Cullu, Nesat; Kalemci, Serdar; Karakas, Omer; Eser, Irfan; Yalcin, Funda; Boyaci, Fatma Nurefsan; Karakas, Ekrem (2013). "Efficacy of CT in diagnosis of transudates and exudates in patients with pleural effusion". Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology. 20: 116–20. doi:10.5152/dir.2013.13066. ISSN 1305-3825. PMC 4463296. PMID 24100060.
- ^ Light Richard W, "Chapter 257. Disorders of the Pleura and Mediastinum" (Chapter). Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J: Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17th Edition
- ^ Light R, Macgregor M, Luchsinger P, Ball W (1972). "Pleural effusions: the diagnostic separation of transudates and exudates". Ann Intern Med. 77 (4): 507–13. PMID 4642731.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wong CL, Holroyd-Leduc J, Straus SE Does this patient have a pleural effusion? JAMA. 2009 Jan 21;301(3):309-17 PMID: 19155458
- ^ Porcel et al Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine 2008, 14:337–342 PMID 18520269
- ^ A modified outer cannula can help thoracentesis after pleural biopsy. de Menezes Lyra R. Chest. 1997 Jul;112(1):296.[1]
