Lipoxygenase: Difference between revisions
Added to the pfambox |
m Inserted the more comprehensive term "eicosanoid" before the terms leukotriene & prostaglandin & the term "nonclassic eicosanoids" |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Biological function and classification== |
==Biological function and classification== |
||
These enzymes are most common in plants where they may be involved in a number of diverse aspects of plant physiology including growth and development, pest resistance, and senescence or responses to wounding<ref name="PUB00005925">{{cite journal |author=Vick BA, Zimmerman DC |title=Oxidative systems for the modification of fatty acids |journal= |volume=9 |issue= |pages=53–90 |year=1987}}</ref>. In mammals a number of lipoxygenases [[isozymes]] are involved in the metabolism of [[prostaglandins]] and [[ |
These enzymes are most common in plants where they may be involved in a number of diverse aspects of plant physiology including growth and development, pest resistance, and senescence or responses to wounding<ref name="PUB00005925">{{cite journal |author=Vick BA, Zimmerman DC |title=Oxidative systems for the modification of fatty acids |journal= |volume=9 |issue= |pages=53–90 |year=1987}}</ref>. In mammals a number of lipoxygenases [[isozymes]] are involved in the metabolism of [[eicosanoid]]s (such as [[prostaglandins]], [[leukotrienes]] and [[nonclassic eicosanoids]])<ref name="PUB00000045">{{cite journal |author=Needleman P, Turk J, Jakschik BA, Morrison AR, Lefkowith JB |title=Arachidonic acid metabolism |journal=Annu. Rev. Biochem. |volume=55 |issue= |pages=69–102 |year=1986 |pmid=3017195 |doi=10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000441}}</ref>. Sequence data is available for the following lipoxygenases: |
||
* Plant lipoxygenases ({{EC number|1.13.11.12}}{{InterPro|IPR001246}}). Plants express a variety of cytosolic isozymes as well as what seems to be a chloroplast isozyme<ref name="PUB00002887">{{cite journal |author=Tanaka K, Ohta |
* Plant lipoxygenases ({{EC number|1.13.11.12}}{{InterPro|IPR001246}}). Plants express a variety of cytosolic isozymes as well as what seems to be a chloroplast isozyme<ref name="PUB00002887">{{cite journal |author=Tanaka K, Ohta |
||
Revision as of 08:13, 22 August 2010
| Lipoxygenase | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Structure of rabbit reticulocyte 15S-lipoxygenase.[1] | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Lipoxygenase | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00305 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR013819 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00077 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 2sbl / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 87 | ||||||||||
| OPM protein | 1zq4 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Lipoxygenases (EC 1.13.11.-) are a family of iron-containing enzymes that catalyse the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4- pentadiene structure. It catalyses the following reaction:
- fatty acid + O2 = fatty acid hydroperoxide
Lipoxygenases are found in plants, animals and fungi. Products of lipoxygenases are involved in diverse cell functions.
Biological function and classification
These enzymes are most common in plants where they may be involved in a number of diverse aspects of plant physiology including growth and development, pest resistance, and senescence or responses to wounding[2]. In mammals a number of lipoxygenases isozymes are involved in the metabolism of eicosanoids (such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes and nonclassic eicosanoids)[3]. Sequence data is available for the following lipoxygenases:
- Plant lipoxygenases (EC 1.13.11.12InterPro: IPR001246). Plants express a variety of cytosolic isozymes as well as what seems to be a chloroplast isozyme[4].
- Mammalian arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase (EC 1.13.11.34InterPro: IPR001885).
- Mammalian arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase (EC 1.13.11.31InterPro: IPR001885).
- Mammalian erythroid cell-specific 15-lipoxygenase (EC 1.13.11.33InterPro: IPR001885).
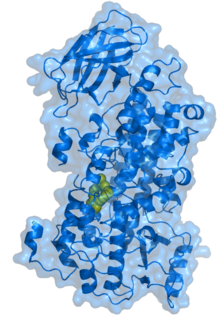
3D structure
The crystal structures of soybean and rabbit lipoxygenases are known. The protein consists of a small N-terminal PLAT domain and a major C-terminal catalytic domain (see Pfam link in this article), which contains the active site. In both plant and mammalian enzymes, the N-terminal domain contains an eight-stranded antiparallel β-barrel, but in the soybean lipoxygenases this domain is significantly larger than in the rabbit enzyme. The plant lipoxygenases can be enzymatically cleaved into two fragments which stay tightly associated while the enzyme remains active; separation of the two domains leads to loss of catalytic activity. The C-terminal (catalytic) domain consists of 18-22 helices and one (in rabbit enzyme) or two (in soybean enzymes) antiparallel β-sheets at the opposite end from the N-terminal β-barrel.
Active site
The iron atom in lipoxygenases is bound by four ligands, three of which are histidine residues[5]. Six histidines are conserved in all lipoxygenase sequences, five of them are found clustered in a stretch of 40 amino acids. This region contains two of the three zinc-ligands; the other histidines have been shown[6] to be important for the activity of lipoxygenases.
The two long central helices cross at the active site; both helices include internal stretches of π-helix that provide three histidine (His) ligands to the active site iron. Two cavities in the major domain of soybean lipoxygenase-1 (cavities I and II) extend from the surface to the active site. The funnel-shaped cavity I may function as a dioxygen channel; the long narrow cavity II is presumably a substrate pocket. The more compact mammalian enzyme contains only one boot-shaped cavity (cavity II). In soybean lipoxygenase-3 there is a third cavity which runs from the iron site to the interface of the β-barrel and catalytic domains. Cavity III, the iron site and cavity II form a continuous passage throughout the protein molecule.
The active site iron is coordinated by Nε of three conserved His residues and one oxygen of the C-terminal carboxyl group. In addition, in soybean enzymes the side chain oxygen of asparagine is weakly associated with the iron. In rabbit lipoxygenase, this Asn residue is replaced with His which coordinates the iron via Nδ atom. Thus, the coordination number of iron is either five or six, with a hydroxyl or water ligand to a hexacoordinate iron.
Biochemical classification
| EC 1.13.11.12 | lipoxygenase | (linoleate:oxygen 13-oxidoreductase) | linoleate + O2 = (9Z,11E,13S)-13-hydroperoxyoctadeca-9,11-dienoate |
| EC 1.13.11.31 | arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase | (arachidonate:oxygen 12-oxidoreductase) | arachidonate + O2 = (5Z,8Z,10E,12S,14Z)-12-hydroperoxyicosa-5,8,10,14-tetraenoate |
| EC 1.13.11.33 | arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase | (arachidonate:oxygen 15-oxidoreductase) | arachidonate + O2 = (5Z,8Z,11Z,13E,15S)-15-hydroperoxyicosa-5,8,11,13-tetraenoate |
| EC 1.13.11.34 | arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase | (arachidonate:oxygen 5-oxidoreductase) | arachidonate + O2 = leukotriene A4 + H2 |
| EC 1.13.11.40 | arachidonate 8-lipoxygenase | (arachidonate:oxygen 8-oxidoreductase) | arachidonate + O2 = (5Z,8R,9E,11Z,14Z)-8-hydroperoxyicosa-5,9,11,14-tetraenoate |
Soybean Lipoxygenase 1 exhibits the largest H/D kinetic isotope effect (KIE) on kcat (kH/kD) (81 near room temperature) so far reported for a biological system.
References
- ^ Choi J, Chon JK, Kim S, Shin W (2008). "Conformational flexibility in mammalian 15S-lipoxygenase: Reinterpretation of the crystallographic data". Proteins. 70 (3): 1023–32. doi:10.1002/prot.21590. PMID 17847087.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Vick BA, Zimmerman DC (1987). "Oxidative systems for the modification of fatty acids". 9: 53–90.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Needleman P, Turk J, Jakschik BA, Morrison AR, Lefkowith JB (1986). "Arachidonic acid metabolism". Annu. Rev. Biochem. 55: 69–102. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000441. PMID 3017195.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Tanaka K, Ohta
H, Peng YL, Shirano Y, Hibino T, Shibata D (1994). "A novel lipoxygenase from rice. Primary structure and specific expression upon incompatible infection with rice blast fungus". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (5): 3755–3761. PMID 7508918.
{{cite journal}}: line feed character in|author=at position 15 (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Boyington JC, Gaffney BJ, Amzel LM (1993). "The three-dimensional structure of an arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase". Science. 260 (5113): 1482–1486. doi:10.1126/science.8502991. PMID 8502991.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Steczko J, Donoho GP, Clemens JC, Dixon JE, Axelrod B (1992). "Conserved histidine residues in soybean lipoxygenase: functional consequences of their replacement". Biochemistry. 31 (16): 4053–4057. doi:10.1021/bi00131a022. PMID 1567851.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- LOX-DB - LipOXygenases DataBase
- Lipoxygenases iron-binding region in PROSITE
- PDB: 1YGE - structure of lipoxygenase-1 from soybean (Glycine max)
- PDB: 1IK3 - structure of soybean lipoxygenase-3 in complex with (9Z,11E,13S)-13-hydroperoxyoctadeca-9,11-dienoic acid
- PDB: 1LOX - structure of rabbit 15-lipoxygenase in complex with inhibitor
- UMich Orientation of Proteins in Membranes families/superfamily-87 - animal lipoxygenases
- Lipoxygenase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
