CORONA (satellite): Difference between revisions
Metricmike (talk | contribs) →Technology: Focal length normally expressed in mm, readability. |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==Technology== |
==Technology== |
||
[[File:Corona spysat camera system.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Diagram of "J-1" type stereo/panoramic constantly rotating Corona reconnaissance satellite camera system used on KH-4A missions from 1963 to 1969.]] |
[[File:Corona spysat camera system.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Diagram of "J-1" type stereo/panoramic constantly rotating Corona reconnaissance satellite camera system used on KH-4A missions from 1963 to 1969.]] |
||
The Corona satellites used special 70 millimeter [[film]] with a {{convert|24|in| |
The Corona satellites used special 70 millimeter [[film]] with a {{convert|24|in|mm|adj=on}} [[focal length]] camera.<ref>Yenne, p. 63; Jensen, p. 81.</ref> Manufactured by [[Kodak|Eastman Kodak]], the film was initially {{convert|0.0003|in|µm}} thick, with a resolution of 170 lines per {{convert|0.04|in|mm}} of film.<ref name="Drells462" /><ref>Brown, Stewart F. "America's First Eyes in Space." ''Popular Science.'' February 1996, p. 46.</ref> The [[Contrast (vision)|contrast]] was 2-to-1.<ref name="Drells462" /> (By comparison, the best aerial photography film produced in World War II could produce just 50 lines per {{convert|0.04|in|mm}} of film.)<ref name="Drells462" /> The [[acetate]]-based film was later replaced with a [[polyester]]-based film stock that was more durable in outer space.<ref name="Brown, Stewart F 1996, p. 46-47">Brown, Stewart F. "America's First Eyes in Space." ''Popular Science.'' February 1996, p. 46-47.</ref> The amount of film carried by the satellites varied over time. Initially, each satellite carried {{convert|8000|ft|m}} of film for each camera, for a total of {{convert|16000|ft|m}} of film.<ref name="Drells462">Drell, "Physics and U.S. National Security," p. S462.</ref> But a reduction in the thickness of the film stock allowed more film to be carried aloft.<ref name="Brown, Stewart F 1996, p. 46-47"/> The amount of film carried was doubled (both by reductions in film thickness and by the addition of additional film capsules) by the time the fifth generation of the satellite (the KH-5s) was built, to {{convert|16000|ft|m}} of film for each camera for a total of {{convert|32000|ft|m}} of film.<ref name="Peebles157">Peebles, p. 157.</ref> Most of the film shot was black and white. [[Infrared photography|Infrared film]] was used on mission 1104, and color film on missions 1105 and 1008. Color film proved to have lower resolution, however, and was never used again.<ref name="Olsen57" /> |
||
The cameras were manufactured by the [[Itek|Itek Corporation]].<ref>Yenne, p. 64.</ref> A {{convert|12|in|cm|adj=on}}, [[F-number|f/5]] [[triplet lens]] was designed for the cameras.<ref>Smith, p. 111-114.</ref> Each lens was {{convert|7|in|cm}} in diameter.<ref name="Drells462" /> They were quite similar to the [[Tessar]] lenses developed in Germany by [[Carl Zeiss AG|Zeiss]].<ref name="Lewis, p. 93">Lewis, p. 93.</ref> The cameras themselves were initially {{convert|5|ft|m}} long, but later extended to {{convert|9|ft|m}} in length.<ref>Monmonier, p. 24.</ref> Beginning with the KH-4 satellites, these lenses were replaced with [[Petzval lens|Petzval]] f/3.5 lens.<ref name="Olsen57" /> The lenses were panoramic, and moved through a 70° arc perpendicular to the direction of the orbit.<ref name="Drells462" /> A [[Wide-angle lens|panoramic lens]] was chosen because it could obtain a wider image. Although the best resolution was only obtained in the center of the image, this could be overcome by having the camera sweep automatically ("reciprocate") back and forth across 70° of arc.<ref>Day, Logsdon, and Latell, p. 192-196.</ref> The lens on the camera was constantly rotating, to counteract the blurring effect of the satellite moving over the planet.<ref name="Olsen57" /> |
The cameras were manufactured by the [[Itek|Itek Corporation]].<ref>Yenne, p. 64.</ref> A {{convert|12|in|cm|adj=on}}, [[F-number|f/5]] [[triplet lens]] was designed for the cameras.<ref>Smith, p. 111-114.</ref> Each lens was {{convert|7|in|cm}} in diameter.<ref name="Drells462" /> They were quite similar to the [[Tessar]] lenses developed in Germany by [[Carl Zeiss AG|Zeiss]].<ref name="Lewis, p. 93">Lewis, p. 93.</ref> The cameras themselves were initially {{convert|5|ft|m}} long, but later extended to {{convert|9|ft|m}} in length.<ref>Monmonier, p. 24.</ref> Beginning with the KH-4 satellites, these lenses were replaced with [[Petzval lens|Petzval]] f/3.5 lens.<ref name="Olsen57" /> The lenses were panoramic, and moved through a 70° arc perpendicular to the direction of the orbit.<ref name="Drells462" /> A [[Wide-angle lens|panoramic lens]] was chosen because it could obtain a wider image. Although the best resolution was only obtained in the center of the image, this could be overcome by having the camera sweep automatically ("reciprocate") back and forth across 70° of arc.<ref>Day, Logsdon, and Latell, p. 192-196.</ref> The lens on the camera was constantly rotating, to counteract the blurring effect of the satellite moving over the planet.<ref name="Olsen57" /> |
||
Revision as of 17:39, 22 February 2013


The Corona program was a series of American strategic reconnaissance satellites produced and operated by the Central Intelligence Agency Directorate of Science & Technology with substantial assistance from the U.S. Air Force. The Corona satellites were used for photographic surveillance of the Soviet Union (USSR), the People's Republic of China, and other areas beginning in June 1959 and ending in May 1972. The name of this program is sometimes seen as "CORONA", but its actual name "Corona" was a codeword, not an acronym.
The Corona satellites were designated KH-1, KH-2, KH-3, KH-4, KH-4A and KH-4B. KH stood for "Key Hole" or "Keyhole" (Code number 1010),[1] and the incrementing number indicated changes in the surveillance instrumentation, such as the change from single-panoramic to double-panoramic cameras. The "KH" naming system was first used in 1962 with KH-4 and the earlier numbers were retroactively applied. There were 144 Corona satellites launched, of which 102 returned usable photographs.
History and costs
Corona started under the name "Discoverer" as part of the WS-117L satellite reconnaissance and protection program of the US Air Force in 1956. The United States Air Force credits the Onizuka Air Force Station as being the "birthplace of the Corona program."[2] In May 1958, the Department of Defense directed the transfer of the WS-117L program to Advanced Research Projects Agency. In FY1958, WS-117L was funded by the AF at a level of US$108.2 million (inflation adjusted US$1.14 billion in 2024). For Discoverer, the Air Force and ARPA spent a combined sum of US$132.3 million in FY1959 (inflation adjusted US$1.38 billion in 2024) and US$101.2 million in FY1960 (inflation adjusted US$1.04 billion in 2024).[3]
The Corona project was pushed forward rapidly following the shooting down of a U-2 spy plane over the Soviet Union in May 1960.
Technology

The Corona satellites used special 70 millimeter film with a 24-inch (610 mm) focal length camera.[4] Manufactured by Eastman Kodak, the film was initially 0.0003 inches (7.6 μm) thick, with a resolution of 170 lines per 0.04 inches (1.0 mm) of film.[5][6] The contrast was 2-to-1.[5] (By comparison, the best aerial photography film produced in World War II could produce just 50 lines per 0.04 inches (1.0 mm) of film.)[5] The acetate-based film was later replaced with a polyester-based film stock that was more durable in outer space.[7] The amount of film carried by the satellites varied over time. Initially, each satellite carried 8,000 feet (2,400 m) of film for each camera, for a total of 16,000 feet (4,900 m) of film.[5] But a reduction in the thickness of the film stock allowed more film to be carried aloft.[7] The amount of film carried was doubled (both by reductions in film thickness and by the addition of additional film capsules) by the time the fifth generation of the satellite (the KH-5s) was built, to 16,000 feet (4,900 m) of film for each camera for a total of 32,000 feet (9,800 m) of film.[8] Most of the film shot was black and white. Infrared film was used on mission 1104, and color film on missions 1105 and 1008. Color film proved to have lower resolution, however, and was never used again.[9]
The cameras were manufactured by the Itek Corporation.[10] A 12-inch (30 cm), f/5 triplet lens was designed for the cameras.[11] Each lens was 7 inches (18 cm) in diameter.[5] They were quite similar to the Tessar lenses developed in Germany by Zeiss.[12] The cameras themselves were initially 5 feet (1.5 m) long, but later extended to 9 feet (2.7 m) in length.[13] Beginning with the KH-4 satellites, these lenses were replaced with Petzval f/3.5 lens.[9] The lenses were panoramic, and moved through a 70° arc perpendicular to the direction of the orbit.[5] A panoramic lens was chosen because it could obtain a wider image. Although the best resolution was only obtained in the center of the image, this could be overcome by having the camera sweep automatically ("reciprocate") back and forth across 70° of arc.[14] The lens on the camera was constantly rotating, to counteract the blurring effect of the satellite moving over the planet.[9]
The first Corona satellites had a single camera, but a two-camera system was quickly implemented.[15] The front camera was tilted 15° forward, and the rear camera tilted 15° aft, so that a stereoscopic image could be obtained.[5] Later in the program, the satellite employed three cameras.[15] The third camera was employed to take "index" photographs of the objects being stereographically filmed.[16] The J-3 camera system, first deployed in 1967, placed the camera in a drum. This "rotator camera" (or drum) moved back and forth, eliminating the need to move the camera itself on a reciprocating mechanism.[17] The drum permitted the use of up to two filters and as many as four different exposure slits, greatly improving the variability of images that Corona could take.[18] The first cameras could resolve images on the ground down to 40 feet (12 m) in diameter. Improvements in the imaging system were rapid, and the KH-3 missions could see objects 10 feet (3.0 m) in diameter. Later missions would be able to resolve objects just 5 feet (1.5 m) in diameter.[19] A single mission was completed with a 1 foot (0.30 m) resolution but the limited field of view was determined to be detrimental to the mission. 3 feet (0.91 m) resolution was found to be the optimum resolution for quality of image and field of view.
The initial Corona missions suffered from mysterious border fogging and bright streaks which appeared irregularly on the returned film. Eventually, a team of scientists and engineers from the project and from academia (among them Luis Alvarez, Sidney Beldner, Malvin Ruderman, and Sidney Drell) determined that electrostatic discharges (called corona discharges) caused by some of the components of the cameras were exposing the film.[20][21] Corrective measures included better grounding of the components, improved film rollers that did not generate static electricity, improved temperature controls, and a cleaner internal environment.[21] Although improvements were made to reduce the corona, the final solution was to load the film canisters with a full load of film, feed the unexposed film through the camera onto the take-up reel with no exposure. This unexposed film was then processed and inspected for corona. If none was found or the corona observed was within acceptable levels, the canisters were certified for use and loaded with fresh film for a launch mission.

The first satellites in the program orbited at altitudes 100 miles (160 km) above the surface of the Earth, although later missions orbited even lower at 75 miles (121 km)).[9] Originally, Corona satellites were designed to spin along their main axis so that the satellite would remain stable. Cameras would take photographs only when pointed at the Earth. The Itek camera company, however, proposed to stabilize the satellite along all three axes—keeping the cameras permanently pointed at the earth.[12] Beginning with the KH-3 version of the satellite, a horizon camera took images of several key stars.[16] A sensor used the satellite's side thruster rockets to align the rocket with these "index stars," so that it was correctly aligned with the Earth and the cameras pointed in the right direction.[22] Beginning in 1967, two horizon cameras were used. This system was known as the Dual Improved Stellar Index Camera (DISIC).[18]
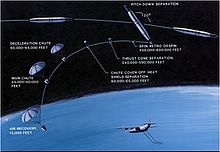
Film was retrieved from orbit via a reentry capsule (nicknamed "film bucket"), designed by General Electric, which separated from the satellite and fell to earth.[23] After the fierce heat of reentry was over, the heat shield surrounding the vehicle was jettisoned at 60,000 feet (18 km) and parachutes deployed.[24] The capsule was intended to be caught in mid-air by a passing airplane[25] towing an airborne claw which would then winch it aboard, or it could land at sea.[26] A salt plug in the base would dissolve after two days, allowing the capsule to sink if it was not picked up by the United States Navy.[27] After Reuters reported on a reentry vehicle's accidental landing and discovery by Venezuelan farmers in mid-1964, capsules were no longer labeled "Secret" but offered a reward in eight languages for their return to the United States.[28] Beginning with flight number 69, a two-capsule system was employed.[20] This also allowed the satellite to go into passive (or "zombie") mode, shutting down for as many as 21 days before taking images again.[8] Beginning in 1963, another improvement was "Lifeboat", a battery-powered system that allowed for ejection and recovery of the capsule in case power failed.[29][30] The film was processed at Eastman Kodak's Hawkeye facility in Rochester, New York.[31]
Coronas were launched by a Thor-Agena rocket, which used a Thor first stage and an Agena booster (which served as the second stage of the rocket lifting the Corona into orbit).[32] With the implementation of the J-1 camera system in 1963, a Thorad rocket was used for the first stage, leading to large improvements in launch reliability.[29] Later launches were made using the Thrust Augmented Thor (TAT).[33] Maneuvering rockets were also added to the satellite beginning in 1963. These were different from the attitude stabilizing thrusters which had been incorporated from the beginning of the program. Corona orbited in very low orbits to enhance resolution of its camera system. But at perigee (the lowest point in the orbit), Corona endured drag from the Earth's atmosphere. In time, this could cause its orbit to decay and force the satellite to re-enter the atmosphere prematurely. The new maneuvering rockets were designed to boost Corona into a higher orbit, and lengthen the mission time even if low perigees were used.[34] For use during unexpected crises, the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) kept a Corona in "R-7" status, meaning ready for launch in seven days. By summer 1965 NRO was able to maintain Corona for launch within one day.[35]
The procurement and maintenance of the Corona satellites was managed by the Central Intelligence Agency, which used cover arrangements lasting from April 1958 to 1969 to get access to the Palo Alto plant of the Hiller Helicopter Corporation for the production.[36] At this facility, the rocket's second stage Agena, the cameras, film cassettes, and reentry capsule were assembled and tested before shipment to Vandenberg Air Force Base.[37] In 1969, assembly duties were relocated to the Lockheed facilities in Sunnyvale, California.[38] (The NRO was worried that, as Corona was phased out, skilled technicians worried about their jobs would quit the program—leaving Corona without staff. The move to Sunnyvale ensured that enough skilled staff would be available.)
The decisions regarding what to photograph were made by the Corona Target Program. Corona satellites were placed into near-polar orbits.[19] This software, run by an on-board computer, was programmed to operate the cameras based on the intelligence targets to be imaged, the weather, the satellite's operational status, and what images the cameras had already captured.[39] Ground control for Corona satellites was initially conduct from Stanford Industrial Park, an industrial park on Page Mill Road in Palo Alto, California. It was later moved to Sunnyvale Air Force Base near Sunnyvale, California.[40]
Corona launches with system types
Below is a list of Corona launches, as compiled by the United States Geological Survey.[41] This table lists government's designation of each type of satellite (C, C-prime, J-1, etc.), the resolution of the camera, and a description of the camera system.
| Time period | No. | Nickname | Resolution | Notes | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jun 1959– Sep 1960 | KH-1 | "Corona", C | 7.5 m | First series of American imaging spy satellites. Each satellite carried a single panoramic camera and a single return vehicle. | 10 systems; 1 recovery. |
| Oct 1960– Oct 1961 | KH-2 | Corona′, C′ (or "C-prime")* | 7.5 m | Single panoramic camera and a single return vehicle. | 7 systems; 4 recoveries. |
| Aug 1961– Jan 1962 | KH-3 | Corona‴, C‴ (or "C-triple-prime")* | 7.5 m | Single panoramic camera and a single return vehicle. | 9 systems; 5 recoveries. |
| Feb 1962- Dec 1963 | KH-4 | Corona-M, Mural | 7.5 m | Film return. Two panoramic cameras. | 26 systems; 20 recoveries. |
| Aug 1963- Oct 1969 | KH-4A | Corona J-1 | 2.75 m | Film return with two reentry vehicles and two panoramic cameras. Large volume of imagery. | 52 systems; 94 recoveries. |
| Sep 1967- May 1972 | KH-4B | Corona J-3 | 1.8 m | Film return with two reentry vehicles and two panoramic rotator cameras. | 17 systems; 32 recoveries. |
| Feb 1961- Aug 1964 | KH-5 | Argon | 140 m | Low-resolution mapping missions; single frame camera. | 12 systems; 5 recoveries. |
| Mar 1963- July 1963 | KH-6 | Lanyard | 1.8 m | Experimental camera in a short-lived program. | 3 systems; 2 recoveries. |
*(The stray "quote marks" are the original designations of the first three generations of cameras.)
Discoverer


The first dozen or more Corona satellites and their launches were cloaked with disinformation as being part of a space technology development program called the Discoverer program. The first test launches for the Corona/Discoverer were carried out early in 1959. The capsule of Discoverer 2 might have been recovered by the Soviets, after landing on Spitsbergen Island.[37] The first Corona launch containing a camera was carried out in June 1959 with the cover name Discoverer 4. This was a 750 kilogram satellite launched by a Thor-Agena rocket.
The return capsule of the Discoverer 13 mission, which launched August 10, 1960, was successfully recovered the next day.[42] This was the first time that any object had been recovered successfully from orbit. After the mission of Discoverer 14, launched on August 18, 1960, its film bucket was successfully retrieved two days later by a C-119 Flying Boxcar transport plane. This was the first successful return of photographic film from orbit. In comparison, Sputnik 5 was launched into orbit on August 19, 1960, one day after the launch of Discoverer 14. Sputnik 5 was a biosatellite that took into orbit the two Soviet space dogs, Belka and Strelka, and then safely returned them to the Earth .[43]
At least two launches of Discoverers were used to test satellites for the Missile Defense Alarm System (MIDAS), an early missile-launch-detection program that used infrared cameras to detect the heat signature of rockets launching to orbit.[citation needed]
The Corona film bucket was later adapted for the KH-7 GAMBIT satellite, which took higher resolution photos.
The last launch under the Discoverer cover name was Discoverer 38 on February 26, 1962. Its bucket was successfully recovered in midair during the 65th orbit (the 13th recovery of a bucket; the ninth one in midair).[44] Following this last use of the Discoverer name, the remaining launches of Corona satellites were entirely top secret. The last Corona launch was on May 25, 1972. The project was abandoned after a Soviet Navy submarine was detected waiting beneath a Corona mid-air retrieval zone in the Pacific Ocean. The best sequence of Corona missions was from 1966 to 1971, when there were 32 consecutive successful missions, including film recoveries.
An alternative program to the Corona program was named SAMOS. This program included several types of satellite which used a different photographic method. This involved capturing an image on photographic film, developing the film on board the satellite and then scanning the image electronically. The image was then transmitted via telemetry to ground stations. The Samos E-1 and E-2 satellite programs used this system, but they were not able to take very many pictures and then relay them to the ground stations each day. Two later versions of the Samos program, such as the E-5 and the E-6, used the bucket-return approach, but neither of these programs carried out any successful missions.
ELINT subsatellites
Nine of the KH-4A and KH-4B missions included ELINT subsatellites, which were launched into a higher orbit.[45][46]
Declassification
The Corona program was officially classified top secret until 1992. Then, on February 22, 1995, the photos taken by the Corona satellites, and also by two contemporary programs (Argon and KH-6 Lanyard) were declassified under an Executive Order signed by President Bill Clinton.[47] The further review by photo experts of the "obsolete broad-area film-return systems other than Corona" mandated by President Clinton's order led to the declassification in 2002 of the photos from the KH-7 and the KH-9 low-resolution cameras.[48]
The declassified imagery has since been used by a team of scientists from the Australian National University to locate and explore ancient habitation sites, pottery factories, megalithic tombs, and Palaeolithic archaeological remains in northern Syria.[49][50]
The "CORONA Digital Atlas of the Middle East Project" hosts a large number of KH-4B imagery where users can view and download spatially corrected images.
Launches
| Mission No. | Cover Name | Launch Date | NSSDC ID No. | Alt. Name | Camera | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R&D | Discoverer | 21 Jan 1959 | 1959-E01 | 1959-E01 | none | Mission Failed. Failed to achieve orbit |
| R&D | Discoverer 1 | 28 Feb 1959 | 1959-002A | 1959 BET | none | First object in polar orbit |
| R&D | Discoverer 2 | 13 Apr 1959 | 1959-003A | 1959 GAM | none | First three-axis stabilized satellite; capsule recovery failed |
| R&D | Discoverer 3 | 03 Jun 1959 | DISCOV3 | 1959-F02 | none | Mission failed. Failed to achieve orbit |
| 9001 | Discoverer 4 | 25 Jun 1959 | DISC4 | 1959-U01 | KH-1 | Mission failed. Failed to achieve orbit. |
| 9002 | Discoverer 5 | 13 Aug 1959 | 1959-005A | 1959 EPS 1 | KH-1 | Mission failed. Power supply failure. No recovery. |
| 9003 | Discoverer 6 | 19 Aug 1959 | 1959-006A | 1959 ZET | KH-1 | Mission failed. Retro rockets malfunctioned negating recovery. |
| 9004 | Discoverer 7 | 07 Nov 1959 | 1959-010A | 1959 KAP | KH-1 | Mission failed. Failed to achieve orbit. |
| 9005 | Discoverer 8 | 20 Nov 1959 | 1959-011A | 1959 LAM | KH-1 | Mission failed. Eccentric orbit negating recovery. |
| 9006 | Discoverer 9 | 04 Feb 1960 | DiSC9 | 1960-F01 | KH-1 | Mission failed. Failed to achieve orbit. |
| 9007 | Discoverer 10 | 19 Feb 1960 | DISC10 | 1960-F02 | KH-1 | Mission failed. Destroyed just after launch due to erratic attitude. |
| 9008 | Discoverer 11 | 15 Apr 1960 | 1960-004A | 1960 DEL | KH-1 | Mission failed. Attitude control system malfunctioned. |
| R&D | Discoverer 12 | 29 Jun 1960 | DISC12 | 1960-F08 | none | Failed to orbit |
| R&D | Discoverer 13 | 10 Aug 1960 | 1960-008A | 1960 THE | none | Tested capsule recovery system; first successful capture. |
| 9009 | Discoverer 14 | 18 Aug 1960 | 1960-010A | 1960 KAP | KH-1 | First successful recovery of IMINT from space. Cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 9010 | Discoverer 15 | 13 Sep 1960 | 1960-012A | 1960 MU | KH-1 | Mission failed. Attained orbit successfully. Capsule sank prior to retrieval. |
| 9011 | Discoverer 16 | 26 Oct 1960 | 1960-F15 | 1960-F15 | KH-2 | Mission failed. Satellite failed to separate from booster. Failed to achieve orbit. |
| 9012 | Discoverer 17 | 12 Nov 1960 | 1960-015A | 1960 OMI | KH-2 | Mission failed. Obtained orbit successfully. Film separated before any camera operation leaving only 1.7 ft (0.52 m) of film in capsule. |
| 9013 | Discoverer 18 | 07 Dec 1960 | 1960-018A | 1960 SIG | KH-2 | First successful mission employing KH-2 camera system. |
| RM-1 | Discoverer 19 | 20 Dec 1960 | 1960-019A | 1960 TAU | none | Test of Midas missile-detection system |
| 9014A | Discoverer 20 | 17 Feb 1961 | 1961-005A | 1961 EPS 1 | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| RM-2 | Discoverer 21 | 18 Feb 1961 | 1961-006A | 1961 ZET | none | Test of restartable rocket engine |
| 9015 | Discoverer 22 | 30 Mar 1961 | DISC22 | 1961-F02 | KH-2 | Mission failed. Second stage failed to obtain orbital velocity. |
| 9016A | Discoverer 23 | 08 Apr 1961 | 1961-011A | 1961 LAM 1 | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9018A | Discoverer 24 | 16 Jun 1961 | DISC24 | 1961-F05 | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9017 | Discoverer 25 | 16 Jun 1961 | 1961-014A | 1961 XI 1 | KH-2 | Capsule recovered from water on orbit 32. Streaks throughout film. |
| 9019 | Discoverer 26 | 07 Jul 1961 | 1961-016A | 1961 PI | KH-2 | Main camera malfunctioned on pass 22. |
| 9020A | Discoverer 27 | 21 Jul 1961 | DISC27 | 1961-F07 | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9021 | Discoverer 28 | 03 Aug 1961 | DISC28 | 1961-F08 | KH-2 | Mission failed. No orbit. Satellite guidance system failed. |
| 9022 | Discoverer 30 | 12 Sep 1961 | 1961-024A | 1961 OME 1 | KH-3 | Best mission to date. Same out-of-focus condition as in 9023. |
| 9023 | Discoverer 29 | 30 Aug 1961 | 1961-023A | 1961 PSI | KH-3 | First use of KH-3 camera system. All frames out of focus. |
| 9024 | Discoverer 31 | 17 Sep 1961 | 1961-026A | 1961 A BET | KH-3 | Mission failed. Power failure and loss of control gas on orbit 33. Capsule was not recovered. |
| 9025 | Discoverer 32 | 13 Oct 1961 | 1961-027A | 1961 A GAM 1 | KH-3 | Capsule recovered on orbit 18. 96% of film out of focus. |
| 9026 | Discoverer 33 | 23 Oct 1961 | DISC33 | 1961-F10 | KH-3 | Mission failed. Satellite failed to separate from Thor booster. No orbit. |
| 9027 | Discoverer 34 | 05 Nov 1961 | 1961-029A | 1961 A EPS 1 | KH-3 | Mission failed. Improper launch angle resulted in extreme orbit. Gas valve failed |
| 9028 | Discoverer 35 | 15 Nov 1961 | 1961-030A | 1961 A ZET 1 | KH-3 | All cameras operated satisfactorily. Grainy emulsion noted. |
| 9029 | Discoverer 36 | 12 Dec 1961 | 1961-034A | 1961 A KAP 1 | KH-3 | Best mission to date. Launch carried OSCAR 1 to orbit. |
| 9030 | Discoverer 37 | 13 Jan 1962 | DISC37 | 1962-F01 | KH-3 | Mission failed. No orbit. |
| 9031 | Discoverer 38 | 27 Feb 1962 | 1962-005A | 1962 EPS 1 | KH-4 | First mission of the KH-4 series. Much of film slightly out of focus. |
| 9032 | Discoverer 39 | 18 Apr 1962 | 1962-011A | 1962 LAM 1 | KH-4 | Best mission to date. |
| 9033 | FTV 1125 | 28 Apr 1962 | 1962-017A | 1962 RHO 1 | KH-4 | Mission failed. Parachute ejector squibs holding parachute container cover failed to fire. No recovery. |
| 9034A | FTV 1126 | 15 May 1962 | 1962-018A | 1962 SIG 1 | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9035 | FTV 1128 | 30 May 1962 | 1962-021A | 1962 PHI 1 | KH-4 | Slight corona static on film. |
| 9036 | FTV 1127 | 02 Jun 1962 | 1962-022A | 1962 CHI 1 | KH-4 | Mission failed. During air catch. Launch carried OSCAR 2 to orbit. |
| 9037 | FTV 1129 | 23 Jun 1962 | 1962-026A | 1962 A BET | KH-4 | Corona static occurs on some film. |
| 9038 | FTV 1151 | 28 Jun 1962 | 1962-027A | 1962 A GAM | KH-4 | Severe corona static. |
| 9039 | FTV 1130 | 21 Jul 1962 | 1962-031A | 1962 A ETA | KH-4 | Aborted after 6 photo passes. Heavy corona and radiation fog. |
| 9040 | FTV 1131 | 28 Jul 1962 | 1962-032A | 1962 A THE | KH-4 | No filters on slave horizon cameras. Heavy corona and radiation fog. |
| 9041 | FTV 1152 | 02 Aug 1962 | 1962-034A | 1962 A KAP 1 | KH-4 | Severe corona and radiation fog. |
| 9042A | FTV 1132 | 01 Sep 1962 | 1962-044A | 1962 A UPS | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9043 | FTV 1133 | 17 Sep 1962 | 1962-046A | 1962 A CHI | KH-4 | placed in highly eccentric orbit (207 km x 670 km), caspule called down after one day, film suffered severe radiation fog due to SAA crossing[51][52][53] |
| 9044 | FTV 1153 | 29 Aug 1962 | 1962-042A | 1962 A SIG | KH-4 | Erratic vehicle attitude. Radiation fog minimal. |
| 9045 | FTV 1154 | 29 Sep 1962 | 1962-050A | 1962 B BET | KH-4 | First use of stellar camera |
| 9046A | FTV 1134 | 09 Oct 1962 | 1962-053A | 1962 B EPS | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9047 | FTV 1136 | 05 Nov 1962 | 1962-063A | 1962 B OMI | KH-4 | Camera door malfunctioned |
| 9048 | FTV 1135 | 24 Nov 1962 | 1962-065A | 1962 B RHO | KH-4 | Some film exposed through base. |
| 9049 | FTV 1155 | 04 Dec 1962 | 1962-066A | 1962 B SIG | KH-4 | Mission failed. During air catch chute tore |
| 9050 | FTV 1156 | 14 Dec 1962 | 1962-069A | 1962 B PHI | KH-4 | Best mission to date. |
| 9051 | OPS 0048 | 07 Jan 1963 | 1963-002A | 1963-002A | KH-4 | Erratic vehicle attitude. Frame ephemeris not created. |
| 9052 | OPS 0583 | 28 Feb 1963 | 1963-F02 | 1963-F02 | KH-4 | Mission failed. Destroyed by range safety officer |
| 9053 | OPS 0720 | 01 Apr 1963 | 1963-007A | 1963-007A | KH-4 | Best imagery to date. |
| 9054 | OPS 0954 | 12 Jun 1963 | 1963-019A | 1963-019A | KH-4 | Some imagery seriously affected by corona. |
| 9055A | OPS 1008 | 26 Apr 1963 | 1963-F07 | 1963-F07 | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9056 | OPS 0999 | 26 Jun 1963 | 1963-025A | 1963-025A | KH-4 | Experimental camera carried. Film affected by light leaks. |
| 9057 | OPS 1266 | 19 Jul 1963 | 1963-029A | 1963-029A | KH-4 | Best mission to date. |
| 9058A | OPS 1561 | 29 Aug 1963 | 1963-035A | 1963-035A | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9059A | OPS 2437 | 29 Oct 1963 | 1963-042A | 1963-042A | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9060 | OPS 2268 | 09 Nov 1963 | 1963-F14 | 1963-F14 | KH-4 | Mission failed. No orbit. |
| 9061 | OPS 2260 | 27 Nov 1963 | 1963-048A | 1963-048A | KH-4 | Mission failed. Return capsule separated from satellite but remained in orbit. |
| 9062 | OPS 1388 | 21 Dec 1963 | 1963-055A | 1963-055A | KH-4 | Corona static fogged much of film. |
| 9065A | OPS 2739 | 21 Aug 1964 | 1964-048A | 1964-048A | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 9066A | OPS 3236 | 13 Jun 1964 | 1964-030A | 1964-030A | KH-5 | See KH-5 |
| 1001 | OPS 1419 | 24 Aug 1963 | 1963-034A | 1963-034A | KH-4A | First mission of KH-4A. Some film was fogged. Two buckets but 1001-2 was never recovered. |
| 1002 | OPS 1353 | 23 Sep 1963 | 1963-037A | 1963-037A | KH-4A | Severe light leaks |
| 1003 | OPS 3467 | 24 Mar 1964 | 1964-F04 | 1964-F04 | KH-4A | Mission failed. Guidance system failed. No orbit. |
| 1004 | OPS 3444 | 15 Feb 1964 | 1964-008A | 1964-008A | KH-4A | Main cameras operated satisfactorily. Minor degradations due to static and light leaks. |
| 1005 | OPS 2921 | 27 Apr 1964 | 1964-022A | 1964-022A | KH-4A | Mission failed. Recovery vehicle impacted in Venezuela. |
| 1006 | OPS 3483 | 04 Jun 1964 | 1964-027A | 1964-027A | KH-4A | Highest quality imagery attained to date from the KH-4 system. |
| 1007 | OPS 3754 | 19 Jun 1964 | 1964-032A | 1964-032A | KH-4A | Out-of-focus area on some film. |
| 1008 | OPS 3491 | 10 Jun 1964 | 1964-037A | 1964-037A | KH-4A | Cameras operated satisfactorily |
| 1009 | OPS 3042 | 05 Aug 1964 | 1964-043A | 1964-043A | KH-4A | Cameras operated successfully. |
| 1010 | OPS 3497 | 14 Sep 1964 | 1964-056A | 1964-056A | KH-4A | Small out of focus areas on both cameras at random times throughout the mission. |
| 1011 | OPS 3333 | 05 Oct 1964 | 1964-061A | 1964-061A | KH-4A | Primary mode of recovery failed on second portion of the mission (1011-2). Small out of focus areas present at random on both cameras. |
| 1012 | OPS 3559 | 17 Oct 1964 | 1964-067A | 1964-067A | KH-4A | Vehicle attitude became erratic on the second portion of the mission necessitating an early recovery. |
| 1013 | OPS 5434 | 02 Nov 1964 | 1964-071A | 1964-071A | KH-4A | Program anomaly occurred immediately after launch when both cameras operated for 417 frames. Main cameras ceased operation on rev 52D of first portion of mission negating second portion. About 65% of aft camera film is out of focus. |
| 1014 | OPS 3360 | 18 Nov 1964 | 1964-075A | 1964-075A | KH-4A | Cameras operated successfully. |
| 1015 | OPS 3358 | 19 Dec 1964 | 1964-085A | 1964-085A | KH-4A | Discrepancies in planned and actual coverage due to telemetry problems during the first 6 revolutions. Small out-of-focus areas on film from aft camera. |
| 1016 | OPS 3928 | 15 Jan 1965 | 1965-002A | 1965-002A | KH-4A | Smearing of highly reflective images due to reflections within camera. |
| 1017 | OPS 4782 | 25 Feb 1965 | 1965-013A | 1965-013A | KH-4A | Capping shutter malfunction occurred during last 5 passes of mission. |
| 1018 | OPS 4803 | 25 Mar 1965 | 1965-026A | 1965-026A | KH-4A | Cameras operated successfully. First KH-4A reconnaissance system to be launched into a retrograde orbit. |
| 1019 | OPS 5023 | 29 Apr 1965 | 1965-033A | 1965-033A | KH-4A | Cameras operated successfully. Malfunction in recovery mode on 1019-2 negated recovery. |
| 1020 | OPS 8425 | 09 Jun 1965 | 1965-045A | 1965-045A | KH-4A | All cameras operated satisfactorily. Erratic attitude caused an early recovery after the second day of 1020-2. |
| 1021 | OPS 8431 | 18 May 1965 | 1965-037A | 1965-037A | KH-4A | Aft camera ceased operation on pass 102. |
| 1022 | OPS 5543 | 19 Jun 1965 | 1965-057A | 1965-057A | KH-4A | All cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 1023 | OPS 7208 | 17 Aug 1965 | 1965-067A | 1965-067A | KH-4A | Program anomaly caused the fore camera to cease operation during revolutions 103-132. |
| 1024 | OPS 7221 | 22 Sep 1965 | 1965-074A | 1965-074A | KH-4A | All cameras operated satisfactorily. Cameras not operated on passes 88D-93D. |
| 1025 | OPS 5325 | 05 Oct 1965 | 1965-079A | 1965-079A | KH-4A | Main cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 1026 | OPS 2155 | 28 Oct 1965 | 1965-086A | 1965-086A | KH-4A | All cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 1027 | OPS 7249 | 09 Dec 1965 | 1965-102A | 1965-102A | KH-4A | Erratic attitude necessitated recovery after two days of operation. All cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 1028 | OPS 4639 | 24 Dec 1965 | 1965-110A | 1965-110A | KH-4A | Cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 1029 | OPS 7291 | 02 Feb 1966 | 1966-007A | 1966-007A | KH-4A | Both panoramic cameras were operational throughout. |
| 1030 | OPS 3488 | 09 Mar 1966 | 1966-018A | 1966-018A | KH-4A | All cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 1031 | OPS 1612 | 07 Apr 1966 | 1966-029A | 1966-029A | KH-4A | The aft-looking camera malfunctioned after the recovery of bucket 1. No material was received in bucket 2 (1031-2). |
| 1032 | OPS 1508 | 3 May 1966 | 1966-F05A | 1966-F05 | KH-4A | Mission failed. Vehicle failed to achieve orbit. |
| 1033 | OPS 1778 | 24 May 1966 | 1966-042A | 1966-042A | KH-4A | The stellar camera shutter of bucket 2 remained open for approximately 200 frames. |
| 1034 | OPS 1599 | 21 Jun 1966 | 1966-055A | 1966-055A | KH-4A | Failure of velocity altitude programmer produced poor imagery after revolution 5. |
| 1035 | OPS 1703 | 20 Sep 1966 | 1966-085A | 1966-085A | KH-4A | All cameras operated satisfactorily. First mission flown with pan geometry modification. |
| 1036 | OPS 1545 | 09 Aug 1966 | 1966-072A | 1966-072A | KH-4A | All cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 1037 | OPS 1866 | 08 Nov 1966 | 1966-102A | 1966-102A | KH-4A | Second pan geometry mission. Higher than normal base plus fog encountered on both main camera records. |
| 1038 | OPS 1664 | 14 Jan 1967 | 1967-002A | 1967-002A | KH-4A | Fair image quality. |
| 1039 | OPS 4750 | 22 Feb 1967 | 1967-015A | 1967-015A | KH-4A | Normal KH-4 mission. Light from horizon camera on both main camera records during 1039-1. |
| 1040 | OPS 4779 | 30 Mar 1967 | 1967-029A | 1967-029A | KH-4A | Satellite flown nose first. |
| 1041 | OPS 4696 | 9 May 1967 | 1967-043A | 1967-043A | KH-4A | Due to the failure of the booster cut-off switch, the satellite went into a highly eccentric orbit. There was significant image degradation. |
| 1042 | OPS 3559 | 16 Jun 1967 | 1967-062A | 1967-062A | KH-4A | Small out-of-focus area in forward camera of 1042-1. |
| 1043 | OPS 4827 | 07 Aug 1967 | 1967-076A | 1967-076A | KH-4A | Forward camera film came out of the rails on pass 230D. Film degraded past this point. |
| 1044 | OPS 0562 | 02 Nov 1967 | 1967-109A | 1967-109A | KH-4A | All cameras operated fine. |
| 1045 | OPS 2243 | 24 Jan 1968 | 1968-008A | 1968-008A | KH-4A | All cameras operated satisfactorily. |
| 1046 | OPS 4849 | 14 Mar 1968 | 1968-020A | 1968-020A | KH-4A | Image quality good for 1046-1 and fair for 1046-2. |
| 1047 | OPS 5343 | 20 Jun 1968 | 1968-052A | 1968-052A | KH-4A | Out-of-focus imagery is present on both main camera records. |
| 1048 | OPS 0165 | 18 Sep 1968 | 1968-078A | 1968-078A | KH-4A | Film in the forward camera separated and camera failed on mission 1048-2 |
| 1049 | OPS 4740 | 12 Dec 1968 | 1968-112A | 1968-112A | KH-4A | Degraded film |
| 1050 | OPS 3722 | 19 Mar 1969 | 1969-026A | 1969-026A | KH-4A | Due to abnormal rotational rates after revolution 22 |
| 1051 | OPS 1101 | 2 May 1969 | 1969-041A | 1969-041A | KH-4A | Imagery of both pan camera records is soft and lacks crispness and edge sharpness. |
| 1052 | OPS 3531 | 22 Sep 1969 | 1969-079A | 1969-079A | KH-4A | Last of the KH-4A missions |
| 1101 | OPS 5089 | 15 Sep 1967 | 1967-087A | 1967-087A | KH-4B | First mission of the KH-4B series. Best film to date. |
| 1102 | OPS 1001 | 09 Dec 1967 | 1967-122A | 1967-122A | KH-4B | Noticeable image smear for forward camera |
| 1103 | OPS 1419 | 1 May 1968 | 1968-039A | 1968-039B | KH-4B | Out-of-focus imagery is present on both main camera records. |
| 1104 | OPS 5955 | 07 Aug 1968 | 1968-065A | 1968-065A | KH-4B | Best imagery to date on any KH-4 systems. Bicolor and color infrared experiments were conducted on this mission, including SO-180 IR camouflage detection film.[54] |
| 1105 | OPS 1315 | 03 Nov 1968 | 1968-098A | 1968-098A | KH-4B | Image quality is variable and displays areas of soft focus and image smear. |
| 1106 | OPS 3890 | 05 Feb 1969 | 1969-010A | 1969-010A | KH-4B | The best image quality to date. |
| 1107 | OPS 3654 | 24 Jul 1969 | 1969-063A | 1969-063A | KH-4B | Forward camera failed on pass 1 and remained inoperative throughout the rest of the mission. |
| 1108 | OPS 6617 | 04 Dec 1969 | 1969-105A | 1969-105A | KH-4B | Cameras operated satisfactorily and the mission carried 811 ft (247 m) of aerial color film added to the end of the film supply. |
| 1109 | OPS 0440 | 04 Mar 1970 | 1970-016A | 1970-016A | KH-4B | Cameras operated satisfactorily but the overall image quality of both the forward and aft records is variable. |
| 1110 | OPS 4720 | 20 May 1970 | 1970-040A | 1970-040A | KH-4B | The overall image quality is less than that provided by recent missions and 2 |
| 1111 | OPS 4324 | 23 Jun 1970 | 1970-054A | 1970-054A | KH-4B | The overall image quality is good. |
| 1112 | OPS 4992 | 18 Nov 1970 | 1970-098A | 1970-098A | KH-4B | The forward camera failed on pass 104 and remained inoperative throughout the rest of the mission. |
| 1113 | OPS 3297 | 17 Feb 1971 | 1971-F01A | 1971-F01 | KH-4B | Mission failed due to failure of Thor booster. Destroyed shortly after launch. |
| 1114 | OPS 5300 | 24 Mar 1971 | 1971-022A | 1971-022A | KH-4B | The overall image quality is good and comparable to the best of past missions. On-board program failed after pass 235 |
| 1115 | OPS 5454 | 10 Sep 1971 | 1971-076A | 1971-076A | KH-4B | Overall image quality is good. |
| 1116 | OPS 5640 | 19 Apr 1972 | 1972-032A | 1972-032A | KH-4B | Very successful mission and image quality was good. |
| 1117 | OPS 6371 | 25 May 1972 | 1972-039A | 1972-039A | KH-4B | Last KH-4B mission. Very successful mission, failure to deploy one solar panel and leak in Agena gas system shortened mission from 19 to 6 days[53] |
Photo gallery
-
AF Sat Ctrl Facility during recovery ops
-
CORONA re-entry parameters
See also
- KH-5-ARGON, KH-6-LANYARD, KH-7, KH-8-GAMBIT
- KH-9-HEXAGON "Big Bird"
- KH-10-DORIAN or Manned Orbital Laboratory
- KH-11, KH-12, KH-13.
- Satellite imagery
- Cold War
- Zenit
Popular culture
The 1963 thriller novel Ice Station Zebra and its 1968 film adaptation were inspired, in part, by news accounts from April 17, 1959, about a missing experimental Corona satellite capsule (Discoverer II) that inadvertently landed near Spitzbergen on April 13. While Soviet agents may have recovered the vehicle,[37][55] it is more likely that the capsule landed in water and sank.[28]
References
- ^ Yenne, Bill (1985). The Encyclopedia of US Spacecraft. Exeter Books (A Bison Book), New York. ISBN 0-671-07580-2.p.82 Key Hole
- ^ "'Mission accomplished' for NRO at Onizuka AFS". USAF. 2007-04-23.
- ^ "Chronology of Air Force space activities" (PDF). National Reconnaissance Office.
- ^ Yenne, p. 63; Jensen, p. 81.
- ^ a b c d e f g Drell, "Physics and U.S. National Security," p. S462.
- ^ Brown, Stewart F. "America's First Eyes in Space." Popular Science. February 1996, p. 46.
- ^ a b Brown, Stewart F. "America's First Eyes in Space." Popular Science. February 1996, p. 46-47.
- ^ a b Peebles, p. 157.
- ^ a b c d Olsen, p. 57.
- ^ Yenne, p. 64.
- ^ Smith, p. 111-114.
- ^ a b Lewis, p. 93.
- ^ Monmonier, p. 24.
- ^ Day, Logsdon, and Latell, p. 192-196.
- ^ a b Ruffner, p. 37.
- ^ a b Kramer, p. 354.
- ^ Ruffner, p. 34, 36.
- ^ a b Ruffner, p. 36.
- ^ a b Chun, p. 75.
- ^ a b Ruffner, p. 31.
- ^ a b Drell, "Reminiscences of Work on National Reconnaissance," p. 42.
- ^ Brown, p. 44; Burrows, p. 231.
- ^ Peebles, p. 48.
- ^ Collins, p. 108.
- ^ Hickam Kukini, page A-4, Vol 15, No 48, Friday December 5, 2008, Base newspaper from Hickam AFB
- ^ Monmonier, p. 22-23.
- ^ Monmonier, p. 23.
- ^ a b Day, Dwayne Allen (2008-02-18). "Spysat down!". The Space Review. Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ^ a b Ruffner, p. 32.
- ^ Peebles, p. 159.
- ^ National Reconnaissance Office. "National Reconnaissance Office Review and Redaction Guide for Automatic Declassification of 25-Year-Old Information. Version 1.0, 2006 edition, p. 58. Accessed 2012-06-06.
- ^ National Aeronautics and Space Administration, p. 292.
- ^ National Reconnaissance Office. "National Reconnaissance Office Review and Redaction Guide for Automatic Declassification of 25-Year-Old Information. Version 1.0, 2006 edition, p. 52. Accessed 2012-06-06.
- ^ Ruffner, p. 32-33.
- ^ Day, Dwayne Allen (2009-01-12). "Ike's gambit: The KH-8 reconnaissance satellite". The Space Review. Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ^ Peebles, p. 51.
- ^ a b c National Reconnaissance Office. "National Reconnaissance Office Review and Redaction Guide for Automatic Declassification of 25-Year-Old Information. Version 1.0, 2006 edition, p. 154. Accessed 2012-06-06.
- ^ National Reconnaissance Office. The Corona Story. BYE 140001-98. December 1988, p. 32. Accessed 2012-06-06.
- ^ National Reconnaissance Office. "National Reconnaissance Office Review and Redaction Guide for Automatic Declassification of 25-Year-Old Information. Version 1.0, 2006 edition, p. 118. Accessed 2012-06-06.
- ^ Chien, Phillip. "High Spies." Popular Mechanics. February 1996, p. 49.
- ^ "Declassified intelligence satellite photographs fact sheet 090-96". United States Geological Survey. February 1998.
- ^ "Discoverer 13 - NSSDC ID: 1960-008A". NASA NSSDC.
- ^ "Sputnik 5 - NSSDC ID: 1960-011A". NASA NSSDC.
- ^ Yenne, Bill (1985). The Encyclopedia of US Spacecraft. Exeter Books (A Bison Book), New York. ISBN 0-671-07580-2.p.37 Discoverer
- ^ "1967-043B". NASA National Space Science Data Center. 2010-10-08.
- ^ "1970-098B". NASA National Space Science Data Center. 2010-10-08.
- ^ Executive Order 12951
- ^ Broad, William J. (12 September 1995). "Spy Satellites' Early Role As 'Floodlight' Coming Clear". The New York Times.
- ^ Satellite images spy ancient history in Syria
- ^ Ancient Syrian Settlements Seen in Spy Satellite Images | LiveScience
- ^ "MISSION 9043 SUCCESSFUL AIR RECOVERY" (PDF). National Reconnaissance Office. 21 September 1962.
- ^ "Photographic Evaluation Report: Mission 9043" (PDF). National Reconnaissance Office. 31 October 1962.
- ^ a b Robery Perry (October 1973). "A History of Satellite Reconnaissance: Volume I - Corona (page 215)" (PDF). Central Intelligence Agency.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ "MEMO: PHOTOGRAPHIC RECONNAISSANCE SYSTEMS, PROGRESS TOWARDS OBJECTIVES" (PDF). NRO. 1972-09-05.
- ^ Taubman, Secret Empire, p. 287.
Bibliography
- Burrows, William E. This New Ocean: The Story of the First Space Age. New York: Random House, 1998.
- Chun, Clayton K.S. Thunder Over the Horizon: From V-2 rockets to Ballistic Missiles. Westport: Praeger Security International, 2006.
- Collins, Martin. After Sputnik: 50 Years of the Space Age. New York: Smithsonian Books/HarperCollins, 2007.
- "Corona." Mission and Spacecraft Library. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. No date. Accessed 2012-60-06.
- Day, Dwayen A.; Logsdon, John M.; and Latell, Brian, eds. Eye in the Sky: The Story of the Corona Spy Satellites. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1998. ISBN 978-1560988304
- "Discoverer/Corona: First U.S. Reconnaissance Satellite. National Air and Space Museum. Smithsonian Institution. 2002. Accessed 2012-06-06.
- Drell, Sidney D. "Physics and U.S. National Security." Reviews of Modern Physics. 71:2 (1999), p. S460-S470.
- Drell, Sidney D. "Reminiscences of Work on National Reconnaissance." in Nuclear Weapons, Scientists, and the Post-Cold War Challenge: Selected Papers on Arms Control. Sidney D. Drell, ed. Hackensack, N.J.: World Scientific, 2007.
- Jensen, John R. Remote Sensing of the Environment: An Earth Resource Perspective. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2007.
- Kramer, Herbert J. Observation of the Earth and Its Environment: Survey of Missions and Sensors. Berlin: Springer, 2002.
- Lewis, Jonathan E. Spy Capitalism: Itek and the CIA. New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 2002.
- Monmonier, Mark S. Spying With Maps: Surveillance Technologies and the Future of Privacy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2004.
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Societal Impact of Spaceflight. Washington, D.C.: NASA, 2009.
- Olsen, Richard C. Remote Sensing From Air and Space. Bellingham, Wash.: SPIE Press, 2007.
- Peebles, Curtis. The Corona Project: America's First Spy Satellites. Annapolis, Md.: Naval Institute Press, 1997.
- Ruffner, Kevin C., ed. Corona: America's First Satellite Program. New York : Morgan James, 1995.
- Smith, F. Dow. "The Design and Engineering of Corona's Optics." in CORONA: Between the Sun & the Earth: The First NRO Reconnaissance Eye in Space. Robert McDonald, ed. Bethesda, Md.: ASPRS, 1997.
- Taubman, Phil. Secret Empire: Eisenhower, the CIA, and the Hidden Story of America’s Space Espionage. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2003. ISBN 0-684-85699-9
- Yenne, Bill. Secret Gadgets and Strange Gizmos: High-Tech (and Low-Tech) Innovations of the U.S. Military. Grand Rapids, Mich.: Publishers Group Worldwide, 2006.
External links
- US Geological Survey Satellite Images: Photographic imagery from the CORONA, ARGON and LANYARD satellites (1959 to 1972).
- Corona page at NRO
- GlobalSecurity.org: Imagery Intelligence
- A Point in Time, a documentary, is available at the Internet Archive
- Declassified Government Records on the Corona Program
- A film clip "Nuclear Navy. First Polaris A-Sub Sails On Ocean Patrol, 1960/11/17 (1960)" is available for viewing at the Internet Archive


