Flexor hallucis longus muscle: Difference between revisions
Anatomist90 (talk | contribs) |
ce: article |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''Flexor hallucis longus muscle''' (FHL) is a [[muscle]] of the [[leg]]. |
The '''Flexor hallucis longus muscle''' (FHL) is a [[muscle]] of the [[leg]]. |
||
It is one of the deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg. The other deep muscles of the leg are [[flexor digitorum longus]] and [[tibialis posterior]]. Tibialis posterior is most powerful of these deep muscles. |
It is one of the deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg. The other deep muscles of the leg are [[flexor digitorum longus]] and [[tibialis posterior]]. Tibialis posterior is the most powerful of these deep muscles. |
||
The Flexor hallucis longus is situated on the fibular side of the leg. It arises from the inferior two-thirds of the posterior surface of the body of the fibula, with the exception of 2.5 cm. at its lowest part; from the lower part of the interosseous membrane; from an intermuscular septum between it and the [[Peronæi]], laterally, and from the fascia covering the [[Tibialis posterior]], medially. |
The Flexor hallucis longus is situated on the fibular side of the leg. It arises from the inferior two-thirds of the posterior surface of the body of the fibula, with the exception of 2.5 cm. at its lowest part; from the lower part of the interosseous membrane; from an intermuscular septum between it and the [[Peronæi]], laterally, and from the fascia covering the [[Tibialis posterior]], medially. |
||
Revision as of 08:53, 8 September 2013
| Flexor hallucis longus muscle | |
|---|---|
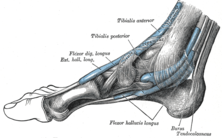 The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle. Medial aspect. (Flexor hallucis longus visible at bottom center.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | fibula, posterior aspect of middle 1/3 |
| Insertion | Plantar surface; base of distal phalanx of hallux |
| Artery | Peroneal artery (peroneal branch of the posterior tibial artery |
| Nerve | tibial nerve, S1 & S2 nerve roots |
| Actions | flexes all joints of the big toe, plantar flexion of the ankle joint |
| Antagonist | Extensor hallucis longus muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus flexor hallucis longus |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.053 |
| TA2 | 2668 |
| FMA | 22593 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The Flexor hallucis longus muscle (FHL) is a muscle of the leg. It is one of the deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg. The other deep muscles of the leg are flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior. Tibialis posterior is the most powerful of these deep muscles.
The Flexor hallucis longus is situated on the fibular side of the leg. It arises from the inferior two-thirds of the posterior surface of the body of the fibula, with the exception of 2.5 cm. at its lowest part; from the lower part of the interosseous membrane; from an intermuscular septum between it and the Peronæi, laterally, and from the fascia covering the Tibialis posterior, medially.
The fibers pass obliquely downward and backward, and end in a tendon which occupies nearly the whole length of the posterior surface of the muscle.
This tendon lies in a groove which crosses the posterior surface of the lower end of the tibia, the posterior surface of the talus, and the under surface of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus; in the sole of the foot it runs forward between the two heads of the Flexor hallucis brevis, and is inserted into the base of the last phalanx of the great toe. The grooves on the talus and calcaneus, which contain the tendon of the muscle, are converted by tendinous fibers into distinct canals, lined by a mucous sheath.
As the tendon passes forward in the sole of the foot, it is situated above, and crosses from the lateral to the medial side of the tendon of the Flexor digitorum longus, to which it is connected by a fibrous slip.
Variations
Usually a slip runs to the Flexor digitorum and frequently an additional slip runs from the Flexor digitorum to the Flexor hallucis. Peroneocalcaneus internus, rare, origin below or outside the Flexor hallucis from the back of the fibula, passes over the sustentaculum tali with the Flexor hallucis and is inserted into the calcaneum.
Additional images
-
Bones of the right leg. Posterior surface.
-
Left calcaneus, inferior surface.
-
Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface.
-
Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joints.
-
Muscles of the back of the leg. Deep layer.
-
Muscles of the sole of the foot. Second layer.
-
The popliteal, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries.
-
Circumpatellar anastomosis.
-
Nerves of the right lower extremity Posterior view.
-
The plantar nerves.
-
Muscles of the sole of the foot.
-
Muscles of the back of the leg. Deep layer.
-
Muscles of the back of the leg. Deep layer.
-
Muscles of the leg.Posterior view
-
Muscles of the sole of the foot.
-
Muscles of the sole of the foot.
-
Dorsum and sole of Foot. Ankle joint. Deep dissection.
-
Ankle joint. Deep dissection. Medial view
External links
- Template:MuscleLoyola
- . GPnotebook https://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=-281739185.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - Anatomy photo:15:st-0404 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- PTCentral
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 485 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 485 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)