1954 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1954 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
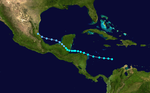
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | June 24, 1954 |
| Last system dissipated | January 6, 1955 (record latest) |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Hazel |
| • Maximum winds | 150 mph (240 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 937 mbar (hPa; 27.67 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 12 |
| Total storms | 11 |
| Hurricanes | 8 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 3 |
| Total fatalities | 1069 |
| Total damage | $751.6 million (1954 USD) |
The 1954 Atlantic hurricane season caused over $750 million in damage,[nb 1] the most of any season at the time. The season officially began on June 15, and nine days later the first named storm developed. Hurricane Alice developed in the Gulf of Mexico and moved inland along the Rio Grande, producing significant precipitation and record flooding that killed 55 people. Activity was slow until late August; only Barbara, a minimal tropical storm, developed in July. In the span of two weeks, hurricanes Carol and Edna followed similar paths before striking New England as a major hurricane.[nb 2] The latter became the costliest hurricane in Maine's history.
In late September, Tropical Storm Gilda killed 29 people after drenching northern Honduras. A tropical depression in early October was captured by a high-altitude photograph on a rocket, thus producing the first large-scale image of a tropical cyclone. The strongest and deadliest hurricane of the season was Hurricane Hazel, which killed thousands in Haiti before striking near the North Carolina/South Carolina border in October. It caused heavy damage in the United States before becoming extratropical and affecting Ontario. Intense rainfall affected Toronto with severe flooding, leaving significant damage. The season officially ended on November 15, although another hurricane named Alice developed on December 30 to the northeast of the Lesser Antilles; it lasted until January 6 of the following year. In total, there were 11 tropical storms, 8 hurricanes, and 3 major hurricanes.
Season summary

The hurricane season officially began on June 15, when the United States Weather Bureau in Miami, Florida began 24 hour operations. The agency, under the direction of Grady Norton had access to 43 other weather stations across the Atlantic basin.[2] Norton died during the season from a stroke while tracking Hurricane Hazel.[3] Additionally, a group of Hurricane Hunters planes were put on standby for the season, able to be flown out into storms and collect data.[2] During the season, there were eight named storms,[3] as well as an unnamed hurricane and a tropical depression.[4] The season officially ended on November 15,[3] although an unnamed tropical storm formed a day later.[4] In addition, Tropical Storm Alice developed on December 31, the latest a tropical cyclone has developed in the calendar year.[5]
Cumulatively, tropical cyclones left 193 deaths and $756 million in damage,[5] becoming the costliest hurricane season at the time.[3] The season was one of six to have three major hurricanes strike the country, along with 2005 (which had four), 1893, 1909, 1933, and 2004.[5] Two of the major hurricanes – Carol and Edna – struck New England; this occurred despite an average of only 5–10 New England hurricanes per century. Carol struck Connecticut as a hurricane and left widespread heavy damage.[6] Only ten days later, Edna became the costliest hurricane in Maine's history.[7] The third major hurricane, Hazel, was the strongest hurricane of the season, attaining winds of 150 mph (240 km/h).[6] Unusually, no tropical cyclones affected Florida.[3]
The season's activity was reflected with a cumulative accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) rating of 113,[8] which is categorized as being "above normal".[9] ACE is, broadly speaking, a measure of the power of the hurricane multiplied by the length of time it existed, so storms that last a long time, as well as particularly strong hurricanes, have high ACEs. ACE is only calculated for full advisories on tropical systems at or exceeding 34 knots (39 mph, 63 km/h) or tropical storm strength. Subtropical cyclones are excluded from the total.[10]
Storms
Hurricane Alice (June)
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 24 – June 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min); |
On June 24, a tropical storm and later hurricane rapidly developed in the western Gulf of Mexico,[6] giving the citizens of southern Texas and northeastern Mexico little time to prepare.[11] Hurricane Alice moved ashore in northeastern Mexico and quickly weakened,[6] producing minor damage and killing one person due to a fallen power line.[11]
On June 26, Alice dissipated, although the system dropped torrential rainfall across southern Texas and northeastern Mexico.[6] The maximum rainfall officially peaked at 24.07 in (611 mm) near Pandale, Texas,[12] concentrated in an area around the Pecos River. High precipitation accumulations occurred in areas that had seen little rains in three years. This led to significant flooding along the Pecos River that produced "probably the greatest rate of runoff for a watershed of [that] size in the United States", as reported by the International Boundary and Water Commission.[13] Ozona, Texas sustained the most impact, estimated at $2 million in damage (1954 USD). Downstream, the Rio Grande rose to the highest level since 1865,[12] which flooded seven towns on either side of the border;[14] Eagle Pass, Texas was flooded with 8 ft (2.4 m) of water.[15] Overall there were at least 55 deaths.[6]
Tropical Storm Barbara
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 27 – July 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min); |
On July 27, a tropical depression developed in the northern Gulf of Mexico, about 100 mi (160 km) south of Grand Isle, Louisiana.[4] A map of the low pressure areas forming in July 1954 indicated that the system originated near the Mississippi Delta and tracked southward.[16] After forming, the depression tracked northwestward, intensifying into Tropical Storm Barbara early on July 28. Maximum sustained winds reached 45 mph (75 km/h),[4] although a tanker offshore named the Henry M. Dawes reported wind gusts of 60 mph (97 km/h).[6] Officials at the United States Weather Bureau posted a storm warning from Cameron to Burrwood, Louisiana, and also advised small craft to remain at port along the entire northern Gulf Coast.[17] Without intensifying further, Barbara made landfall near Vermilion Bay, Louisiana on July 29,[6] dissipating the next day over Texas.[4] The storm dropped heavy rainfall along its path,[6] including over 2 in (51 mm) in New Orleans.[18] The rains caused flooding as well as some damage to the rice crop.[19] However, the Monthly Weather Review yearly summary described the precipitation as "far more beneficial than damaging". There was no wind damage.[6]
Hurricane Carol
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 25 – September 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min); 957 mbar (hPa) |
Carol developed from a tropical wave near the Bahamas on August 25. It quickly intensified as it tracked generally to the north, becoming a hurricane on August 27. Moving parallel to the coastline of the southeastern United States, Carol passed just east of Cape Hatteras with winds between 75 mph (120 km/h) to 125 mph (200 km/h).[6] It intensified further as it accelerated, striking eastern Long Island as upper Category 2 or a Category 3 hurricane.[20] Carol made its final landfall on Old Saybrook, Connecticut late on August 31. Within a few hours, the hurricane became extratropical over New Hampshire, which later dissipated over Quebec.[6]
In North Carolina, hurricane-force winds left minor damage to houses,[21] estimated around $228,000.[6] Rains from Carol alleviated drought conditions in the Washington, D.C. area.[22] On Long Island, the storm surge flooded the Montauk Highway with 4 ft (1.2 m) of water about a mile across. High winds left 275,000 homes without power, and damage totaled $3 million on the island.[23]
The hurricane moved ashore in Connecticut shortly after high tide, producing a storm surge of 10–15 ft (3–4.5 m) from New London eastward. The surge in Narragansett Bay reached 14.4 ft (4.4 m), which surpassed that of the 1938 New England hurricane, which flooded downtown Providence with 12 feet (3.7 m) of water. In New London, rainfall peaked around 6 in (150 mm).[24] The hurricane produced winds of over 115 mph (185 km/h) in Connecticut and Rhode Island,[5] including a record-high gust of 135 mph (215 km/h) at Block Island.[24] Widespread areas were left without power from eastern Connecticut to southern Massachusetts.[24] Further north, Hurricane Carol downed hundreds of trees, as well as destroying widespread apple groves and corn fields. It became the costliest natural disaster in the state's history,[25] only to be surpassed by Hurricane Edna ten days later.[7] Across New England, the hurricane destroyed about 4,000 homes, 3,500 cars, and 3,000 boats.[24] Damage totaled $460 million,[6] and there were 60 deaths.[5] In neighboring Canada, high rains caused flooding while strong winds downed trees and power lines.[26]
Hurricane Dolly
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 31 – September 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min); |
A tropical wave spawned a tropical depression on August 31 to the northwest of Puerto Rico. It moved rapidly north-northwestward, intensifying into Tropical Storm Dolly later that day and into a hurricane early on September 1.[6][4] Early in the storm's duration, the U.S. Weather Bureau noted the potential for Dolly to affect the same areas of New England that Hurricane Carol struck just days prior.[27] However, the hurricane turned to the north away from land. The Hurricane Hunters estimated maximum sustained winds of 100–115 mph (155–185 km/h) on September 2 after the storm passed about halfway between the Outer Banks and Bermuda. Dolly turned to the northeast on September 2 and became extratropical later that day to the south of Nova Scotia. It was tracked until September 4, until it was last located to the north of the Azores. There was no reported damage.[6][4]
Hurricane Edna
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 2 – September 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min); 954 mbar (hPa) |
As Dolly became extratropical, the tropical depression that later became Hurricane Edna developed east of the Lesser Antilles on September 2.[4] It moved northwestward, dropping heavy rainfall on Puerto Rico as it passed north of the island.[28] On September 7 Edna became a hurricane, and the next day reached peak winds of 120 mph (195 km/h). It turned to the north and northeast, bypassing the Outer Banks and skirting Cape Cod.[4] On September 11, Edna became one of only three major hurricanes to strike Massachusetts, along with a hurricane in 1869 and the 1938 Long Island hurricane.[5] The hurricane later moved ashore near the border between Maine and New Brunswick around the time it became extratropical. The remnants persisted a few more days before dissipating south of Greenland.[4]
Early in its duration, Edna produced high seas and gale force winds in the Bahamas, but there was no damage there. Hurricane force winds occurred in the Outer Banks, although damage was minor.[6] As it passed New England, Edna produced a 6 ft (1.8 m) storm surge during a high tide, which caused severe flooding in Martha's Vineyard, Nantucket, and Cape Cod. Wind gusts peaked at 120 mph (190 km/h) on Martha's Vineyard, and the strong winds across the region left widespread power outages. The hurricane dropped additional heavy rainfall to areas affected by Carol, resulting in flooding in Massachusetts and Rhode Island.[29] In Long Island and New England, the hurricane left over $42 million in damage and 20 deaths, only 11 days after Carol affected the same area.[6] About a third of the damage occurred in Maine,[7] becoming the costliest hurricane on record in the state.[25] Hurricane force winds extended into Canada, causing $6 million in damage (1954 CAD), mostly from crop damage. There was one death in Nova Scotia.[30]
Hurricane Florence
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 11 – September 12 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 mph (120 km/h) (1-min); |
A tropical storm formed in the Bay of Campeche on September 11. Given the name Florence, the storm moved generally west-southwestward with a small radius of maximum winds. Hurricane Hunters reported winds of 65 mph (105 km/h), although winds were estimated to have reached minimal hurricane force, or 75 mph (120 km/h).[6][4] Before the storm moved ashore, officials in Veracruz evacuated residents from low-lying areas, and overall about 90,000 people left their homes.[31] On September 12, Florence moved ashore between Tuxpan, and Nautla, Veracruz and quickly dissipated.[6][4] The hurricane flooded coastal cities with up to 3 ft (0.91 m) of water, cutting off communications throughout the state.[31] Damage was heaviest around Poza Rica, primarily from the destruction of banana plantations. Monetary damage was estimated around $1.5 million (1954 USD), and there were five reported deaths.[6]
Tropical Storm Gilda
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 24 – September 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min); |
On September 24, Tropical Storm Gilda developed in the central Caribbean Sea about halfway between Jamaica and Colombia. A small storm, it moved westward throughout its duration. On September 26, Gilda attained peak winds of 70 mph (110 km/h) while nearing northeastern Honduras. The storm paralleled the coastline a short distance offshore, maintaining its intensity before hitting and later dissipating over Belize on September 27.[4][6] While moving just offshore the coast of Honduras, Gilda dropped intense rainfall,[6] which flooding about 680 mi2 (1760 km2 of land along the Chamelecon and Ulúa rivers. The waters caused the widespread destruction of banana plantations and houses, leaving about 3,000 people homeless. Honduras President Juan Manuel Gálvez appealed for aid from the United States. In response, U.S. Air Force planes flew food, medicine, rafts, and water purification tablets to the most affected regions.[32] A total of 29 people were killed in Honduras. When Gilda made its landfall in Belize, it left little property damage and no deaths.[4][6]
Hurricane Eight
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 25 – October 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min); |
A tropical depression formed in the Central Atlantic on September 25. It drifted east-northeastward, eventually becoming a tropical storm on September 29. The storm curved to the west and west-southwest, becoming a hurricane on October 2. It turned to the northeast on October 3, and reached a peak of 100 mph (155 km/h) winds about halfway between Bermuda and the Azores. By that point it began accelerating, and late on October 6 the hurricane became extratropical over the Northeastern Atlantic. Early the next day it was last observed to the south of Iceland.[4] The hurricane was not named due to its presence in the eastern Atlantic and not being a threat to land.[33]
Unnumbered Tropical Depression
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 2 – October 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min); |
On October 2, a tropical depression moved westward from the coast of Cuba into the Gulf of Mexico. It moved westward without intensifying beyond winds of 35 mph (55 km/h), moving ashore about 40 mi (65 km) north of Brownsville, Texas. The depression weakened as it across southern Texas and dropped heavy rainfall. Brownsville recorded over 3 in (75 mm) in a 45 minute period, as well as about 6 in (150 mm) in six hours.[34] The rainfall rates of about an inch per hour was the heaviest since June 1950. The depression also moved ashore with high waves and tides.[35]
When the system reached the Big Bend region on October 5 it reintensified slightly. Around that time, the United States Navy conducted a rocket test from White Sands, New Mexico; this was despite that such tests were rarely performed when the skies were cloudy. The rocket took an unintended photograph of the depression from an altitude of about 100 miles (160 km), which became the first such large-scale image of a tropical cyclone.[34] The depression later moved into New Mexico and dropped additional rainfall,[34] interacting with an approaching cold front.[36] Flooding was reported around Roswell,[34] as well as along the Pecos River system. Rainfall in the state peaked at 9.8 in (250 mm) in Canton, New Mexico. The system dissipated on October 7.[36]
Hurricane Hazel
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 5 – October 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 mph (240 km/h) (1-min); 937 mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Hazel was the deadliest and costliest hurricane of the season.[6] The storm killed as many as 1,000 people in Haiti before striking the United States near the border between North and South Carolina, as a Category 4 hurricane.[5][37] After causing 95 fatalities in the U.S.,[6] Hazel struck Canada as an extratropical storm, raising the death toll by 81 people, mostly in Toronto.[38]
Hazel formed on October 5 just east of the Windward Islands and intensified into a major hurricane while crossing the Caribbean Sea.[6] In Haiti, Hazel destroyed 40% of the coffee trees and 50% of the cacao crop, affecting the economy for several years to come.[39][40] The hurricane made landfall in the Carolinas, and destroyed most waterfront dwellings near its point of impact.[41] It affected several more states, including Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia, bringing gusts near 100 mph (160 km/h) and causing $308 million (1954 USD) in damage.[6][42]
When Hazel arrived in Ontario, rivers and streams passing through the Greater Toronto Area overflowed their banks, causing severe flooding.[43] As a result, many residential areas located in floodplains, such as the Raymore Drive area, were subsequently converted to parkland.[44] In Canada alone, over C$135 million (2009: $1.1 billion) of damage was incurred.[45] Hazel was particularly destructive in Toronto, as a result of a combination of a lack of experience in dealing with tropical storms and the storm's unexpected retention of power. Hazel had traveled 680 mi (1,090 km) over land, but while approaching Canada, it had merged with an existing powerful cold front. The storm stalled over the Greater Toronto Area, and although it was now extratropical, it remained as powerful as a category 1 hurricane.[46][47] To help with the cleanup, 800 members of the military were summoned, and a Hurricane Relief Fund was established that distributed $5.1 million (2009: $41.7 million) in aid.[45]
Tropical Storm Ten
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 16 – November 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); |
On November 16, a tropical depression developed about halfway between the Lesser Antilles and the Azores. It moved to the west, quickly intensifying into a tropical storm and reaching peak winds of 50 mph (85 km/h). The storm maintained that intensity on November 21 when it began weakening, dissipating later that day.[4]
Hurricane Alice (December)
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 30 – January 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min); 987 mbar (hPa) |
The final storm of the season, Alice, developed on December 30 from a trough of low pressure in the central Atlantic Ocean in an area of unusually favorable conditions. The storm moved southwestward and gradually strengthened to reach hurricane status. It persisted into the following calendar year, passing through the Leeward Islands on January 2. Alice reached peak winds of 80 mph (130 km/h) before encountering cold air and turning to the southeast. It dissipated on January 6 over the southeastern Caribbean Sea.[48]
Alice produced heavy rainfall and moderately strong winds across several islands along its path. Saba and Anguilla were affected the most, with total damage amounting to $623,500 (1955 USD).[48][49] Operationally, lack of definitive data prevented the U.S. Weather Bureau from declaring the system a hurricane until January 2. It received the name Alice in early 1955, though re-analysis of the data supported extending its track to the previous year, resulting in two tropical cyclones of the same name in one season. It was one of only two storms to span two calendar years, along with Tropical Storm Zeta in 2005 and 2006.[48][50][51]
Storm names
The following names were used for named storms (tropical storms and hurricanes) that formed in the North Atlantic in 1954. The list was the same as 1953 with the exception of Gilda, which replaced Gail due to the name's confusion with the term gale.[52] Names that were not assigned are marked in gray.
|
|
Retirement
The name Carol was re-used in the 1965 season, but was retroactively retired when the modern naming system was introduced. Edna was reused in 1968 and retired. Hazel was not re-used and was retired.[53][4]
See also
Notes
- ^ All damage figures in the article are in 1954 United States dollars (USD) unless otherwise stated
- ^ A major hurricane is a tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of at least 111 mph (179 km/h), or a Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson scale.[1]
References
- ^ National Hurricane Center (2010-07-11). "Glossary of NHC Terms". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2011-07-23.
- ^ a b Rose Mallory (1954-06-15). "1954 Season Opens Officially". Miami Daily News. Retrieved 2011-08-19.
- ^ a b c d e Staff Writer (1954-11-15). "Hurricane Season Ends". Reading Eagle. United Press International. Retrieved 2011-09-05.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c d e f g Eric S. Blake (August 2011). "The Deadliest, Costliest, and Most Intense United States Tropical Cyclones from 1851 to 2010 (and Other Frequently Requested Hurricane Facts)" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-08-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab Walter R. Davis (December 1954). "Hurricanes of 1954" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 370–373. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ a b c Wayne Cotterly (2002). "Hurricane Edna (1954)". Retrieved 2006-11-10.
- ^ Hurricane Research Division (March 2011). "Atlantic basin Comparison of Original and Revised HURDAT". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2011-07-23.
- ^ "Extended range forecast of Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity and landfall strike probability for 2010" (PDF). Colorado State University. 2009-12-09. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ David Levinson (2008-08-20). "2005 Atlantic Ocean Tropical Cyclones". National Climatic Data Center. Retrieved 2011-07-23.
- ^ a b Staff Writer (1954-06-23). "Gale Hits Mexico". The Victoria Advocate. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-08-06.
- ^ a b David Roth (2010-01-13). "Hurricane Alice - June 24–27, 1954". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved 2011-08-05.
- ^ Jonathan Burnett (2008). Flash floods in Texas. Texas A&M University Press. pp. 151–161. ISBN 1-58444-590-8. Retrieved 2011-08-05.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: checksum (help) - ^ Staff Writer (1954-06-28). "Rio Grande Floods 7 Towns; 6 Die, Thousand Homeless". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. United Press. Retrieved 2011-08-06.
- ^ F. J. Von Zuben, Jr.; et al. (November 1957). "Public Health Disaster Aid in the Rio Grande Flood of 1954". Public Health Reports. 72 (11). PMC 2031412. PMID 13485295.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ H.F. Hawkins (July 1954). "The Weather and Circulation of July 1954" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. National oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 94. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Staff Writer (1954-07-29). "Gulf Storm of Louisiana Coast". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. United Press International. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Staff Writer (1954-07-30). "Tropical Storm Hits Louisiana". Lewiston Morning Tribune. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Staff Writer (1954-07-30). "Gulf Storm Dwindles But Damages Rice Crop". Sarasota Herald Tribune. United Press. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Hurricane Research Division (2006). "Chronological List of All Hurricanes which Affected the Continental United States: 1851-2005". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2006-11-02.
- ^ James E. Hudgins (2000). "Tropical cyclones affecting North Carolina since 1586: An Historical Perspective". Blacksburg, Virginia National Weather Service Office. Retrieved 2006-11-03.
- ^ David Roth & Hugh Cobb (2000). "Virginia Hurricane History". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2006-11-03.
- ^ "Section 5.4.4: Risk Assessment - Hurricane" (PDF). Suffolk County, New York Government. October 2008. Retrieved 2011-08-19.
- ^ a b c d David R. Vallee and Michael R. Dion (1997). "Hurricane Carol". Taunton, MA National Weather Service. Retrieved 2011-08-19.
- ^ a b Wayne Cotterly (2002). "Hurricane Carol (1954)". Retrieved 2006-11-10.
- ^ Canadian Hurricane Centre (2010-09-14). "1954-Carol". Retrieved 2011-08-19.
- ^ Glenn Alter (1954-09-01). "Hurricane Dolly Now Far East of Jacksonville". The Miami news. Retrieved 2011-08-04.
- ^ William Malkin; George C. Holzworth (September 1954). "Hurricane Edna, 1954" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. 82 (9). American Meteorological Society: 267–279. Bibcode:1954MWRv...82..267M. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1954)082<0267:HE>2.0.CO;2. Retrieved February 1, 2011.
- ^ David R. Vallee (2005-12-05). "Hurricane Edna". Tauton, Massachusetts National Weather Service. Retrieved 2011-08-22.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "1954-Edna". Environment Canada. 2010-09-14. Retrieved 2011-08-22.
- ^ a b Staff Writer (1954-09-12). "Mexican Coast is Battered by Florence". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. Retrieved 2011-08-04.
- ^ Daniel Haulman (1998). "The United States Air Force and Humanitarian Airlift Operations 1947–1994" (PDF). Air Force History and Museums Program. Retrieved 2011-08-06.
- ^ Gordon E. Dunn; et al. (1955). "Addendum to "Hurricanes 1954"" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. 82 (12): 314.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d L.F. Hubert; Otto Berg (1955). "A Rocket Portrait of a Tropical Storm" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review: 119–124. Retrieved 2011-08-04.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Staff Writer (1954-10-03). "Tropical Disturbance Blows Toward Texas". The Tuscaloosa News. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-08-04.
- ^ a b David M. Roth (2007-06-20). "Tropical Depression - October 3–7, 1954". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved 2011-04-26.
- ^ Milt Sosin (1954-10-13). "Hazel's Toll is 200 Dead; 500 Hurt in Haiti". The Miami News. p. 1. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ^ "Hurricane Hazel". Environment Canada. 2009-08-17. Retrieved 2011-09-06.
- ^ "Hurricane Dents Economy of Haiti". New York Times. 1956-01-05. Retrieved 2009-06-14.
- ^ Robert I. Rotberg; Christopher K. Clague (1971). Haiti: the politics of squalor. Houghton Mifflin. p. 182. ISBN 0-395-12105-1.
- ^ John Hairr (2008). The Great Hurricanes of North Carolina. Stroud, United Kingdom: The History Press. p. 135. ISBN 1-59629-391-8.
- ^ Associated Press (1954-10-16). "Floods Rise in Hazel's Wake". The Miami News. p. 1. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
{{cite news}}: Text "e" ignored (help) - ^ Peter Bowyer (2004). "Hurricane Hazel Impacts — Long Branch". Canadian Hurricane Centre. Retrieved 2009-06-17.
- ^ Peter Bowyer (2004). "Hurricane Hazel Impacts — Humber River". Canadian Hurricane Centre. Retrieved 2009-06-17.
- ^ a b Peter Bowyer (2004). "Hurricane Hazel - Evaluation of Organizational Response". Canadian Hurricane Centre. Retrieved 2009-06-17.
- ^ Peter Bowyer (2004). "Hurricane Hazel Impacts — Transportation". Canadian Hurricane Centre. Retrieved 2009-06-17.
- ^ Peter Bowyer (2004). "Hurricane Hazel Impacts". Canadian Hurricane Centre. Retrieved 2009-06-17.
- ^ a b c José A. Colón (1955). "On the formation of Hurricane Alice, 1955" (PDF). U.S. Weather Bureau. Retrieved 2006-12-07.
- ^ Gordon E. Dunn, Walter R. Davis, Paul L. Moore (1955). "Hurricanes of 1955" (PDF). Miami, Florida Weather Bureau Office. Retrieved 2006-12-07.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ National Weather Service (2006). "Has there ever been a Tropical Storm so late in the year before?". Retrieved 2006-12-07.
- ^ Hurricane Enterprises LLC (2006). "Oddball Tropical Systems" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-12-07.
- ^ Staff Writer (1954-09-10). "Plenty of Names Left for Hurricane Season". The Victoria Advocate. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-08-04.
- ^ "Retired Hurricane Names Since 1954". National Hurricane Center. 2011-03-16. Retrieved 2011-07-14.