Hannibal's crossing of the Alps
| Hannibal's crossing of the Alps | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Punic Wars | |||||||
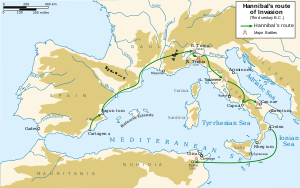 Hannibal's route to Italy | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Roman Republic | Carthage | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Publius Cornelius Scipio Tiberius Sempronius Longus |
Hannibal Hasdrubal Mago Hasdrubal Gisco Syphax Hanno the Elder Hasdrubal the Bald Hampsicora Maharbal | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 94,000+ | |||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 68,000+ | |||||||
This article may be too long to read and navigate comfortably. (February 2014) |
Hannibal crossing the Alps, in 218 BC, was one of the major achievements of the Second Punic War, and one of the most celebrated achievements of any military force in ancient warfare.[1]
Background
After the final Carthaginian naval defeat at the Aegates Islands[2] the Carthaginians surrendered and accepted defeat in the First Punic War.[3] Hamilcar Barca (meaning lightning),[4] a leading member of the Patriotic party in Carthage and a general who operated with ability in the course of the First Punic War, sought to remedy the losses that Carthage had suffered in Sicily to the Romans.[5] In addition to this, the Carthaginians (and Hamilcar personally)[6] were embittered by the loss of Sardinia. After the loss of the war to the Romans, the Romans imposed terms upon the Carthaginians that were designed to make Carthage a tribute paying city to Rome and simultaneously strip it of its fleet.[7] There had been a time when Carthage was the sole maritime power of the Western Mediterranean,[8] and had contended with many powerful nations for control of the primary sea lanes of the Mediterranean.[8] Concerning many of these, Carthage was indeed the undisputed master. Eratosthenes relates how the Carthaginians would seize every ship found sailing towards the Straights of Gades or Sardinia and throw anyone on board into the ocean.[8] While the terms of the peace treaty were harsh, the Romans did not strip Carthage of her strength; Carthage was the most prosperous maritime trading port of its day, and the tribute that was imposed upon them by the Romans was easily paid off on a yearly basis while Carthage was simultaneously engaged by Carthaginian mercenaries who were in revolt.[7]
The Carthaginian patriot party was interested in conquering Iberia, a land whose variety of natural resources would fill its coffers with sorely needed revenue,[9] replacing the riches of Sicily that, following the end of the First Punic War, were now flowing into Roman coffers. In addition, it was the ambition of the Barcas, one of the leading noble families of the patriotic party, to some day employ the Iberian peninsula as a base of operations for waging a war of revenge against the Roman military alliance to destroy it. Those two things went hand in hand, and in spite of conservative opposition to his expedition, Hamilcar set out in 238 BC[9][10][11] to begin his conquest of the Iberian peninsula with these objectives in mind. Marching west from Carthage[12] towards the Pillars of Hercules,[13] where his army crossed the strait and proceeded to subdue the peninsula, in the course of nine years[10][11][13] Hamilcar conquered the south eastern portion of the peninsula.[10] His administration of the freshly conquered provinces led Cato the Elder to remark of Hamilcar, "there was no king equal to Hamilcar Barca."[14]
In 228 BC,[10] Hamilcar was killed, witnessed by Hannibal,[15] during a campaign against the Celtic natives of the peninsula.[11] His son in law, and the commanding naval officer,[11] also a member of the Patriotic party – Hasdrubal "The Handsome"[10][11] – was rewarded by the officers of the Carthiginian Iberian army with the chief command.[11][16] There were a number of Grecian colonies along the eastern coast of the Iberian peninsula - the most notable one being the trade emporium of Saguntum.[16] These colonies expressed concern about the consolidation of Carthaginian power on the peninsula, which Hasdrubal's deft military leadership and diplomatic skill[13] procured. For protection, Saguntum turned to Rome, who sent a garrison to the city and a diplomatic mission to Hasdrubal's camp, based out of Cartagena,[16] and informed him that the Iberus river must be the limit of the Carthaginian advance in Spain.[13][17] The conclusion of the treaty and the embassy were sent to Hasdrubal's camp in 226 BC.[17][18]
In 221 BC,[15] Hasdrubal was killed by an assassin.[19][20][21] It was in that year that the officers of the Carthaginian army in Iberia expressed their high opinion of Hamilcar's 29 year old[15] son, Hannibal,[21] by electing him to the chief command of the army.[15][19] Having assumed the command (retroactively confirmed by the Carthaginian Senate[19]) of the army that his father had welded through nine years of hard mountain fighting, Hannibal declared that he was going to finish his father's project of conquering the Iberian peninsula, which had been the first objective in his father's plan to bring a war to Rome in Italy and defeat it there.
Hannibal spent the first two years of his command seeking to complete his father's ambition, while simultaneously putting down several potential revolts — resulting in part from the death of Hasdrubal — that menaced the Carthaginian possessions already conquered thus far . He attacked the tribe known as the Olcades,[19] and captured their chief town of Althaea.[19] A number of the neighboring tribes were astonished at the vigor and rapacity of this attack,[19] as a result of which they submitted to the Carthaginians.[2] He received tribute from all of these recently subjected tribes, and marched his army back to Cartagena, where he rewarded his troops with gifts and promises of more gifts in the future.[19] During the next two years, Hannibal successfully reduced all of Iberia south of the Ebro to subjection, excepting the city of Saguntum, which, under the aegis of Rome, was outside of his immediate plans. Catalonia and Saguntum were now the only areas of the peninsula not in Hannibal's possession.[22]
Roman Foreign Relations
Hannibal was informed of Roman politics, and saw that this was the opportune time to attack. He had Gallic spies in every corner of the Roman symmachy,[23] even within the inner circles of the Senate itself.[23] The Romans had spent the years since the end of the First Punic War (264-241)[24] tightening their grip on the peninsula by taking important geographical positions in the Peninsula in addition to extending Rome's grip on Sicily, Corsica and Sardinia. Sardinia was taken despite not being part of the original treaty.[2][25] It was captured[26] after a group of mercenaries she had stationed there declared in favor of mercenaries[25] who had revolted against their Carthaginian paymasters who had not paid them.[27] These mercenaries came to appreciate that they would not be able to hold themselves against the natives of the Island- and therefore invited[28] the Romans to garrison the Island (238 BC).[25] The Carthaginians prepared for war in order to take this possession back from the mercenaries, however, the Roman Senate chose to interpret this as a declaration of war[2] and in its turn declared war on Carthage.[29] Carthage, completely exhausted from its exertions with the Romans, chose to give in and allow the Romans this acquisition.[29] In addition to this, the Roman Senate also ordered the Carthaginians to pay 1,200 talents.[2][29] This was a major issue of contention between the Carthaginians and the Romans between the end of the First Punic War and the beginning of the Second Punic War.[25]
The Latin Confederacy, which was one of the political alliances through which the Romans exerted influence over their subjects, extended from Arminum all the way to Massana, the point in Sicily that was closest to Italy. The Constitution of the Roman Confederacy/Symmachy was a vast and complicated network of rules. One of those rules being that, upon the conquest of new communities, those communities would be stripped of half their possessions (unless otherwise stipulated; Sicily and Sardinia for example were left unchanged[30]) and Roman and allied legionnaires would be able to divide that land between them. One notable aspect of this arrangement; in that it expresses the nature of the relationship between the Romans and their allies, was that the land that was taken from the communities was split half, one half going to the Romans (exclusively) and the other half would go to the Latin/Italian communities that had participated in the campaign. Previous claims to this property were null and void, and all of the provincials who were citizens of the conquered territories had no legal right to purchase land that was beyond the bounds of his communities delineated territory.[30] This resulted in the dispossession of many locals. A permanent grip in the area could only be established by force in the face of such measures.
However, these rules applied primarily to the Roman continental possessions.[31] The Romans employed rules like these in order to Romanize their possessions, and they would employ either people from their city, Latins (who were culturally and linguistically cognate) and Italians. In any case, this was done in order to place a certain stamp upon the said area.
The diplomatic situation of Rome was haphazardly conducted, and Hannibal saw this. They acquired land in Illyria.[32] The coastal cities of Corcyra,[33] Epidamnus,[33] Apollonia[33] and the towns of the Atintanes[33] and Parthini [33] were incorporated into the symmachy. These were all clearly within the traditional sphere of influence of Macedonia. Beyond the mountain range of the Apennines Rome's influence was more pretended than real.
In addition to this, The Romans had been at war with the Padane Gauls off and on for more than a century.[34] A 45 year peace had been imposed on the Gauls,[35] which had been preserved due to the fearful outrages visited by the Romans on the Gallic homeland in Italy.[35] During the consulship of Marcus Aemilius Lepidus,[35] the senate passed a measure to establish a colony in the region that the Senones[35] had formerly possessed - they had been systematically rounded up and expelled after they had been subdued by the Romans in 283 BC.[35] Picenum was a colony introduced in a legislative programme by the "demagogue"[35] Tribune Gaius Flaminius and it abutted the territory of the Boii. This programme was designed to empower the lower classes of the citizen-burgesses by increasing their property holdings and thereby increasing their power in the voting process (voting was done according to property, the richest propertied class voting first, then the second, and each grouping counting for one vote. The wealthier the qualifications for voting in a given voting unit were, the fewer members there were in it. When a majority of these groupings had been attained, voting ceased, the poorer classes rarely voted as long as there was even the most basic concord of political sentiment amongst the higher classes because the votes of their voting blocs could be excluded from the legislative process altogether. These measures were introduced by Flaminius in order to raise poorer people into a higher class, and thereby give them a chance to participate in the voting process.). It is not specified in the sources what the Gauls knew of Roman politics, but clearly they did not know much. They interpreted this colony as the first of many blows aimed directly at them,[36] not merely to establish Roman power over the Gauls, but to remove them from the land altogether, by forceful migration or outright extermination.[36] They, for whatever reason, did not fully appreciate that this colony was part and parcel of Roman politics, a blow aimed at the ensconced oligarchy in Rome who exercised a disproportionate influence in the Roman legislative process. This is indicative of the fact that Roman internal politics, including the pursuit of personal fame and influence among Roman politicians was effecting their external politics.
As a consequence, the Boii waged war upon the Romans in 238 BC, a war that lasted until 236 BC.[37] In 225 BC,[38] the natives of northern Italy, seeing that Rome was again moving aggressively to colonize their territory, progressed to the attack.[38] They hired the Gaesatae,[36] a warlike tribe that lent out its prowess in a mercenary capacity.[36] This was the same year that the Battle of Telamon took place, and in spite of the Gauls placing themselves between a consular army and an army of irregulars, the Romans eventually secured a victory.[39][40] The Gauls took up a formidable position, the Taurisci and the Boii were surrounded.[40] Backing against each other and placing the chariots and wagons they used for logistical transportation on either flank, the fought a fierce battle in which the Romans were almost defeated.[41] The Insubres and the Gaesatae were also present during this battle.[41] During this battle, one of the consuls was killed and his head was brought to a Gallic king as a gift.[42] 40,000 Gauls were slain during the course of this defeat and 10,000 of them were taken prisoner.[43]
After this near defeat, the Romans were determined to drive their borders right up to the Alps.[44] In 224 BC,[44][45] the Boii submitted to Roman hegemony, and the next year[44][45] the Anari also submitted to the Romans. In 223 BC,[44] the Romans engaged in another battle with the Gauls, this time the Insubres.[46] The Romans at first sustained significant losses against the Insubres while they were attempting to cross a ford near the junction of the Po and the Adda.[44] After encamping in this country for some days without taking any decisive action, the Roman consul on the spot decided to negotiate a settlement with the Insubres.[44] Under the terms of this freshly negotiated truce, the Romans marched out with full honors into the territory of their allies, the Cenomani.[44] However, once they were safe within the territory of the Cenomari, the Romans again marched their army into the territory of the Insubres and started to burn their crops and pillage their country.[44] There was a battle that took place in which the commanding tribunes managed with skill,[47] but the Consul managed negligently. The Romans were victorious.[47]
In 222 BC, the Celts sent an embassy to the Roman Senate,[48] beseeching that they have peace with the Romans. Seeing an opportunity for a triumph for themselves,[48] The Consuls (Marcus Cladius and Gnaeus Cornelius)[48] vigorously rejected the embassy, and the Gauls prepared for war with the Romans.[48] They hired 30,000 mercenaries[48] from beyond the Alps and awaited the arrival of the Romans.[48] When the campaigning season began, the Consular legions were marched into the Insubres territory again.[48] A vigorous combat took place near Mediolanum,[48] which resulted in the leaders of the Gallic revolt turning themselves over to the Romans.[48] With this victory, the Padane gauls were unhappily subdued, and ripe for revolt.
Preparations
Hannibal, aware of the situation, sent a number of embassies to the Gallic tribes in the Po valley.[49] In 220 BC,[49] he had begun to communicate intimately with the Padane Gauls (called the "Padane Gauls" because the Po in this era was called the "Padus" by the Romans), and these embassies brought with them offers of money, food and guides to the Carthaginian.[49]
This mission had the specific aim of establishing a safe place for Hannibal to debouch from the Alps into the Po valley.[49] Hannibal did not know a great deal about the Alps, but he knew enough to know that it was going to be a difficult march. He had had some scouts give him reports concerning this mountain chain, and he received reports of the difficulties to be encountered there from the Gauls themselves.[49] He did not desire to cross this rugged mountain chain and to descend into the Po valley with exhausted troops only to have to fight a battle.
| Hannibal | |
|---|---|
 A marble bust, reputedly of Hannibal. |
Hannibal knew enough about the Alps to know in particular that the descent was steeper than the ascent into the Alps. This was one of the reasons he wanted to have allies into whose territory he could march. Italy is a part of the African continental plate, not the European plate; the Italian peninsula has been jammed into Europe through tectonic plate movements, which created the Alps and more particularly, made the Italian side of the Alps considerably steeper.
The Romans had poorly treated those Gauls whom they had recently conquered, distributing their land to Roman colonists and taking other unscrupulous measures to ensure the fidelity of these freshly conquered tribes. The Insubres, whose tribal territory immediately abutted the Alps, and the Boii, farther down the Po, were particularly pleased with Hannibal's proposed invasion. In addition, much of the Iberian peninsula was populated by related Gallic tribes[50], and those same Gauls were serving in Hannibal's army. It would be easy indeed to establish intimate relations with these disaffected tribes, especially once he had debouched from the Alps and was amongst them and the Insubres and Boii and other tribes could see and speak with this army for themselves. Polybius had this to say about Hannibal's plans:
Conducted his enterprise with consummate judgement; for he had accurately ascertained the excellent nature of the country in which he was to arrive, and the hostile disposition of its inhabitants towards the Romans; and he had for guides and conductors through the difficult passes which lay in the way of natives of the country, men who were to partake of the same hopes with himself
Siege of Saguntum
These preparations being completed, Hannibal sought to induce the Saguntines to come to arms with him and thereby declare war on Rome through her proxy. He did not desire to break the peace himself,[52][53] and resorted to a variety of strategems in order to induce the Saguntines to attack.[52] However, the Saguntines did nothing except send a diplomatic mission to the Romans to complain about the belligerence of the Carthaginians.[52][54] The Senate, in its turn, sent a committee to Iberia[54] to attempt to settle the issue diplomatically.[52] Hannibal had no interest in treating with this commission, and treated it with contumely, hoping that it would drive the commission to declare war. However, the commission was not fooled and knew that war was in the air.[52] The commission kept its peace, but brought news to Rome that Hannibal was prepared and was going to strike soon.[52][54] The Senate took a number of measures in order to free up its hands for the coming conflict with the Carthaginian.[52] An Illyrian revolt was put down with energy,[52] and the Romans sped up the construction of a number of fortresses in Cisalpine Gaul.[52] Demetrius of Pharos had abandoned his previous alliance with Rome and was now attacking Illyrian cities that had been incorporated into the Roman State.[55]
Hannibal could not achieve the ends that he had hoped for, and in the end he sent news to Carthage (where the peace party, his political enemies, were in power)[56] to the effect that the Saguntines were aggressively handling one of their subject tribes, the Torboletes,[52] and encamped in front of Saguntum to besiege it without awaiting any reply from Carthage. Words were exchanged in the Carthaginian Senate to the effect that Hannibal should be handed over to the Romans and his actions disavowed.[52] However, the multitude in Carthage was too much in support of the conflict to order a stop to the war.[52]
The Siege took place over the course of eight months,[52] and it is notable that the Romans did not send any aid to the Saguntines in spite of this being a part of the terms of their alliance. The Romans allowed themselves to be tied up in a war against the Illyrians,[52] and did not treat the Carthaginian threat from Iberia with the attention that it deserved.
After the siege, Hannibal sold all the inhabitants as slaves,[57] and distributed the proceeds from those sales to his soldiers.[57] In addition, all the booty from the sacking of the city was taken back to Carthage and distributed to the populace, in order to rally their support to his cause.[57] The rest of the city's treasures were put into his war chest for his planned expedition.[57]
March through the Pyrenees

Hannibal had spent the winter after the siege of Saguntum in Cartagana,[58] during which time he dismissed his troops to their own localities.[58] He did this with the hope of cultivating the best possible morale in his army for the upcoming campaign,[58] which he knew was going to be difficult. He left his brother, Hasdrubal[58] in charge of the administration of Carthaginian Iberia, as well as its defense against the Romans.[58] In addition to this, he swapped the native troops of Iberia to Africa, and the native troops of Africa to Iberia.[58] This was done in order to minimize desertion and assure the loyalty of the troops while he was himself busy with the destruction of the Roman Symmachy. He also left his brother a number of ships.[59]
Hannibal foresaw problems if he left Catalonia as a bridgehead for the Romans. They had a number of allies in this country, and he could not allow the Romans a place to land in his base unopposed. As he was relying upon contingents of forces coming to him in Italy via the land route he was about to head out upon, he must take and conquer this country. He had no intention of leaving Iberia to its fate once he was in Italy. Hannibal opted to take the region in a swift campaign, and to that effect he divided his army into three columns, in order to subdue the entirety of the region at the same time.

After receiving news of the route he was about to take from his scouts and messages from the Celtic tribes that resided around the Alps, the Carthaginians set out.[60] He set out with 90,000 infantry from various African and Iberian nations, and 12,000 cavalry.[60] From the Ebro to the Pyrenees the Carthaginians confronted four tribes,[60] the Illergetes,[60] the Bargusii,[60] the Aeronosii[60] and the Andosini.[60] There were a number of cities here that Hannibal took, which Polybius does not specify.[60] This campaign was conducted with speed in order to take as little time as possible in the reduction of this region.[60] Polybius reports severe losses on Hannibal's part.[60] Having reduced this area, he left his brother Hanno[60] in command of this area, specifically over the Bargusii, whom he had reason to distrust due to their affiliation with the Romans.[60] He left his brother in control of this country with 10,000[60] infantry and 1,000[60] Cavalry.[60]
At this early juncture in the campaign, he opted to send home another 10,000[60] infantry and 1,000 [60] Cavalry.[60] This was done to serve two purposes: he wanted to leave a force of men behind who would retain positive sentiments towards Hannibal himself; and he wanted the rest of the Iberians (in his army, as well as out)[60] to believe that the chances of success in the expedition were good, and as a result of which they would be more inclined to join the contingents of reinforcements that he anticipated calling up during the course of his expedition.[60] The remaining force consisted of 50,000 infantry and 9,000 cavalry.[61]
The principal column was the right column, and with it was the treasure chest, the cavalry, with baggage, all the other necessities of war and Hannibal himself.[62] This was the critical column, and it was no coincidence that Hannibal was with this column. As long as Hannibal had no ships to keep himself abreast of the exact movements of the Romans, as to whose exact location he was unaware of, he wanted to be present in person in case the Romans should make a landing in an attempt to attack his army on its ascent or descent through the Pyrenees. This column crossed the Ebro at the town of Edeba,[63] and proceeded directly along the coast through Tarraco, Barcino, Gerunda, Emporiae and Illiberis.[62] Each of those oppidums was taken and garrisoned in turn.
The second, or central, column crossed the Ebro at the oppidum of Mora and from there information is fairly sparse.[63] It proceeded through a number of valleys in this country, and had orders to subdue any tribes that resisted its advance. It eventually rejoined the principal column when it had completed its task.
The third, or left, column crossed the Ebro where it touches with the Sicoris River and proceeded along the river valley and into the mountain countries. It performed the same task as the second and the first columns did. When planning each of these marches, Hannibal ensured that the Rubrucatus river was athwart each of the columns' paths, so if any of the columns should be placed in a disadvantageous situation the other columns could march up and down the river in support of each other should one be placed in a perilous position by the Barbarians.[62]
The campaign was conducted over the course of two months, and was incredibly costly. Over the course of the two-month campaign, Hannibal lost 13,000 men.
March to the Rhone
The most conspicuous detail concerning the march to the Rhone from the descent through the Pyrenees is that there is nothing at all conspicuous about it. This march must have been a pleasant change of pace for the Carthaginians, who had just spent the previous July[64] and August[64] subduing numerous fierce peoples living in the Pyrenees. The history of Catalonia is littered with numerous examples of the fierce resistance that native people of this area have put up against invading armies. The Peninsular war being just one example amongst many, the broken topography of this region affords resistance movements many advantages that they might not otherwise have in flatter more even terrain. The countries through which he passed were of different opinions concerning the Carthaginians, the Romans and the passage of Hannibal's army through their land. Some of these tribes were friendly to his cause,[65] others were opposed to him.[65] Hannibal's skill in dealing with these people is made manifest to us through his march in this country, no reports are made of any fighting taking place in this country, in spite of the lack of homogeneity in political leadership amongst the peoples of this area. He dealt with each tribe as he marched through their territory.[65] Employing only the means of persuasion at his disposal; his personal magnetism and his war chest.
Massilia (modern Marseille),[66] a successful Greek trade emporium had for some time been under the influence of the Romans, and the Romans had even settled colonists there. Massilia feared the arriving Carthaginian army, and to this effect had sought to influence the native tribes on the left bank of the Rhone (The Eastern Bank) to take up the cause of the Romans.[66] This they were able to do, as the barbarians in this country were to make his crossing of the Rhone problematical.
Publius Scipio,[13][66] one of the Consuls for 218 BC, received orders from the Senate to confront Hannibal in the theatre of the Ebro or the Pyrenees.[66][67][68] The Senate delegated to him 60 ships for this purpose.[69] However, he did not move with the speed that the issue required of him. When he arrived in the Po area, there was an uprising amongst the freshly conquered Gauls.[66][70] More colonies were being established in the Po region, and this caused the Boii and Insubres to arise afresh who were now aware that Hannibal was heading to them.[67] Instead of employing the legions that were on hand for their intended Iberian expedition, the Senate ordered[69] that they should be sent to the Po under the command of a Praetor and new legions should be levied by the Consul.[69][70] The formation of a new army was a fairly easy matter for the Romans. There were so many citizens who were qualified for service in the army that all the government had to do was inform the citizenry that more soldiers were needed and they would be required to serve. Many Romans, being required to serve at some point, spent portions of their youth training to serve in the legions. One historian has stated that the Romans had a more rigerous and militaristically oriented society then the Ancient Spartans did.
Finally, having got these new legions together - in a much more leisurely fashion than the urgency of the situation demanded of him - he set sail from Ostia. In this day there were no compasses, and it was the habit of navigators to sail their ships along the coast and to stop at night for victuals.[71] So, after sailing North along the peninsula's (the Italian) coast and then turning west towards the Iberian peninsula, the Consul ordered the fleet to stop in Massilia.[69][72] The time from Ostia to Massilia was 5 days.[69] When he arrived there, to his surprise he learned from the Massiliots that instead of Hannibal still being in Catalonia, as he had anticipated,[72] Hannibal was about 4 days march[73] north of their city on the far side of the Rhone.
Crossing the Rhone
Much of Hannibal's marches are shrouded in debate, especially the debate concerning the path he opted to employ over the Alps. However, modern historians agree on where Hannibal encamped his army on the western bank on the Rhone and see the river crossing as clearly conceived and crisply executed.[citation needed]
While Rome had been idle and leaving her allies in Catalonia to their fate at the hands of the Carthiginians, the Massiliots, the Allies of the Romans, were busy rousing the tribes on the left (eastern) bank of the Rhone against the Carthaginians.[66] Upon the arrival of the intelligence of the Carthaginians in the neighborhood of Massilia, the Consul threw up his proposed Iberian expedition and in its stead thought to do the next logical thing, to prevent Hannibal's crossing of the Rhone as best he could.[72] To this effect he sent a column of 300 horse[73] up the left (east) bank of the Rhone with orders to ascertain the exact location of Hannibal's army.[72] Hannibal received similar news to the effect that the Romans had just arrived with one of their Consular armies (22,000 Legionaires and 2,000 horse)[74]
Hannibal took advantage of the pre-existing hatred the celts had for the Romans on the right (west) bank, and persuaded them to aid him in his crossing of this formidable obstacle.[72][73] He secured from them a number of boats that were capable of making trips at sea, and a numerous collection of canoes of all sorts that must have been employed by the natives of that country.[72] In addition to purchasing these,[72] he was able to acquire their aid in building still other boats.[69][75] This process of preparing to cross the Rhone took two days.[75]
Awaiting the Carthaginian army on the left bank of the Rhone was a tribe of Gauls called the Cavares.[75] This tribe had fortified a camp on the far side of the river,[76] and was awaiting Hannibal's army to cross[73] - as to attack them during the process of crossing.[76] There can be no doubt that Hannibal knew of Alexander the Great's crossing of the Hydaspes river in India as from a tactical and strategic standpoint, it is almost exactly the same. Hannibal formulated his plan according to this model (as indeed it is held up as a cookie cutter way to cross rivers, even to cadets at military institutions to this day) ordered one of his lieutenants; Hanno, Son of Bomilcar[73][76] to make a northern circuit,[76] to cross the Rhone at a location that he deemed to be suitable for the purpose, and then by forced marches, march south and to take the Barbarian army in flank while he was crossing the river.[76]
The day and the night after all of the boats had been built and gathered,[76] Hanno was ordered up the bank and guided by native Gauls,[73][76] approximately 25 miles[73][76] upriver at Pont St. Esprit[76] there was an island that divided the Rhone into two small streams.[73][76] It was here that Hanno decided to cross, and ordered that boats and rafts should be constructed from materials that were at hand.[77][78] The Carthaginian detachment chopped down trees, lashing the logs together with reliable ropes they had brought with them from the army's stores.[76][77] By this means, Hanno's corps crossed the river and immediately proceeded south to the barbarian location.
During this time, Hannibal had been completing his preparations to cross the Rhone.[78] At this, the Carthaginian preparations had been particularly obvious and loud.[78] - Hannibal had ordered the preparations to be made without concern for secrecy,[76] knowing full well that Hanno's corps was marching down the left (eastern) bank of the Rhone to attack the Cavares. His preparations were designed to draw their attention away from their northern flank and focus their attention on his own preparations.[78]
Three days after setting out, Hanno arrived behind a tributary of the Rhone[76] and gave the previously agreed upon signal to let Hannibal know that his force had arrived.[78] Hannibal immediately ordered the boats to cross.[76][77] The small corps was observing the principal army closely,[76] and on seeing it start its crossing, prepared to descend on the Cavares while the army was crossing.
The crossing itself was carefully designed to be as smooth as possible. Every detail was well thought out. The heavy horsemen were put across furthest upstream, and in the largest boats,[77][78] so that the boats that Hannibal had less confidence in could be rowed to the left (eastern) bank in the lee of the larger and more sturdy craft.[77][78] As for the horses themselves, most of them were swam across the river[77][78] at the side and stern of each boat.[76][77] However, some were put on boats fully saddled and ready for immediate use,[77] so that, once they debouched from the river, they could cover the infantry and the rest of the army while it formed up to attack the barbarians.[78]
Seeing that the Carthaginians were finally crossing, the Cavares rose from their entrenchments and prepared their army on the shore near the Carthaginian landing point.[77][79] The armies started to shout and jeer at each other while the Carthaginian army was in the midst of crossing.[80] These sort of exchanges consisted primarily of encouraging their own men and challenging the other army to battle. Often in antiquity, to intimidate their enemy, armies would be ordered to pound their shields with their weapons and raise loud cries at exactly the same moment to create the greatest amount of noise.

It was at precisely this moment, while the Carthiginian army was in the middle of the stream jeering[77] at the enemy from the boats and the Cavares were challenging them to come on from the left bank that Hanno's corp revealed itself and charged down on the rear and flanks of the Cavares.[80][81] A small detachment of Hanno's force was assigned to set the Cavares camp on fire,[80][81] but the majority of this force reeled in on the stunned Cavares.[81] Some of the Cavares rushed to the defense of their camp,[80][81][82] but the majority remained at the location where they had been awaiting the arrival of what they had thought was all of Hannibal's army.[80][82] They were divided; and Hannibal, who was on one of the first boats,[80] landed his men on the left bank of the Rhone amidst the dazed and confused Cavares and with a will lead his men in upon them. There was barely even a semblance of resistance;[80] surrounded as they were, pandemonium took control of their ranks, and each man looked to his own safety as they retreated pell mell away from the carefully arrayed Carthaginian phalanx.
While the actual conflict only took a matter of minutes, Hannibal had spent five days[82] preparing this dangerous and risky operation from every angle, ensuring that it was ready at all points and nothing was left to chance.
From the Rhone to the Alps

Having crossed the Rhone in the face of a formidable enemy, Hannibal needed to reach the Alps quickly in order to beat the season. This was one of the reasons that he marched his army with such speed from Catalonia to this point; Hannibal was bent on debouching his army and encamping it in Italy as soon as he could. He desired this because if he encamped it on the far side of the Alps, the Romans would have plenty of time to raise another army to fight him, maybe on the far side of the Alps. He had previously ascertained that the Consular armada was at the Mouth of the Rhone.[79] At this point, he sent 500[79] of his finest cavalry men, the Numidians, down the left (east) bank[79] of the Rhone in order to acquire better intelligence concerning the consular army. These Numidians ran into 300[79] Roman horses that had been sent up the river along the left bank for the same purpose. The Numidians were defeated, and 240 of them were killed in this conflict between scouting parties; in addition to 140 Roman losses.[79] The Numidians were followed back to the Carthaginian camp - which was almost complete except for the elephants, which required more time getting across.[79] Seeing that Hannibal had not crossed with the whole of his force, the scouts raced back to the coast to alert the Consul.[79] Upon receiving this information, the Consul marched his army up the river and in the boats,[79] but arrived too late.[79]

In the face of hostile tribes,[79] the Consul opted to return to Italy and await the arrival of Hannibal as he debouched from the Alps.[79] However, in pursuance of the Senate's orders, the Consul ordered his brother, Gnaeus Scipio[79] to take a majority of the army to Spain.[79] The Consul was proposing menacing Hannibal's ever-extending and vulnerable lines of communications and cut them near their source. In spite of their established tactical system (formations and troop evolutions, etc.), the Romans were used to fighting (albeit very aggressively) by marching their troops to their enemies' army, forming their army up and attacking. They did not know how to force an enemy to battle by cutting off their communications, they were not aware of which flank was the strategic flank of an enemy in a battle. In addition, they were negligent about their order of march,[83] and early Roman history is littered with massacres of Consular armies by other nations because of their lack of proper precaution against these evils.[84]
The Numidians were some of the best Cavalry of all antiquity, but they were defeated by the outnumbered Roman cavalry. Some military critics believe that Hannibal ordered the Numidians to lead the Roman scouts back to the camp on the Rhone in order to entice the Consul to march in that direction while he made his escape.[79] The Romans have been criticized by military historians[who?] for their lack of a competent cavalry arm. They would later resort to auxiliaries for this arm in order to bring it up to standard; they never had a native Roman corps of cavalry which was a fine fighting force.[citation needed]
On getting the whole of his army on the left bank of the Rhone, Hannibal introduced his army to Magilus,[79] and some other less notable Gallic chiefs of the Po valley.[79][85] Hannibal's purpose was to inspire his men with confidence in the planned expedition by showing them Padane Gallic chieftans who offered them their aid. Speaking through an interpreter,[85] Magilus spoke of the support that the recently conquered Padane Gauls had for the Carthaginians and their mission of destroying the Roman symmachy.[79] Hannibal then addressed the officers himself.[79] The troops' enthusiasm was uplifted by Hannibal's inspiring address.[79]
Upon crossing the river, Hannibal ordered his infantry to start their march the day after the assembly, followed by the supply train.[86] Not knowing that the Romans were eventually going to set out for Italy, when his cavalry had crossed the river he ordered them to curtain his march on his southern flank, towards the sea.[79] His cavalry would have formed a screen which would have been employed to protect him from the Romans were they to advance upon him from that direction. The cavalry would skirmish with the Roman scouts, while giving the rest of the army time to form up. This contingency did not occur. Hannibal was in the rearguard with the elephants.[86] This was the direction that he assumed that the Romans would be most likely to advance from (that is from the west) as he had some idea that they were behind him. The rearguard was well manned to ensure that it could skirmish with the Roman army while the main body of his infantry and cavalry could form up for battle against the Romans if they should attack from that quarter. This contingency, however, also did not occur.
While assuming this order of march, Hannibal marched towards the Insula.[86] He had ordered his infantry to get a head start, and it marched to the Isere in six days,[87] marching 12.5 miles per day.[87] The cavalry and rear guard only took four days, a march of 19 miles per day.[87] In this period, the body as a whole had marched 75 miles.[87]
When Hannibal's army made contact with the Insula, he arrived in a Gallic chiefdom that was in the midst of a civil conflict.[88] For whatever reason, Hannibal chose the cause of the elder of the two combatants, Brancus.[87] After putting away the cause of the younger and less popularly supported one,[87] he formed an alliance with Brancus. From this tribe he received supplies that were required for the expedition across the Alps. In addition, he received Brancus' diplomatic protection. Up until the Alps proper, he did not have to fend off any tribes.
Ascent of the Alps
Hannibal marched in the direction of Mt. Du Chat towards the village of Aquste[89] and from there to Chevelu,[90] to the pass by Mt. Du Chat. There he found that the passes were fortified by the Allobroges.[91] He sent out spies to ascertain if there was any weakness in their disposition.[91] These spies found that the barbarians only maintained their position at the camp during the day, and left their fortified position at night.[91] In order to make the Allobroges believe that he did not deem a night assault prudent, he ordered that as many camp-fires be lit as possible, in order to induce them into believing that he was settling down before their encampment along the mountains. However, once they left their fortifications, he led his best troops up to their fortifications and seized control of the pass.[91]
Hiding his men in the mountain brush[92] on a cliff that arose immediately above and to the right off Hannibal's route of march, about 100 feet or so above the path,[92] Hannibal stationed his slingers and archers there. This overhang was an excellent place from which to attack an enemy while it was marching in column through the pass.[92] The descent from this pass was steep, and the Carthaginians were having a hard time marching down this side of the pass,[92] especially the baggage animals.[91] The Barbarians, seeing this, attacked anyway, in spite of their disadvantageous position.[92] More baggage animals were lost in the confusion of the Barbarian attack, and they rolled off of the precipices to their deaths.[92] The situation put Hannibal in a difficult situation. However, Hannibal, at the head of the same elite corps that he led to take the overhang,[91] led them against these determined barbarians. Virtually all of these barbarians died in the ensuing combat, as they were fighting with their backs to a steep precipice, trying to throw their arrows and darts uphill at the advancing Carthaginians.[91] After this contest of arms, the baggage was held together in good order and the Carthaginian army followed the road down to the plain that begins roughly at modern Bourget[disambiguation needed].[93]
This plain was 4–6 miles wide[93] at most places, and was almost entirely stripped of defenders since they were all stationed at the Mt. Du Chat pass. Hannibal marched his army to modern Chambery[93] and took their city easily, stripping it of all its horses, captives, beasts of burden and corn.[93] In addition, there were enough supplies for three days' rations for the army. This must have been welcome considering that no small portion of their supplies had been lost when the pack animals had fallen over the precipice in the course of the previous action. He then ordered this town to be destroyed, in order to demonstrate to the Barbarians of this country what would happen if they opposed him in the same fashion as this tribe had.[93]
He encamped there to give his men time to rest after their exhausting work, and to collect further rations.[94] Hannibal then addressed his army,[94] and we are informed that they were made to appreciate the extent of the effort they were about to undergo and were raised to good spirits in spite of the difficult nature of their undertaking.[94]
The Carthaginians continued their march after this. At modern Albertville[94] they came across the Centrones, who brought gifts and cattle for the troops.[94] In addition, they brought hostages in order to convince Hannibal of their commitment to his cause.[94] However, Hannibal, we are led to believe, was concerned and suspicious of these kind natives.[94] However, for whatever reason he concealed his suspicion of them. He marched with the guides they offered to him, in addition to his Insubrian[95] guides. However, in spite of their kind gestures, Hannibal found that his suspicions of the barbarians was correct, as the Barbarians attacked near where the pass of the Little St. Bernard tightens near the village of Seez. However, the military critics of esteem challenge that this was the place where the actual ambush took place. Napoleon,[96] notably believes that it could not have taken place at this spot. In spite of this, the valley through which the Carthaginians were marching was the only one that could sustain a population that was capable of attacking the Carthaginian army and simultaneously sustaining the Carthaginians on their march.[96]
Hannibal's concern led him to prepare for the possibility of an attack.[97] To ameliorate any potential evils that could arise, Hannibal arranged his army with the elephants in the front with the cavalry and the baggage, while the heavily armed troops were placed in the rear. While they were marching through a defile that had a white rock near its center (near modern St. Germain,[97]), the barbarians attacked. This attack took place after giving the Carthaginian army some time to start passing through the defile.[97] This was done in order to ensure that the army was divided and could not concentrate in order to drive the Barbarians back. Also, the Barbarians lobbed rocks at the Carthaginian army from above the pass.[97] Many more pack animals were killed, in addition to the confusion that this introduced into the ranks. However, Hannibal had made sure not to order his rearguard through.[97] Most of the Barbarians descended on his rearguard, which had not yet attempted to move through the pass and had been held in hand in battle order in case just such a contingency arose. The rearguard was able to hold the Barbarian attack back, and Hannibal saw that if he could keep the Barbarians away from the entrance of the defile, he would be able to get his army through the defile.[97]
This fierce action took place along the Reclus River,[97] which goes through a defile that had a large white rock by it.[97] This rock was three hundred feet high.[97] Among the natives of the Alps in latter days, a tradition existed in which large bones were dug out of the river bed.[97] Regardless of whether or not this is true, many of the elephants died in this action. On either side of the defile the Barbarians had placed troops in order to entrap the Carthaginians and massacre them while they were marching through.[97] The majority of the Barbarians were concentrated below,[97] and charged up once the Carthaginian marching column had made significant progress through the gap. This was done because once the Carthaginian marching column was stretched out because of the actual width of the defile, it would be more difficult for the Carthaginians to reconcentrate in time and drive back the Barbarians. However, backing the rear guard against the defile,[97] as the Barbarians would only be able to place a small front against the Carthaginian front, as it was backed against the defile which, prior to the actual ravine itself becomes progressively tighter[98] Hannibal planned to use his rear-guard to fight off as many as necessary for as long as necessary while the army passed through.[98]
Hannibal left the rear guard to complete its work during the evening[98] and sped ahead of the troops to lead the army to the summit.[98] There was a valley here that was a couple of miles long.[99] On the sides of the valley were steep slopes that protected the Carthaginian army. The army was enclosed in them.[99] This valley slopes in a North Easterly direction.[99] It accords completely with Polybius. In latter days, there was an enclosure built from stone that was constructed along the lines of druidic traditions The Carthaginian religion was druidic in its form, so the presence of this at least supports the idea that his army passed through this place.[99]

The army rested in this valley for two days.[100] There was snow at this point,[100] it was the end of October.[100] The weather conditions in the Alps at this time were more severe than they are in the present. The Army was dejected and seriously lacking in morale; many of their comrades had slipped and fallen or had been killed by barbarians. They had been marching for over five months (from their outset in Iberia)[100] and the army was seriously reduced in size. The army consisted of men from nations that did not experience such extreme cold, mostly from Africa and Iberia.[101] Hannibal therefore assembled his men, and is alleged by Polybius[100] to have indicated to them that the end of their labors was near and that soon they would be in the Po Valley.[100] He is said to have gestured to Italy, showing his soldiers where the Po was and the plains near it, and to have reminded them of Magilus, who had assured him of Gallic friendship and aid.[100] He is said to have gestured in the direction of Rome.[100] Their spirits were said to have been raised by this.[100] However, from the Little Saint Bernard, there is absolutely no way to see the Po.[100] Hannibal's speech, as depicted, could never have occurred.[100] Regardless, after this address occurred, in whatever form it did, if at all, after two days of resting, Hannibal ordered that the descent should be begun the next day.[100]
Descent to Italy
The snow on the Southern side of the Alps melts and thaws to a greater or lesser extent during the course of the day,[101] and then refreezes at night.[101] In addition, the Italian side of the Alps is much steeper;[101] many men lost their footing down this side of the Alps and died.
At an early point in their descent, the army came upon a section of the path that had been blocked by a landslide.[102] This section of the path was broken for about 300 yards.[102] Hannibal attempted to detour, by marching through a place where there was a great deal of snow [103] - the Alps are so high at this point that the snow from previous years does not even melt.[103] They made some headway, at the cost of no small portion of the baggage animals that were left,[103] before Hannibal came to appreciate that this route was impossible for an army.[103] Hannibal marched his men back to the point in their path prior to their detour, near the broken stretch of the path and set up camp.[103]
From here, Hannibal ordered his men to set about fixing the mule path.[103] Working in relays, the army set about this labor-intensive task under the eyes of Hannibal, who was constantly encouraging them.[103] Both the sick men,[103] and the men in health were put to this.[103] The next day the road was in sufficient condition to permit the cavalry and pack animals to cross the broken stretch of road;[103] Hannibal ordered that these should instantly race down below the foliage line (2 miles below the summit of the Alps)[104] and should be allowed access to the pastures there.[103]
However, Hannibal's remaining elephants, which were completely famished,[103] were still unable to proceed along the path. Hannibal's Numidian cavalry carried on working on the road,[103] taking three more days to fix it sufficiently to allow the elephants to cross.[103] Getting these creatures across this stretch of road, Hannibal raced ahead of the rearguard to the part of the army that was below the pasture line.[105] It took the army three days to march from this place into "the plains which are near the Po"[104] according to Polybius. Hannibal then focused on, according to Polybius, "[the] best means of reviving the spirits of his troops and restoring the men and horses to their former vigor and condition"[104] Hannibal ordered his men to encamp, at a point which is near modern Ivrea.[106]
References
- ^ Lancel, Serge, Hannibal, p. 71
- ^ a b c d e Walbank 1979, p. 187
- ^ Jr, Hans Delbrück; translated from the German by Walter J. Renfroe, (1990). History of the art of war. Lincoln, Neb.: University of Nebraska Press/ Bison Book. ISBN 978-0-8032-9199-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Dodge 1994, p. 131
- ^ Dodge, Theodore (1994). Hannibal. Mechanicsburg, PA: Greenhill Books.
- ^ Walbank 1979, p. 189
- ^ a b Delbrück 1990, p. 303
- ^ a b c Mommsen 1862, p. 15
- ^ a b Delbrück 1990, p. 312
- ^ a b c d e Dodge 1994, p. 146
- ^ a b c d e f Paton 1922, p. 243
- ^ Walbank, Polybius; transl. by Ian Scott-Kilvert; selected with an introduction by F.W. (1981). The rise of the Roman Empire (Reprint. ed.). Harmondsworth: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-044362-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e Walbank 1979, p. 111
- ^ Winlow, C.V. "Heritage History". Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- ^ a b c d Mommsen 1862, p. 94
- ^ a b c Dodge 1994, p. 147
- ^ a b Paton 1922, p. 273
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 92
- ^ a b c d e f g Walbank 1979, p. 190
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 148
- ^ a b Paton 1922, p. 331
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 157
- ^ a b Mommsen 1862, p. 95
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 62
- ^ a b c d Mommsen 1862, p. 65
- ^ Edwards, H.J. "The Histories". Loeb.
- ^ Paton, Polybius; with an English translation by W.R. (1922). The histories (Reprint. ed.). Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-99142-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Paton 1922, p. 237
- ^ a b c Paton 1922, p. 239
- ^ a b Mommsen 1862, p. 68
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 71
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 74
- ^ a b c d e Mommsen 1862, p. 75
- ^ Paton 1922, p. 287
- ^ a b c d e f Walbank 1979, p. 132
- ^ a b c d Walbank 1979, p. 133
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 77
- ^ a b Mommsen 1862, p. 78
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 80
- ^ a b Paton 1922, p. 309
- ^ a b Paton 1922, p. 311
- ^ Paton 1922, p. 313
- ^ Paton 1922, p. 317
- ^ a b c d e f g h Paton 1922, p. 319
- ^ a b Mommsen 1862, p. 81
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 82
- ^ a b Paton 1922, p. 321
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Paton 1922, p. 325
- ^ a b c d e Dodge 1994, p. 164
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 165
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 166-167
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Mommsen 1862, p. 96
- ^ Walbank 1979, p. 191
- ^ a b c Walbank 1979, p. 192
- ^ Walbank 1979, p. 193
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 91
- ^ a b c d Walbank 1979, p. 194
- ^ a b c d e f Walbank 1979, p. 209
- ^ Walbank 1979, p. 210
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Walbank 1979, p. 211
- ^ Walbank 1979, p. 212
- ^ a b c Dodge 1994, p. 173
- ^ a b Dodge 1994, p. 172
- ^ a b Dodge 1994, p. 171
- ^ a b c Dodge 1994, p. 176
- ^ a b c d e f Dodge 1994, p. 177
- ^ a b Walbank 1979, p. 213
- ^ Mommsen, Theodor (2009). The history of Rome (Digitally printed version ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-108-00974-4.
- ^ a b c d e f Walbank 1979, p. 214
- ^ a b Mommsen 1862, p. 102
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 127
- ^ a b c d e f g Dodge 1994, p. 178
- ^ a b c d e f g h Walbank 1979, p. 215
- ^ Mommsen 1862, p. 103
- ^ a b c Dodge 1994, p. 179
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Dodge 1994, p. 180
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Walbank 1979, p. 216
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Dodge 1994, p. 181
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u Dodge 1994, p. 184
- ^ a b c d e f g Dodge 1994, p. 182
- ^ a b c d Walbank 1979, p. 217
- ^ a b c Mommsen 1862, p. 104
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 63
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 64
- ^ a b Mommsen 1862, p. 105
- ^ a b c Dodge 1994, p. 187
- ^ a b c d e f Dodge 1994, p. 199
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 200
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 202
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 203
- ^ a b c d e f g Dodge 1994, p. 205
- ^ a b c d e f Dodge 1994, p. 206
- ^ a b c d e Dodge 1994, p. 208
- ^ a b c d e f g Dodge 1994, p. 210
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 211
- ^ a b Dodge 1994, p. 212
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Dodge 1994, p. 216
- ^ a b c d Dodge 1994, p. 218
- ^ a b c d Dodge 1994, p. 220
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Dodge 1994, p. 222
- ^ a b c d Dodge 1994, p. 223
- ^ a b Dodge 1994, p. 224
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Dodge 1994, p. 225
- ^ a b c Dodge 1994, p. 228
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 229
- ^ Dodge 1994, p. 230

