Hydrogen selenide
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hydrogen selenide
| |||
| Other names
Hydroselenic acid
selane selenium hydride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.071 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2202 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2Se | |||
| Molar mass | 80.98 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | decayed horseradish[1] | ||
| Density | 3.553 g/dm3 | ||
| Melting point | −65.73 °C (−86.31 °F; 207.42 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −41.25 °C (−42.25 °F; 231.90 K) | ||
| 0.70 g/100 mL | |||
| Solubility | soluble in CS2, phosgene | ||
| Vapor pressure | 9.5 atm (21°C)[1] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.89 | ||
| Conjugate acid | Selenonium | ||
| Conjugate base | Selenide | ||
| Structure | |||
| Bent | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Extremely toxic and flammable | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H220, H280, H330, H410 | |||
| P210, P260, P271, P273, P284, P304+P340, P310, P320, P377, P381, P391, P403, P403+P233, P405, P410+P403, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | flammable gas | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
0.3 ppm (guinea pig, 8 hr) 5.9 ppm (rat, 1 hr)[2] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm (0.2 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm (0.2 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1 ppm[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0284 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
H2O H2S H2Te H2Po | ||
Other cations
|
Na2Se Ag2Se | ||
Related compounds
|
Arsine | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Hydrogen selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula H2Se. This hydrogen chalcogenide is the simplest and most commonly encountered hydride of selenium. H2Se is a colorless, flammable gas under standard conditions. It is the most toxic selenium compound[3] with an exposure limit of 0.05 ppm over an 8-hour period.[4][5] Even at extremely low concentrations, this compound has a very irritating smell resembling that of decayed horseradish or 'leaking gas', but smells of rotten eggs at higher concentrations.
Structure and properties
H2Se adopts a bent structure with a H−Se−H bond angle of 91°[citation needed]. Consistent with this structure, three IR-active vibrational bands are observed: 2358, 2345, and 1034 cm−1.
The properties of H2S and H2Se are similar, although the selenide is more acidic with pKa = 3.89,[6] and the second pKa = 11,[6] or 15.05 ± 0.02 at 25 °C.[7]
Preparation
Industrially, it is produced by treating elemental selenium at T > 300 °C with hydrogen gas.[8] A number of routes to H2Se have been reported, which are suitable for both large and small scale preparations. In the laboratory, H2Se is usually prepared by the action of water on Al2Se3, concomitant with formation of hydrated alumina. A related reaction involves the acid hydrolysis of FeSe.[9]
- Al2Se3 + 6 H2O ⇌ 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 H2Se
H2Se can also be prepared by means of different methods based on the in situ generation in aqueous solution using boron hydride, Marsh test and Devarda's alloy. According to the Sonoda method, H2Se is generated from the reaction of H2O and CO on Se in the presence of Et3N.[10] H2Se can be purchased in cylinders.
Reactions
Elemental selenium can be recovered from H2Se through a reaction with aqueous sulfur dioxide (SO2).
- 2 H2Se + SO2 ⇌ 2 H2O + 2 Se + S
Its decomposition is used to prepare the highly pure element.
Applications
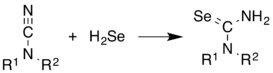
H2Se is commonly used in the synthesis of Se-containing compounds. It adds across alkenes. Illustrative is the synthesis of selenoureas from cyanamides.[11]
H2Se gas is used to dope semiconductors with selenium.
Safety
Hydrogen selenide is hazardous, being the most toxic selenium compound[3] and far more toxic than its congener hydrogen sulfide. The threshold limit value is 0.05 ppm. The gas acts as an irritant at concentrations higher than 0.3 ppm, which is the main warning sign of exposure; below 1 ppm, this is "insufficient to prevent exposure", while at 1.5 ppm the irritation is "intolerable".[5] Exposure at high concentrations, even for less than a minute, causes the gas to attack the eyes and mucous membranes; this causes cold-like symptoms for at least a few days afterwards. In Germany, the limit in drinking water is 0.008 mg/L, and the US EPA recommends a maximum contamination of 0.01 mg/L.[8][12]
Despite being highly toxic, no human fatalities have yet been reported. It is suspected that this is due to the gas' tendency to oxidise to form red selenium in mucous membranes; elemental selenium is less toxic than selenides are.[4]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0336". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Hydrogen selenide". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b http://www.epa.gov/ttnatw01/hlthef/selenium.html, US Environmental Protection Agency, Air Toxins website
- ^ a b https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/7783075.html, Documentation of Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations: Hydrogen Selenide, The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ a b https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/81-123/pdfs/0336.pdf Occupational Health Guideline for Hydrogen Selenide, The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, 1978
- ^ a b William M. Haynes; David R. Lide; Thomas J. Bruno, eds. (2017). CRC handbook of chemistry and physics : a ready-reference book of chemical and physical data (97th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida. ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3. OCLC 957751024.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Levy, D. E.; Myers, R. J. "Spectroscopic Determination of the Second Dissociation Constant of H2Se and the Activity Coefficients and Spectral Shifts of Its Ions" J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94(20), 7842-1847. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/j100383a020
- ^ a b Bernd E. Langner "Selenium and Selenium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a23_525.
- ^ Féher, F. In "Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry"; Brauer, E., Ed.; Academic: New York, 1963; 1, p 418.
- ^ Sonoda, N.; Kondo K.; Nagano, K.; Kambe, N.; Morimoto, F. Angewandte Chemie International Edition English 1980, vol. 19, page 308
- ^ Cohen, V.I. (1980). "A Convenient Synthesis of Mono-, N,N′-Di-, and Trisubstituted Selenoureas from Methyl Carbamimidothioates (S-Methylpseudothioureas)". Synthesis. 1980: 60–63. doi:10.1055/s-1980-28927.
- ^ https://www.osha.gov/dts/chemicalsampling/data/CH_246700.html, OSHA GENERAL INDUSTRY PEL: 0.05 ppm, 0.2 mg/m3 ,OSHA CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY PEL: 0.05 ppm, 0.2 mg/m3 TWA