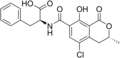
Ochratoxin
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2015) |
Ochratoxins are a group of mycotoxins produced by some Aspergillus species (mainly A. ochraceus and A. carbonarius, but also by 33% of A. niger industrial strains) and some Penicillium species, especially P. verrucosum. Ochratoxin A is the most prevalent and relevant fungal toxin of this group, while ochratoxins B and C are of lesser importance.
Ochratoxin A is known to occur in commodities such as cereals, coffee, dried fruit, and red wine. It is possibly a human carcinogen and is of special interest as it can be accumulated in the meat of animals. Exposure to ochratoxins through diet can cause acute toxicity in mammalian kidneys. Exposure to ochratoxin A has been associated with Balkan endemic nephropathy, a kidney disease with high mortality in people living near tributaries of the Danube River in Eastern Europe.[1]
It has been suggested that carriers of alleles associated with phenylketonuria may have been protected from spontaneous abortion caused by ochratoxin exposure, providing a heterozygous advantage for the alleles despite the possibility of severe intellectual disability in the more rare instance of inheritance from both parents.[2][3]
-
Ochratoxin B
-
Ochratoxin C
-
Ochratoxin TA
References
- ^ Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Manderville RA (2007). "Ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans". Mol Nutr Food Res. 51 (1): 61–99. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200600137. PMID 17195275.
- ^ "#261600 ICD+ PHENYLKETONURIA; PKU". Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man.
- ^ Woolf, L. I. "The heterozygote advantage in phenylketonuria." (Letter) Am. J. Hum. Genet. 38: 773-775, 1986.
External links
 Media related to Ochratoxins at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ochratoxins at Wikimedia Commons- Extensive information about mycotoxins and animal feed