Superior frontal gyrus
| Superior frontal gyrus | |
|---|---|
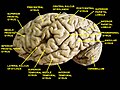
 Superior frontal gyrus of the human brain | |
 Coronal section through anterior cornua of lateral ventricles. Superior frontal gyrus is shown as yellow. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Frontal lobe |
| Artery | Anterior cerebral |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | gyrus frontalis superior |
| NeuroNames | 83 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1303 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.121 |
| TA2 | 5456 |
| FMA | 61857 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
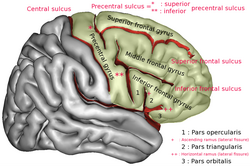
In neuroanatomy, the superior frontal gyrus (SFG, also marginal gyrus) is a gyrus – a ridge on the brain's cerebral cortex – which makes up about one third of the frontal lobe. It is bounded laterally by the superior frontal sulcus.[1]
The superior frontal gyrus is one of the frontal gyri.
Function
Self-awareness
In fMRI experiments, Goldberg et al. have found evidence that the superior frontal gyrus is involved in self-awareness, in coordination with the action of the sensory system.[2][3]
Laughter
In 1998, neurosurgeon Itzhak Fried described a 16-year-old female patient (referred to as "patient AK") who laughed when her SFG was stimulated with electric current during treatment for epilepsy.[4] Electrical stimulation was applied to the cortical surface of AK's left frontal lobe while an attempt was made to locate the focus of her epileptic seizures (which were never accompanied by laughter).
Fried identified a 2 cm by 2 cm area on the left SFG where stimulation produced laughter consistently (over several trials). AK reported that the laughter was accompanied by a sensation of merriment or mirth. AK gave a different explanation for the laughter each time, attributing it to an (unfunny) external stimulus. Thus, laughter was attributed to the picture she was asked to name (saying "the horse is funny"), or to the sentence she was asked to read, or to persons present in the room ("you guys are just so funny... standing around").
Increasing the level of stimulation current increased the duration and intensity of laughter. For example, at low currents only a smile was present, while at higher currents a louder, contagious laughter was induced. The laughter was also accompanied by the stopping of all activities involving speech or hand movements.
Additional images
-
Position of superior frontal gyrus (shown in red)
-
Left cerebral hemisphere seen from above
-
Lateral surface of left cerebral hemisphere
-
Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere
-
Cerebrum. Lateral view. Deep dissection. Superior frontal gyrus labelled at top-left.
-
Medial surface of right cerebral hemisphere.
-
Superior frontal gyrus highlighted in green on coronal T1 MRI images
-
Superior frontal gyrus highlighted in green on sagittal T1 MRI images
-
Superior frontal gyrus highlighted in green on transversal T1 MRI images
References
- ^ "BrainInfo". braininfo.rprc.washington.edu.
- ^ Goldberg I, Harel M, Malach R (2006). "When the brain loses its self: prefrontal inactivation during sensorimotor processing". Neuron. 50 (2): 329–39. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2006.03.015. PMID 16630842.
- ^ Watching the brain 'switch off' self-awareness at newscientist.com
- ^ Fried I, Wilson C, MacDonald K, Behnke E (1998). "Electric current stimulates laughter". Nature. 391 (6668): 650. doi:10.1038/35536. PMID 9490408.