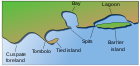
Inlet

An inlet is a (usually long and narrow) indentation of a shoreline, such as a small arm, bay, sound, fjord, lagoon or marsh,[1] that leads to an enclosed larger body of water such as a lake, estuary, gulf or marginal sea.
Overview

In marine geography, the term "inlet" usually refers to either the actual channel between an enclosed bay and the open ocean and is often called an "entrance", or a significant recession in the shore of a sea, lake or large river. A certain kind of inlet created by past glaciation is a fjord, typically but not always in mountainous coastlines and also in montane lakes.
Multi-arm complexes of large inlets or fjords may be called sounds, e.g., Puget Sound, Howe Sound, Karmsund (sund is Scandinavian for "sound"). Some fjord-type inlets are called canals, e.g., Portland Canal, Lynn Canal, Hood Canal, and some are channels, e.g., Dean Channel and Douglas Channel.
Tidal amplitude, wave intensity, and wave direction are all factors that influence sediment flux in inlets.[2]
On low slope sandy coastlines, inlets often separate barrier islands and can form as the result of storm events.[3] Alongshore sediment transport can cause inlets to close if the action of tidal currents flowing through an inlet do not flush accumulated sediment out of the inlet.[4]
See also
Notes
- ^ "inlet". Dictionary.com. Ask.com. Retrieved July 6, 2014.
- ^ Chen, Jia-Lin; Hsu, Tian-Jian; Shi, Fengyan; Raubenheimer, Britt; Elgar, Steve (2015-06-01). "Hydrodynamic and sediment transport modeling of New River Inlet (NC) under the interaction of tides and waves". Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 120 (6): 4028–4047. Bibcode:2015JGRC..120.4028C. doi:10.1002/2014JC010425. hdl:1912/7468. ISSN 2169-9291.
- ^ Safak, Ilgar; Warner, John C.; List, Jeffrey H. (2016-12-01). "Barrier island breach evolution: Alongshore transport and bay-ocean pressure gradient interactions". Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. 121 (12): 8720–8730. Bibcode:2016JGRC..121.8720S. doi:10.1002/2016jc012029. hdl:1912/8812. ISSN 2169-9291.
- ^ Swart, H. E. de; Zimmerman, J. T. F. (2009). "Morphodynamics of Tidal Inlet Systems". Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics. 41 (1): 203–229. Bibcode:2009AnRFM..41..203D. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.010908.165159.
References
- Bruun, Per; A.J. Mehta (1978). Stability of Tidal Inlets: Theory and Engineering. Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co. p. 510. ISBN 978-0-444-41728-2. be pub co