Supratrochlear artery
| Supratrochlear artery | |
|---|---|
 The ophthalmic artery and its branches (supratrochlear artery labeled at center top) | |
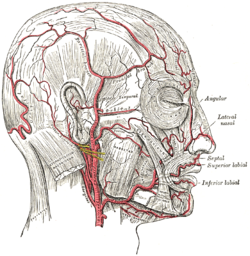 The arteries of the face and scalp (supratrochlear artery labeled at upper right, above eye) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Ophthalmic artery |
| Supplies | skin of medial forehead and scalp, underlying pericranium and frontalis muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria supratrochlearis, arteria frontalis |
| TA98 | A12.2.06.048 |
| TA2 | 4499 |
| FMA | 50025 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The supratrochlear artery (or frontal artery) is one of the terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It arises within the orbit.[1][2] It exits the orbit alongside the supratrochlear nerve. It contributes arterial supply to the skin, muscles and pericranium of the forehead.[3]
Anatomy
It branches from the ophthalmic artery near the trochlea of the superior oblique muscle in the orbit.[1][2]
Origin
The supratrochlear artery branches from the ophthalmic artery in the orbit near the trochlea of the superior oblique muscle.[1][2]
Course
After branching from the ophthalmic artery, it passes anteriorly through the superomedial orbit. It travels medial to the trochlear nerve. With the supratrochlear nerve, the supratrochlear artery exits the orbit through the supratrochlear notch (variably present), medial to the supraorbital foramen. It then ascends on the forehead.[citation needed]
Anastomoses
The supratrochlear artery anastomoses with the contralateral supratrochlear artery, and the ipsilateral supraorbital artery.[3]
Distribution
The supratrochlear artery supplies blood to the skin of the medial aspect of the forehead and scalp, as well as the underlying pericranium and frontalis muscle.[citation needed]
References
- ^ a b c Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (41st ed.). Philadelphia. ISBN 978-0-7020-5230-9. OCLC 920806541.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b c Agorgianitis, Loukas; Panagouli, Eleni; Tsakotos, George; Tsoucalas, Gregory; Filippou, Dimitrios (2020-02-29). "The Supratrochlear Artery Revisited: An Anatomic Review in Favor of Modern Cosmetic Applications in the Area". Cureus. 12 (2): e7141. doi:10.7759/cureus.7141. ISSN 2168-8184. PMC 7105260. PMID 32257686.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42nd ed.). New York. p. 780. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
