Barnsley fern

The Barnsley fern is a fractal named after the British mathematician Michael Barnsley who first described it in his book Fractals Everywhere.[1] He made it to resemble the black spleenwort, Asplenium adiantum-nigrum.
History
The fern is one of the basic examples of self-similar sets, i.e. it is a mathematically generated pattern that can be reproducible at any magnification or reduction. Like the Sierpinski triangle, the Barnsley fern shows how graphically beautiful structures can be built from repetitive uses of mathematical formulas with computers. Barnsley's 1988 book Fractals Everywhere is based on the course which he taught for undergraduate and graduate students in the School of Mathematics, Georgia Institute of Technology, called Fractal Geometry. After publishing the book, a second course was developed, called Fractal Measure Theory.[1] Barnsley's work has been a source of inspiration to graphic artists attempting to imitate nature with mathematical models.
The fern code developed by Barnsley is an example of an iterated function system (IFS) to create a fractal. This follows from the collage theorem. He has used fractals to model a diverse range of phenomena in science and technology, but most specifically plant structures.
IFSs provide models for certain plants, leaves, and ferns, by virtue of the self-similarity which often occurs in branching structures in nature. But nature also exhibits randomness and variation from one level to the next; no two ferns are exactly alike, and the branching fronds become leaves at a smaller scale. V-variable fractals allow for such randomness and variability across scales, while at the same time admitting a continuous dependence on parameters which facilitates geometrical modelling. These factors allow us to make the hybrid biological models... ...we speculate that when a V -variable geometrical fractal model is found that has a good match to the geometry of a given plant, then there is a specific relationship between these code trees and the information stored in the genes of the plant.
—Michael Barnsley et al.[2]
Construction

Barnsley's fern uses four affine transformations. The formula for one transformation is the following:
Barnsley shows the IFS code for his Black Spleenwort fern fractal as a matrix of values shown in a table.[3] In the table, the columns "a" through "f" are the coefficients of the equation, and "p" represents the probability factor.
| w | a | b | c | d | e | f | p | Portion generated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ƒ1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | Stem |
| ƒ2 | 0.85 | 0.04 | −0.04 | 0.85 | 0 | 1.60 | 0.85 | Successively smaller leaflets |
| ƒ3 | 0.20 | −0.26 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0 | 1.60 | 0.07 | Largest left-hand leaflet |
| ƒ4 | −0.15 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0 | 0.44 | 0.07 | Largest right-hand leaflet |
These correspond to the following transformations:
Computer generation
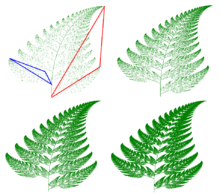
Though Barnsley's fern could in theory be plotted by hand with a pen and graph paper, the number of iterations necessary runs into the tens of thousands, which makes use of a computer practically mandatory. Many different computer models of Barnsley's fern are popular with contemporary mathematicians. As long as math is programmed correctly using Barnsley's matrix of constants, the same fern shape will be produced.
The first point drawn is at the origin (x0 = 0, y0 = 0) and then the new points are iteratively computed by randomly applying one of the following four coordinate transformations:[4][5]
ƒ1
- xn + 1 = 0
- yn + 1 = 0.16 yn
This coordinate transformation is chosen 1% of the time and just maps any point to a point in the first line segment at the base of the stem. In the iterative generation, it acts as a reset to the base of the stem. Crucially it does not reset exactly to (0,0) which allows it to fill in the base stem which is translated and serves as a kind of "kernel" from which all other sections of the fern are generated via transformations ƒ2, ƒ3, ƒ4.
ƒ2
- xn + 1 = 0.85 xn + 0.04 yn
- yn + 1 = −0.04 xn + 0.85 yn + 1.6
This transformation encodes the self-similarity relationship of the entire fern with the sub-structure which consists of the fern with the removal of the section which includes the bottom two leaves. In the matrix representation, it can be seen to be a slight clockwise rotation, scaled to be slightly smaller and translated in the positive y direction. In the iterative generation, this transformation is applied with probability 85% and is intuitively responsible for the generation of the main stem, and the successive vertical generation of the leaves on either side of the stem from their "original" leaves at the base.
ƒ3
- xn + 1 = 0.2 xn − 0.26 yn
- yn + 1 = 0.23 xn + 0.22 yn + 1.6
This transformation encodes the self-similarity of the entire fern with the bottom left leaf. In the matrix representation, it is seen to be a near-90° counter-clockwise rotation, scaled down to approximately 30% size with a translation in the positive y direction. In the iterative generation, it is applied with probability 7% and is intuitively responsible for the generation of the lower-left leaf.
ƒ4
- xn + 1 = −0.15 xn + 0.28 yn
- yn + 1 = 0.26 xn + 0.24 yn + 0.44
Similarly, this transformation encodes the self-similarity of the entire fern with the bottom right leaf. From its determinant it is easily seen to include a reflection and can be seen as a similar transformation as ƒ3 albeit with a reflection about the y-axis. In the iterative-generation, it is applied with probability 7% and is responsible for the generation of the bottom right leaf.
Mutant varieties


By playing with the coefficients, it is possible to create mutant fern varieties. In his paper on V-variable fractals, Barnsley calls this trait a superfractal.[2]
One experimenter has come up with a table of coefficients to produce another remarkably naturally looking fern however, resembling the Cyclosorus or Thelypteridaceae fern. These are:[6][7]
| w | a | b | c | d | e | f | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ƒ1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 | −0.4 | 0.02 |
| ƒ2 | 0.95 | 0.005 | −0.005 | 0.93 | −0.002 | 0.5 | 0.84 |
| ƒ3 | 0.035 | −0.2 | 0.16 | 0.04 | −0.09 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| ƒ4 | −0.04 | 0.2 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.083 | 0.12 | 0.07 |
Pseudocode
draw all pixels on screen white
x = 0.0
y = 0.0
n = 0.0
xn = 0.0
yn = 0.0
while n < maximum iterations:
r = random() between 0 and 1
if r < 0.01
xn = 0.0
yn = 0.16 * y
else if r < 0.86
xn = 0.85 * x + 0.04 * y
yn = -0.04 * x + 0.85 * y + 1.6
else if r < 0.93
xn = 0.2 * x - 0.26 * y
yn = 0.23 * x + 0.22 * y + 1.6
else
xn = -0.15 * x + 0.28 * y
yn = 0.26 * x + 0.24 * y + 0.44
draw pixel (xn, yn) green on screen
x = xn
y = yn
increment n
References
- ^ a b Fractals Everywhere, Boston, MA: Academic Press, 1993, ISBN 0-12-079062-9
- ^ a b Michael Barnsley, et al.,""V-variable fractals and superfractals"" (PDF). (2.22 MB)
- ^ Fractals Everywhere, table III.3, IFS code for a fern.
- ^ Barnsley, Michael (2000). Fractals everywhere. Morgan Kaufmann. p. 86. ISBN 0-12-079069-6. Retrieved 2010-01-07.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric. "Barnsley's Fern". Retrieved 2010-01-07.
- ^ Other fern varieties with supplied coefficients
- ^ A Barnsley fern generator





