Polysporangiophyte
| Polysporangiophyte Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
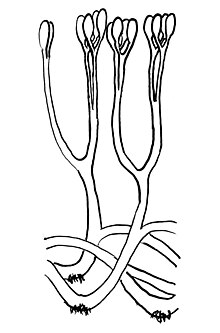
| Reconstruction of Aglaophyton, illustrating bifurcating axes with terminal sporangia, and rhizoids. | |

| |
| Modern polysporangiophyte, monarch fern is a vascular plant. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Embryophytes |
| Clade: | Polysporangiophytes Kenrick & Crane (1997) |
| Subgroups | |
| |
Polysporangiophytes, also called polysporangiates or formally Polysporangiophyta, are plants in which the spore-bearing generation (sporophyte) has branching stems (axes) that bear sporangia. The name literally means 'many sporangia plant'. The clade includes all land plants (embryophytes) except for the bryophytes (liverworts, mosses and hornworts) whose sporophytes are normally unbranched, even if a few exceptional cases occur.[1] While the definition is independent of the presence of vascular tissue, all living polysporangiophytes also have vascular tissue, i.e., are vascular plants or tracheophytes. Extinct polysporangiophytes are known that have no vascular tissue and so are not tracheophytes.
Early polysporangiophytes
History of discovery
Paleobotanists distinguish between micro- and megafossils. Microfossils are primarily spores, either single or in groups. Megafossils are preserved parts of plants large enough to show structure, such as stem cross-sections or branching patterns.[2]
Dawson, a Canadian geologist and paleobotanist, was the first to discover and describe a megafossil of a polysporangiophyte. In 1859 he published a reconstruction of a Devonian plant, collected as a fossil from the Gaspé region of Canada, which he named Psilophyton princeps. The reconstruction shows horizontal and upright stem-like structures; no leaves or roots are present. The upright stems or axes branch dichotomously and have pairs of spore-forming organs (sporangia) attached to them. Cross-sections of the upright axes showed that vascular tissue was present. He later described other specimens. Dawson's discoveries initially had little scientific impact; Taylor et al. speculate that this was because his reconstruction looked very unusual and the fossil was older than was expected.[3]
From 1917 onwards, Robert Kidston and William H. Lang published a series of papers describing fossil plants from the Rhynie chert – a fine-grained sedimentary rock found near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, now dated to the Pragian of the Lower Devonian (around 411 to 408 million years ago). The fossils were better-preserved than Dawson's, and showed clearly that these early land plants did indeed consist of generally naked vertical stems arising from similar horizontal structures. The vertical stems were dichotomously branched with some branches ending in sporangia.[3]
Since these discoveries, similar megafossils have been discovered in rocks of Silurian to mid-Devonian age throughout the world, including Arctic Canada, the eastern US, Wales, the Rhineland of Germany, Kazakhstan, Xinjiang and Yunnan in China, and Australia.[4]
As of 2019[update], Eohostimella, dated to the Llandovery epoch (444 to 433 million years ago), is one of the earliest fossils that has been identified as a polysporangiophyte.[5][6] Fossils assigned to the genus Cooksonia, which is more certainly a polysporangiophyte, have been dated to the succeeding Wenlock epoch (433 to 427 million years ago).[7][8]
Taxonomy
The concept of the polysporangiophytes, more formally called Polysporangiophyta, was first published in 1997 by Kenrick and Crane.[9] (The taxobox at the right represents their view of the classification of the polysporangiophytes.) The defining feature of the clade is that the sporophyte branches and bears multiple sporangia. This distinguishes polysporangiophytes from liverworts, mosses and hornworts, which have unbranched sporophytes each with a single sporangium. Polysporangiophytes may or may not have vascular tissue – those that do are vascular plants or tracheophytes.[citation needed]
Prior to that, most of the early polysporangiophytes had been placed in a single order, Psilophytales, in the class Psilophyta, established in 1917 by Kidston and Lang.[10] The living Psilotaceae, the whisk-ferns, were sometimes added to the class, which was then usually called Psilopsida.[11]
As additional fossils were discovered and described, it became apparent that the Psilophyta were not a homogeneous group of plants. In 1975, Banks expanded on his earlier 1968 proposal that split it into three groups at the rank of subdivision.[12][13] These groups have since been treated at the ranks of division,[14] class[15] and order.[16] A variety of names have been used, which the table below summarizes.
| Division | Subdivision | Class | Order | Informal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhyniophyta | Rhyniophytina | Rhyniopsida (Rhyniophytopsida)[17] | Rhyniales | rhyniophyte |
| Zosterophyllophyta | Zosterophyllophytina | Zosterophyllopsida | Zosterophyllales | zosterophyll (zosterophyllophyte) |
| Trimerophyta (Trimerophytophyta)[18] | Trimerophytina (Trimerophytophytina) | Trimeropsida (Trimerophytopsida) | Trimerophytales | trimerophyte |
For Banks, rhyniophytes comprised simple leafless plants with terminal sporangia (e.g., Cooksonia, Rhynia) with centrarch xylem; zosterophylls comprised plants with lateral sporangia that split distally (away from their attachment) to release their spores, and had exarch strands of xylem (e.g., Gosslingia). Trimerophytes comprised plants with large clusters of downwards curving terminal sporangia that split along their length to release their spores and had centrarch xylem strands (e.g., Psilophyton).[19]
Research by Kenrick and Crane that established the polysporangiophytes concluded that none of Banks' three groups were monophyletic. The rhyniophytes included "protracheophytes", which were precursors to vascular plants (e.g., Horneophyton, Aglaophyton); basal tracheophytes (e.g., Stockmansella, Rhynia gwynne-vaughanii); and plants allied to the lineages that led to the living club-mosses and allies as well as ferns and seed plants (e.g., Cooksonia species). The zosterophylls did contain a monophyletic clade, but some genera previously included in the group fell outside this clade (e.g., Hicklingia, Nothia). The trimerophytes were paraphyletic stem groups to both the crown group ferns and the crown group seed plants.[20][21]
Many researchers have urged caution in the classification of early polysporangiophytes. Taylor et al. note that basal groups of early land plants are inherently difficult to characterize since they share many characters with all later-evolving groups (i.e., have multiple plesiomorphies).[14] In discussing the classification of the trimerophytes, Berry and Fairon-Demaret say that reaching a meaningful classification requires "a breakthrough in knowledge and understanding rather than simply a reinterpretation of the existing data and the surrounding mythology".[22] Kenrick and Crane's cladograms have been questioned – see the Evolution section below.
As of February 2011[update], there appears to be no complete Linnean (i.e., rank-based) classification for early polysporangiophytes that is consistent with Kenrick and Crane's cladistic analysis and subsequent research, though Cantino et al. have published a Phylocode classification.[23] Banks' three groups continue to be used for convenience.[14]
Phylogeny
A major cladistic study of land plants was published in 1997 by Kenrick and Crane; this both established the concept of the polysporangiophytes and presented a view of their phylogeny.[9] Since 1997 there have been continual advances in understanding plant evolution, using RNA and DNA genome sequences and chemical analyses of fossils (e.g., Taylor et al. 2006[24]), resulting in revisions to this phylogeny.
In 2004, Crane et al. published a simplified cladogram for the polysporangiophytes (which they call polysporangiates), based on a number of figures in Kenrick and Crane (1997).[10] Their cladogram is reproduced below (with some branches collapsed into 'basal groups' to reduce the size of the diagram). Their analysis is not accepted by other researchers; for example Rothwell and Nixon say that the broadly defined fern group (moniliforms or monilophytes) is not monophyletic.[25]
| polysporangiophytes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
More recently, Gerrienne and Gonez have suggested a slightly different characterization of the early diverging polysporangiophytes:[26]
| Polysporangiophytes |
| ||||||||||||
The paraphyletic protracheophytes, such as Aglaophyton, have water-conducting vessels like those of mosses, i.e., without cells containing thickened cell walls. The paratracheophytes, a name intended to replace Rhyniaceae or Rhyniopsida, have 'S-type' water-conducting cells, i.e., cells whose walls are thickened but in a much simpler fashion than those of true vascular plants, the eutracheophytes.[26]
Evolution

If the cladogram above is correct it has implications for the evolution of land plants. The earliest diverging polysporangiophytes in the cladogram are the Horneophytopsida, a clade at the 'protracheophyte' grade that is sister to all other polysporangiophytes. They had essentially an isomorphic alternation of generations (meaning that the sporophytes and gametophytes were equally free living), which might suggest that both the gametophyte-dominant life style of bryophytes and the sporophyte-dominant life style of vascular plants evolved from this isomorphic condition. They were leafless and did not have true vascular tissues. In particular, they did not have tracheids: elongated cells that help transport water and mineral salts, and that develop a thick lignified wall at maturity that provides mechanical strength. Unlike plants at the bryophyte grade, their sporophytes were branched.[27]
According to the cladogram, the genus Rhynia illustrates two steps in the evolution of modern vascular plants. Plants have vascular tissue, albeit significantly simpler than modern vascular plants. Their gametophytes are distinctly smaller than their sporophytes (but have vascular tissue, unlike almost all modern vascular plants).[28]
The remainder of the polysporangiophytes divide into two lineages, a deep phylogenetic split that occurred in the early to mid Devonian, around 400 million years ago. Both lineages have developed leaves, but of different kinds. The lycophytes, which make up less than 1% of the species of living vascular plants, have small leaves (microphylls or more specifically lycophylls), which develop from an intercalary meristem (i.e., the leaves effectively grow from the base). The euphyllophytes are by far the largest group of vascular plants, in terms of both individuals and species. Euphyllophytes have large 'true' leaves (megaphylls), which develop through marginal or apical meristems (i.e., the leaves effectively grow from the sides or the apex). (Horsetails have secondarily reduced megaphylls resembling microphylls.)[29]
Both the cladogram derived from Kenrick and Crane's studies and its implications for the evolution of land plants have been questioned by others. A 2008 review by Gensel notes that recently discovered fossil spores suggest that tracheophytes were present earlier than previously thought; perhaps earlier than supposed stem group members. Spore diversity suggests that there were many plant groups, of which no other remains are known. Some early plants may have had heteromorphic alternation of generations, with later acquisition of isomorphic gametophytes in certain lineages.[30]
The cladogram above shows the 'protracheophytes' diverging earlier than the lycophytes; however, lycophytes were present in the Ludfordian stage of the Silurian around 430 to 420 million years ago, long before the 'protracheophytes' found in the Rhynie chert, dated to the Pragian stage of the Devonian around 410 million years ago.[31] However, it has been suggested that the poorly preserved Eohostimella, found in deposits of Early Silurian age (Llandovery, around 440 to 430 million years ago), may be a rhyniophyte.[6]
Boyce has shown that the sporophytes of some Cooksonia species and allies ('cooksonioids') had stems that were too narrow to have supported sufficient photosynthetic activity for them to be independent of their gametophytes – inconsistent with their position in the cladogram.[32]
Because the stomata in mosses, hornworts and polysporangiophytes are viewed as homologous, it has been suggested they belong in a natural group named stomatophytes.[33]
The evolutionary history of plants is far from settled.[citation needed]
Notes and references
- ^ Harrison, C. Jill; Morris, Jennifer L. (2017). "The origin and early evolution of vascular plant shoots and leaves". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 373 (1739): 20160496. doi:10.1098/rstb.2016.0496. PMC 5745332. PMID 29254961.
- ^ See, e.g., Edwards, D. & Wellman, C. (2001), "Embryophytes on Land: The Ordovician to Lochkovian (Lower Devonian) Record" in Gensel & Edwards 2001, pp. 3–28
- ^ a b Taylor, T.N.; Taylor, E.L. & Krings, M. (2009), Paleobotany, The Biology and Evolution of Fossil Plants (2nd ed.), Amsterdam; Boston: Academic Press, ISBN 978-0-12-373972-8, p. 225ff
- ^ Gensel, P.G. & Edwards, D., eds. (2001), Plants invade the Land : Evolutionary & Environmental Perspectives, New York: Columbia University Press, ISBN 978-0-231-11161-4, chapters 2, 6, 7
- ^ Edwards, D. & Wellman, C. (2001), "Embryophytes on Land: The Ordovician to Lochkovian (Lower Devonian) Record", in Gensel, P. & Edwards, D. (eds.), Plants Invade the Land : Evolutionary and Environmental Perspectives, New York: Columbia University Press, pp. 3–28, ISBN 978-0-231-11161-4, p. 4
- ^ a b Niklas, Karl J. (1979), "An Assessment of Chemical Features for the Classification of Plant Fossils", Taxon, 28 (5/6): 505–516, doi:10.2307/1219787, JSTOR 1219787
- ^ Edwards, D. & Feehan, J. (1980), "Records of Cooksonia-type sporangia from late Wenlock strata in Ireland", Nature, 287 (5777): 41–42, Bibcode:1980Natur.287...41E, doi:10.1038/287041a0, S2CID 7958927
- ^ Libertín, Milan; Kvaček, Jiří; Bek, Jiří; Žárský, Viktor & Štorch, Petr (2018), "Sporophytes of polysporangiate land plants from the early Silurian period may have been photosynthetically autonomous", Nature Plants, 4 (5): 269–271, doi:10.1038/s41477-018-0140-y, PMID 29725100, S2CID 19151297
- ^ a b Kenrick & Crane 1997a, pp. 139–140, 249
- ^ a b Crane, P.R.; Herendeen, P. & Friis, E.M. (2004), "Fossils and plant phylogeny", American Journal of Botany, 91 (10): 1683–99, doi:10.3732/ajb.91.10.1683, PMID 21652317
- ^ Taylor, Taylor & Krings 2009, p. 226.
- ^ Banks, H.P. (1968), "The early history of land plants", in Drake, E.T. (ed.), Evolution and Environment: A Symposium Presented on the Occasion of the 100th Anniversary of the Foundation of Peabody Museum of Natural History at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, pp. 73–107, cited in Banks 1980
- ^ Banks, H.P. (1975), "Reclassification of Psilophyta", Taxon, 24 (4): 401–413, doi:10.2307/1219491, JSTOR 1219491
- ^ a b c Taylor, Taylor & Krings 2009, p. 227
- ^ See, e.g., Berry, C.M. & Fairon-Demaret, M. (2001), "The Middle Devonian Flora Revisited", in Gensel & Edwards 2001, pp. 120–139
- ^ Banks, H.P. (1970), Evolution and Plants of the Past, London: Macmillan Press, ISBN 978-0-333-14634-7, p. 57
- ^ Although this name has appeared in some sources, e.g., Knoll, Andrew H. (1998-01-01), "Review of The Origin and Early Diversification of Land Plants: A Cladistic Study by Paul Kenrick; Peter Crane", International Journal of Plant Sciences, 159 (1): 172–174, doi:10.1086/297535, JSTOR 2474949, it appears to be a mistake, as it is not in accord with Article 16 of the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature.
- ^ The name is based on the genus Trimerophyton; Article 16.4 of the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature allows the phyton part to be omitted before -ophyta, -ophytina, and -opsida.
- ^ Banks, H.P. (1980), "The role of Psilophyton in the evolution of vascular plants", Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 29: 165–176, doi:10.1016/0034-6667(80)90056-1
- ^ Kenrick, Paul & Crane, Peter R. (1997a), The Origin and Early Diversification of Land Plants: A Cladistic Study, Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press, ISBN 978-1-56098-730-7
- ^ Kenrick, P. & Crane, P.R. (1997b), "The origin and early evolution of plants on land", Nature, 389 (6646): 33–39, Bibcode:1997Natur.389...33K, doi:10.1038/37918, S2CID 3866183
- ^ Berry, C. M. & Fairon-Demaret, M. (2001), "The Middle Devonian Flora Revisited", in Gensel & Edwards 2001, p. 127
- ^ Cantino, Philip D.; James A. Doyle; Sean W. Graham; Walter S. Judd; Richard G. Olmstead; Douglas E. Soltis; Pamela S. Soltis; Michael J. Donoghue (2007), "Towards a Phylogenetic Nomenclature of Tracheophyta", Taxon, 56 (3): 822–846, doi:10.2307/25065865, JSTOR 25065865
- ^ Taylor, D.W.; Li, Hongqi; Dahl, Jeremy; Fago, F.J.; Zinneker, D.; Moldowan, J.M. (2006), "Biogeochemical evidence for the presence of the angiosperm molecular fossil oleanane in Paleozoic and Mesozoic non-angiospermous fossils", Paleobiology, 32 (2): 179–90, doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2006)32[179:BEFTPO]2.0.CO;2, ISSN 0094-8373, S2CID 83801635
- ^ Rothwell, G.W. & Nixon, K.C. (2006), "How Does the Inclusion of Fossil Data Change Our Conclusions about the Phylogenetic History of Euphyllophytes?", International Journal of Plant Sciences, 167 (3): 737–749, doi:10.1086/503298, S2CID 86172890
- ^ a b Gerrienne, P. & Gonez, P. (2011), "Early evolution of life cycles in embryophytes: A focus on the fossil evidence of gametophyte/sporophyte size and morphological complexity", Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 49: 1–16, doi:10.1111/j.1759-6831.2010.00096.x, S2CID 29795245
- ^ Bateman, R.M.; Crane, P.R.; Dimichele, W.A.; Kenrick, P.R.; Rowe, N.P.; Speck, T.; Stein, W.E. (1998), "Early Evolution of Land Plants: Phylogeny, Physiology, and Ecology of the Primary Terrestrial Radiation", Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 29 (1): 263–92, doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.29.1.263, S2CID 44508826, p. 270
- ^ Kerp, H.; Trewin, N.H.; Hass, H. (2004), "New gametophytes from the Early Devonian Rhynie chert", Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 94 (4): 411–28, doi:10.1017/s026359330000078x, S2CID 128629425
- ^ Pryer, K.M.; Schuettpelz, E.; Wolf, P.G.; Schneider, H.; Smith, A.R.; Cranfill, R. (2004), "Phylogeny and evolution of ferns (monilophytes) with a focus on the early leptosporangiate divergences", American Journal of Botany, 91 (10): 1582–98, doi:10.3732/ajb.91.10.1582, PMID 21652310, pp. 1582–3
- ^ Gensel, Patricia G. (2008), "The Earliest Land Plants", Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst., 39: 459–77, doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.39.110707.173526, pp. 470–2
- ^ Kotyk, M.E.; Basinger, J.F.; Gensel, P.G.; de Freitas, T.A. (2002), "Morphologically complex plant macrofossils from the Late Silurian of Arctic Canada", Am. J. Bot., 89 (6): 1004–1013, doi:10.3732/ajb.89.6.1004, PMID 21665700
- ^ Boyce, C.K. (2008), "How green was Cooksonia? The importance of size in understanding the early evolution of physiology in the vascular plant lineage", Paleobiology, 34 (2): 179–194, doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2008)034[0179:HGWCTI]2.0.CO;2, ISSN 0094-8373, S2CID 36688488
- ^ Ligrone, R.; Duckett, J.G.; Renzaglia, K.S. (2012). "Major transitions in the evolution of early land plants: a bryological perspective". Annals of Botany. 109 (5): 851–71. doi:10.1093/aob/mcs017. PMC 3310499. PMID 22356739.
External links
- Cladogram Archived 2012-12-04 at archive.today from Crane, Herendeen & Friis 2004
