.32 S&W
| .32 S&W | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||
| Type | Handgun | |||||||||||
| Place of origin | United States | |||||||||||
| Production history | ||||||||||||
| Designer | Smith & Wesson | |||||||||||
| Designed | 1878 | |||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||
| Case type | Rimmed, straight | |||||||||||
| Bullet diameter | .312 in (7.9 mm) | |||||||||||
| Neck diameter | .334 in (8.5 mm) | |||||||||||
| Base diameter | .335 in (8.5 mm) | |||||||||||
| Rim diameter | .375 in (9.5 mm) | |||||||||||
| Rim thickness | .045 in (1.1 mm) | |||||||||||
| Case length | .61 in (15 mm) | |||||||||||
| Overall length | .92 in (23 mm) | |||||||||||
| Primer type | Berdan or Boxer small pistol | |||||||||||
| Ballistic performance | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Source(s): "Cartridges of the World" [1] | ||||||||||||
The .32 S&W cartridge (also known as the .32 S&W Short) was introduced in 1878 for Smith & Wesson pocket revolvers. It was originally designed as a black powder cartridge. The .32 S&W was offered to the public as a light defense cartridge for "card table" distances.[2]
Design
Originally designed by the Union Metallic Cartridge Company (UMC) as a black powder cartridge using nine grains of black powder, the round has been loaded with smokeless powder exclusively since 1940.[3] It is low-powered and perfect for use in small frame concealable revolvers and derringers. The round remained popular in the United States and Europe long after the firearms chambered for it were out of production.[1] At one time, it was considered to be the bare minimum for a self-defense round and was judged unsuitable for police work.[1]
For defensive uses, the .32 S&W is grouped with other turn-of-the-century cartridges designed for use in "belly guns"—guns meant for use in point-blank defensive situations, such as in a carriage or an alleyway. These cartridges include the .25 ACP, and the .22 Short, Long, and Long Rifle. For comparison, the .32 S&W projectile is over 40% larger in diameter and over twice as heavy as the 40-grain lead round-nose bullet used in the .22 Long Rifle of its day (known as standard velocity today). The .32 S&W's velocity of approximately 700 feet per second (210 m/s) was very close to the .22 Long Rifle's performance from a sub-3-inch (76 mm) barrel, but with larger diameter and better sectional density.
Although the .32 S&W's round-nose bullet was less than optimal for defense, it did offer significant improvement over these other common handgun calibers of the day. This performance made guns chambered in the cartridge very popular as a gentleman's "vest gun".[citation needed]
Derivatives
The .32 S&W Long cartridge is derived from the .32 S&W, by increasing the overall brass case length, to hold more powder. Since the .32 S&W headspaces on the rim and shares the rim dimensions and case and bullet diameters of the longer .32 S&W Long, the .32 H&R Magnum cartridges, and the .327 Federal Magnum, .32 S&W cartridges may be fired in arms chambered for these longer cartridges. Longer cartridges are unsafe in short chambers, so none of these longer and more powerful cartridges should be loaded into arms designed for the .32 S&W.[4]
The .32 Merwin & Hulbert cartridge is the same as the .32 S&W. Merwin & Hulbert rebranded the .32 S&W and .38 S&W with their own name, but dimensionally they were the same.[citation needed]
Use in assassinations
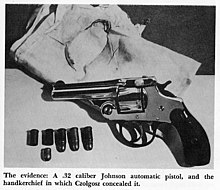
Guns chambered in .32 S&W have been used in at least three notable assassinations:
- Gaetano Bresci used an Iver Johnson revolver chambered in .32 S&W to assassinate King Umberto I of Italy on July 29, 1900.[5] Bresci hit his victim with four shots.
- Leon Czolgosz also used an Iver Johnson revolver chambered in .32 S&W to assassinated United States President William McKinley at the Temple of Music in Buffalo, New York, on September 6, 1901.[6] McKinley was shot twice in the abdomen at close range, and although he did not die immediately, he eventually succumbed to gangrene on September 14.
- Giuseppe Zangara used a United States Revolver Company (a subsidiary of Iver Johnson) revolver chambered in .32 S&W to assassinate Anton Cermak, Mayor of Chicago, on February 15, 1933, in what may have been an attempt to assassinate President-elect Franklin D. Roosevelt.[7] Cermak was shot in the lung and died on March 6, 1933.
Chambered weapons
|
Notable guns chambered in .32 S&W include: |
 |
Other gun types, or gun manufacturers, using .32 S&W include:
|
See also
References
- ^ a b c Barnes, Frank C. (2006) [1965]. Skinner, Stan (ed.). Cartridges of the World (11th ed.). Iola, WI, USA: Gun Digest Books. pp. 290, 337. ISBN 0-89689-297-2.
- ^ Chicoine, David (28 September 2005). Antique Firearms Assembly/Disassembly: The Comprehensive Guide to Pistols, Rifles & Shotguns. Iola, Wisconsin: Krause Publications. pp. 177–181. ISBN 0-87349-767-8.
- ^ Barnes, Frank C. (2016). Cartridges of the World (15th ed.). p. 430.
- ^ Treakle, John W. American Rifleman (May 2011) p.42
- ^ Allen, John L., Jr. 2001, September 14. "He executed justice - papal execution Giovanni Battista Bugatti's life and work". National Catholic Reporter.
- ^ Gun Review: Iver Johnson .32 S&W - The Truth About Guns
- ^ Robert Sherrill (February 1975). The Saturday night special: and other guns with which Americans won the West, protected bootleg franchises, slew wildlife, robbed countless banks, shot husbands purposely and by mistake, and killed presidents--together with the debate over continuing same. Penguin Books. p. 167.
