Lecompton, Kansas
Lecompton, Kansas | |
|---|---|
 Constitution Hall (2009) | |
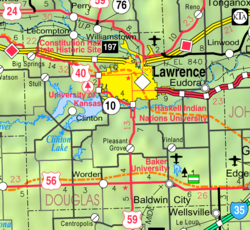
 Location within Douglas County and Kansas | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 39°2′40″N 95°23′41″W / 39.04444°N 95.39472°W[1] | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Kansas |
| County | Douglas |
| Founded | 1854 |
| Incorporated | 1855 |
| Named for | Samuel Lecompte |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1.76 sq mi (4.57 km2) |
| • Land | 1.76 sq mi (4.55 km2) |
| • Water | 0.01 sq mi (0.02 km2) |
| Elevation | 925 ft (282 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 625 |
| • Estimate (2019)[4] | 654 |
| • Density | 372.44/sq mi (143.79/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| Area code | 785 |
| FIPS code | 20-39150 [1] |
| GNIS ID | 478805 [1] |
| Website | lecompton.org |
Lecompton (pronounced /lɪˈkɒmptən/)[5] is a city in Douglas County, Kansas, United States.[1] As of the 2010 census, the city population was 625.[6]
Lecompton was the former territorial capital of Kansas from 1855–61, and during much of the 1850s, the Douglas County seat. During this time, the city played a major historical role in pre-Civil War America, as it was a hotbed of proslavery sentiment. This time period was known as Bleeding Kansas, due to the violence perpetrated by both the pro- and anti-slavery factions in the eastern part of the state.
History
19th century
Lecompton was founded in 1854 and planted on a bluff on the south bank of the Kansas River. It was originally called "Bald Eagle", but the name was changed to Lecompton in honor of Samuel Lecompte, the chief justice of the territorial supreme court.[7] In August 1855, the town became the capital of the Kansas Territory after President James Buchanan appointed Andrew Horatio Reeder as governor and charged him and his officials with establishing government offices in Lecompton.[8] The city soon became a stronghold of pro-slavery politics and southern sympathy, which put it in conflict with nearby Lawrence (which had been founded by Free-Staters from Massachusetts).
The first post office in Lecompton was established in September, 1855.[9] From 1854 until 1858, the town served as the seat of Douglas County.
In the fall of 1857, a convention met in Constitution Hall and drafted the famous Lecompton Constitution, which would have admitted Kansas as a slave state. The constitution was rejected after intense national debate and was one of the prime topics of the Lincoln-Douglas debates. The controversy contributed to the growing dispute soon to erupt in civil war. The Lecompton Constitution failed, in part, because the antislavery party won control of the territorial legislature in the election of 1857. The new legislature met at Constitution Hall and immediately began to abolish the pro-slavery laws of the Bogus Legislature, the territory's lawmakers since July, 1855.
The free-staters briefly attempted to move the territorial capital to Minneola through a vote, although the resulting bill was later vetoed by Kansas territorial governor James W. Denver, and ruled void by Jeremiah S. Black, Attorney General of the United States.[10] As such, Lecompton remained the de jure territorial capital until the victorious free-state leaders officially chose Topeka as capital when Kansas became a state on January 29, 1861. The American Civil War began on April 12, 1861.
In 1865, the United Brethren Church established a university in Lecompton. Occupying the Rowena hotel that was originally built for the Territorial Legislature and town visitors, the university later built a stone building in 1882 on the foundation of the started, but not completed, capitol building. Named "Lane University" after the free-stater James H. Lane, the university brought professors and students to town. It thrived until 1902 when Lane University moved to Holton, Kansas and merged to form Campbell College (which in turn merged with the now-defunct Kansas City University).[11][12][13] The bell from Lane University went with the move, and today can be found on the campus of Holton High School. The Lane University building was then used for the high school in Lecompton until a larger brick building was built just to the south of it in 1926.[14] The Lane University building fell into disrepair. In the 1970s, the townspeople wrote grants and raised funds to rehabilitate the old building. Today it is used as the Territorial Capital Museum, maintained by the Lecompton Historical Society.[15] Two blocks away is Constitution Hall where the infamous Lecompton Constitution was written in 1857. Today Constitution Hall is a museum operated by the Kansas Historical Society.[16]

At one time, Lecompton had six active churches. One church, the United Methodist Church, is still located in a unique building. When the Lane building was sold to the school district, the former United Brethren Church bought the Windsor Hotel. For a comfortable, easily accessible meeting place, they removed part of the second floor making a large, beautiful, high ceiling sanctuary. They also renovated the basement to give them ample class room space. The church is unusual in its appearance both inside and out.
In the 1880s there was some dissension in the United Brethren Church concerning secret organizations, causing the congregation to split. One group built another church on adjoining land which they named the Radical United Brethren Church. It burned about 1902 and a lovely limestone church replaced it. The former church was used as the Lecompton City Hall until about 2006, when a newer city hall was built in the old Lecompton Fire Station. The church is now a community building and Douglas County sheriff substation. In 2016, the Radical United Brethren Church was placed on the Kansas Register for Historic Places. With the building's addition to the historic register, Lecompton now has four buildings on either Kansas or national registers. The other three are Constitutional Hall, where two state constitutions were drafted in the 1850s in hopes of bringing Kansas into the union as a slave state; the Democratic Headquarters from the Bleeding Kansas era; and the Lane University building, which is now the Territorial Capital Museum.[17]
When the frame business buildings on the east side of main street (Elmore) were destroyed by fire in 1916, they were replaced with brick structures that are still in use. A mural depicting the town as it appeared before the fire is located in the local post office building.
20th century
In 1998, the Lecompton Historical Society had the good fortune to purchase and begin restoration on the remains of the native limestone Democratic Headquarters Building (circa 1850s). Originally there was a log cabin connected to the west side of this building located on East Second Street. Today, the historic building sits along the south limestone bluff of the Kansas River, overlooking the Kaw Valley basin to the north on a majestic Riverview Park area. This park area is open to visitors.
21st century
On July 26, 2010, the town's "Wood 'N Stuff" (a popular cabinetry) burned down due to an explosion. The building itself burned to the ground while the town's local Methodist church, LUMC (Lecompton United Methodist Church) was melted on one side. There were no fatalities or injuries.
After decades of empty storefronts, numerous businesses are calling downtown Lecompton home. As of 2015[update], there is an Antique Shop, Cafe/Dinner, art work shop and an automobile restoration garage. Also, there is a convenience store/meat market on the edge of town. The City of Lecompton has also bought the old Lecompton High School from the local school district and is working to remodel it into a community building. A branch of the Perry-Lecompton Community Library is located in the former high school.
In November 2016, Lecompton was voted a "best small town" in Kansas by the readers of KANSAS! Magazine. Lecompton was one of five small towns in the state to receive this distinction.[18]
Geography
Lecompton is located at 39°2′40″N 95°23′41″W / 39.04444°N 95.39472°W (39.0444449, -95.3946967).[1] According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 1.78 square miles (4.61 km2), of which, 1.77 square miles (4.58 km2) is land and 0.01 square miles (0.03 km2) is water.[19]
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Lecompton has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[20]
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | 284 | — | |
| 1890 | 450 | 58.5% | |
| 1900 | 408 | −9.3% | |
| 1910 | 386 | −5.4% | |
| 1920 | 310 | −19.7% | |
| 1930 | 288 | −7.1% | |
| 1940 | 250 | −13.2% | |
| 1950 | 263 | 5.2% | |
| 1960 | 304 | 15.6% | |
| 1970 | 434 | 42.8% | |
| 1980 | 576 | 32.7% | |
| 1990 | 619 | 7.5% | |
| 2000 | 608 | −1.8% | |
| 2010 | 625 | 2.8% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 654 | [4] | 4.6% |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
Lecompton is part of the Lawrence, Kansas Metropolitan Statistical Area.
2010 census
As of the census[3] of 2010, there were 625 people, 240 households, and 162 families residing in the city. The population density was 353.1 inhabitants per square mile (136.3/km2). There were 254 housing units at an average density of 143.5 per square mile (55.4/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 94.9% White, 0.5% African American, 2.2% Native American, 0.5% Asian, 0.3% from other races, and 1.6% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.4% of the population.
There were 240 households of which 37.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 49.2% were married couples living together, 8.8% had a female householder with no husband present, 9.6% had a male householder with no wife present, and 32.5% were non-families. 22.5% of all households were made up of individuals and 7.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.60 and the average family size was 3.09.
The median age in the city was 36.7 years. 29% of residents were under the age of 18; 8.4% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 24% were from 25 to 44; 26.7% were from 45 to 64; and 11.8% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 48.8% male and 51.2% female.
2000 census
As of the census of 2000,[21] there were 608 people, 228 households, and 168 families residing in the city. The population density was 677.9 people per square mile (260.8/km2). There were 233 housing units at an average density of 259.8 per square mile (100.0/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 93.59% White, 0.16% African American, 2.96% Native American, 0.66% Asian, 0.16% Pacific Islander, 0.16% from other races, and 2.30% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2.30% of the population.
There were 228 households out of which 41.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.8% were married couples living together, 11.4% had a female householder with no husband present, and 26.3% were non-families. 21.9% of all households were made up of individuals and 6.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.67 and the average family size was 3.06.
In the city, the population was spread out with 31.6% under the age of 18, 8.2% from 18 to 24, 31.6% from 25 to 44, 17.8% from 45 to 64, and 10.9% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33 years. For every 100 females, there were 93.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 93.5 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $38,281, and the median income for a family was $46,111. Males had a median income of $37,813 versus $20,577 for females. The per capita income for the city was $15,433. About 4.4% of families and 4.7% of the population were below the poverty line, including 3.4% of those under age 18 and none of those age 65 or over.
Education
Lecompton is served by USD 343 Perry-Lecompton. School unification consolidated Perry and Lecompton schools forming USD 343 in 1970. Perry-Lecompton High School is located in Perry. Lecompton Elementary School is located in Lecompton. The Perry-Lecompton High School mascot is Perry-Lecompton Kaws.[22]
Lecompton High School was closed through school unification in 1970. The Lecompton High School mascot was Lecompton Owls.[23]
Notable people
- William East - United States District Court judge
- Kris Kobach - Kansas Secretary of State
- Robert Stevens - former US Congressman
- Chuck Wright – Mayor of Topeka, Kansas, from 1965 to 1969[24]
Gallery
-
Downtown Lecompton
-
Former Kansas Democratic Headquarters in River View Park
-
Former Lane University, now the Territorial Capital Museum
-
The Radical United Brethren Church
-
Former Lecompton City Jail
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) details for Lecompton, Kansas; United States Geological Survey (USGS); October 13, 1978.
- ^ "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 24, 2020.
- ^ a b "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2012-07-06.
- ^ a b "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- ^ William Allen White School of Journalism and Public Information (1955). A pronunciation guide to Kansas place names. Lawrence, KS: University of Kansas. p. 15.
- ^ "2010 City Population and Housing Occupancy Status". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved April 6, 2012.[dead link]
- ^ Heim, Michael (2007). Exploring Kansas Highways. p. 49. ISBN 9780974435886. Archived from the original on 2016-12-23. Retrieved 2016-04-06.
- ^ "About Lecompton". Historic Lecompton. Lecompton, Kansas. Archived from the original on April 28, 2018. Retrieved May 26, 2018.
- ^ "Kansas Post Offices, 1828-1961 (archived)". Kansas Historical Society. Archived from the original on 10 March 2013. Retrieved 8 June 2014.
- ^ Fitzgerald, Daniel (1988). "Centropolis/Minneola". Ghost Towns of Kansas. University Press of Kansas. pp. 61–65. ISBN 0700603689.
- ^ "Campbell University/Lane University". Lecompton Kansas. Archived from the original on April 19, 2017. Retrieved April 18, 2017.
- ^ Blackmar, Frank (1912). "Campbell College". Kansas: A Cyclopedia of State History. Chicago: Standard Pub. Co. p. 275. Archived from the original on November 2, 2015. Retrieved January 6, 2016.
- ^ Batesel, Paul. "Campbell College Holton, Kansas 1880-1913". Lost Colleges. Archived from the original on September 12, 2017. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ "Lecompton High School History". Lecompton Kansas. Archived from the original on 2017-04-19. Retrieved 2017-04-18.
- ^ "Lane University". Lecompton Kansas. Archived from the original on 2017-04-19. Retrieved 2017-04-18.
- ^ "Lecompton Constitution". Lecompton Kansas. Archived from the original on 2017-02-26. Retrieved 2017-04-18.
- ^ "Lecompton building placed on historic register; Eudora wireless metering moving forward; Baldwin Education Foundation awards grants; final 2016 art walk set for Baldwin City | Area Roundup / LJWorld.com". www2.ljworld.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-19. Retrieved 2017-04-18.
- ^ "Lecompton voted "a best small town in Kansas!"". Lecompton Kansas. Archived from the original on 2017-04-19. Retrieved 2017-04-18.
- ^ "US Gazetteer files 2010". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2012-07-02. Retrieved 2012-07-06.
- ^ "Climate Summary for Lecompton, Kansas". Archived from the original on 2015-09-27. Retrieved 2014-04-29.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Perry-Lecompton USD 343". USD 343. Archived from the original on 28 November 2016. Retrieved 4 January 2017.
- ^ "Lansing Stampedes By Lecompton", The Leavenworth Times, 6 January 1965, p.8.
- ^ Hall, Mike (2016-12-27). "Chuck Wright, Topeka mayor during the 1966 tornado, dies at age 97". The Topeka Capital-Journal. Archived from the original on 2017-01-18. Retrieved 2017-01-14.
Further reading
External links
- City
- Schools
- USD 343, local school district
- Historical
- Maps
- Lecompton City Map, KDOT