Baudh State
Appearance
| Baudh State ବୌଦ୍ଧ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely State of British India | |||||||
| 1874–1948 | |||||||
|
Flag | |||||||
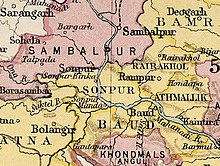 Baudh State in the Imperial Gazetteer of India | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
• 1921 | 3,274 km2 (1,264 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1921 | 130,103 | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | 1874 | ||||||
| 1948 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Baudh Princely State | |||||||
Baudh State, also known as Boudh State, was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It was recognized as a state in 1874[1] and had its capital in Boudh town. Its last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 1 January 1948.
History
Baudh was one among the 26 Feudatory states of Orissa. According to legend the state originated in a preexisting state that had been founded centuries before by a Brahmin who adopted as successor a nephew of the Raja of Keonjhar, belonging to the Bhanj Rajput Dynasty who ruled Mayurbhanj State.[2]
The formerly princely state's territory is now within Boudh District.
Rulers of Athmallik
The Rajas of the princely state were:
- 1874-1879 Pitamber Deo
- 1879-1913 Jogendra Deo
- 1913-1947 Narayan Prasad Deo
See also
References
- ^ Princely States of India A-J
- ^ Malleson, G. B. An historical sketch of the native states of India, London 1875, Reprint Delhi 1984

