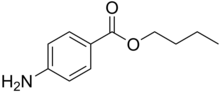
Butamben
Appearance
This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (May 2015) |  |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | n-butyl p-aminobenzoate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.107 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15NO2 |
| Molar mass | 193.242 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 58 °C (136 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Butamben is a local anesthetic. It is the ester of 4-aminobenzoic acid and butanol.[1] A white, odourless, crystalline powder. that is mildy soluble in water (1 part in 7000) and soluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform, fixed oils, and dilute acids. It slowly hydrolyses when boiled with water. Synonyms include Butamben, Butilaminobenzoato, and Butoforme. Proprietary names includes Alvogil in Spain and Alvogyl in Switzerland. It is one of three components in the topical anesthetic Cetacaine.
