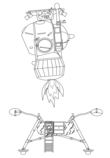
Kosmos 379
 LK Lander | |
| Operator | Soviet Union |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1970-099A |
| SATCAT no. | 04760 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | T2K |
| Launch mass | 7,495 kilograms (16,524 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 24 November 1970, 11:00:00 UTC |
| Rocket | Soyuz-L |
| Launch site | Baikonur 31/6 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.004161 |
| Perigee altitude | 198 kilometres (123 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 253 kilometres (157 mi) |
| Inclination | 51.6 degrees |
| Period | 88.7 m |
Kosmos 379 (Russian: Космос 379 meaning Cosmos 379) was a test of the LK Lander (the Soviet version of the Apollo LEM).
Mission
Earth orbit simulated propulsion system operations of a nominal lunar landing mission. Kosmos 379 entered a 192 to 232 km orbit. After three days fired its motor to simulate hover and touchdown on the moon, because of the burn in earth orbit the apogee increased to 1210 km. After a simulated stay on the Moon, it increased its speed by 1.5 km/s, simulating ascent to lunar orbit making the final apogee 14,035 km. These main maneuvers were followed by a series of small adjustments simulating rendezvous and docking with the Soyuz 7K-L3. The LK Lander tested out without major problems and decayed from orbit on September 21, 1983.
Parameters
- Spacecraft: LK Lander
- Mass: 5500 kg
- Crew: None
- Launched: November 24, 1970
- Landed:Reentered September 21, 1983
- Orbit: 192 km
External links
- Mir Hardware Heritage