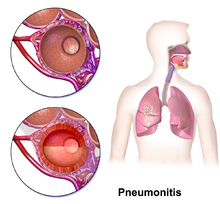
Pneumonitis
| Pneumonitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Pulmonitis |
 | |
| Pneumonitis | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology |
| Causes | Fungi ,Virus, Bacteria, Parasite |
Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue.[1][2] Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest,[3] exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris (e.g., animal dander), aspiration, herbicides or fluorocarbons and some systemic diseases. If unresolved, continued inflammation can result in irreparable damage such as pulmonary fibrosis.[4]
Pneumonitis is distinguished from pneumonia on the basis of causation as well as its manifestation. Pneumonia can be described as pneumonitis combined with consolidation and exudation of lung tissue due to infection with microorganisms.[5] The distinction between pneumonia and pneumonitis can be further understood with pneumonitis being the encapsulation of all respiratory infections (incorporating pneumonia and pulmonary fibrosis as major diseases), and pneumonia as a localized infection.[6] For most infections, the immune response of the body is enough to control and apprehend the infection within a couple days, but if the tissue and the cells can't fight off the infection, the creation of pus will begin to form in the lungs which then hardens into lung abscess or suppurative pneumonitis.[6] Patients that are immunodeficient and don't get treated immediately for any type of respiratory infection may lead to more severe infections and/or death.[6]
Pneumonitis can be classified into several different specific subcategories, including hypersensitivity pneumonitis, radiation pneumonitis, acute interstitial pneumonitis, and chemical pneumonitis. These all share similar symptoms, but differ in causative agents. Diagnosis of pneumonitis remains challenging,[7] but several different treatment paths (corticosteroids, oxygen therapy, avoidance) have seen success.[8]
Causes
[edit]Alveoli are the primary structure affected by pneumonitis. Any particles that are smaller than 5 microns can enter the alveoli of the lungs.[9] These tiny air sacs facilitate the passage of oxygen from inhaled air to the bloodstream.[citation needed] In the case of pneumonitis, it is more difficult for this exchange of oxygen to occur since irritants have caused inflammation of the alveoli.[3] Due to the lack of a definitive determination of a single irritant causing pneumonitis, there are several possible causes.[3]
- Viral infection. Measles can cause severe pneumonitis, and ribavirin has been proposed as a possible treatment. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is another cause.
- Pneumonia
- Radiation therapy
- Immunotherapy[10]
- Inhaling chemicals, such as sodium hydroxide[11]
- Interstitial lung disease
- Sepsis
- Adverse reaction to medications
- Hypersensitivity to inhaled agents[4]
- Inhalation of spores of some species of mushroom (bronchoalveolar allergic syndrome)[12]
- Mercury exposure
- Smoking
- Overexposure to chlorine
- Bronchial obstruction (obstructive pneumonitis or post-obstructive pneumonitis)
- Ascariasis (during parasite migration)
- Aspirin overdose, some antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs[3]
- “Farmer’s lung” and “hot tub lung” are common names for types of hypersensitivity pneumonitis that result from exposure to some types of thermophilic actinomyces, mycobacteria and molds.[3][7]
- Avian proteins in bird feces and feathers [3][7]
- Whole body or chest radiation therapy used for cancer treatment[3]
Symptoms
[edit]Physical manifestations of Pneumonitis range from mild cold-like symptoms to respiratory failure. Most frequently, those with pneumonitis experience shortness of breath, and sometimes a dry cough.[8] Symptoms usually appear a few hours after exposure and peak at approximately eighteen to twenty-four hours.[7]
Other symptoms may include:
- Malaise[7]
- Fever[7]
- Dyspnea[7]
- Flushed and/or discolored skin[6]
- Sweating[6]
- Small and fast inhalations[6]
Without proper treatment, pneumonitis may become chronic pneumonitis, resulting in fibrosis of the lungs and its effects:
End-stage fibrosis and respiratory failure eventually lead to death in cases without proper management of chronic pneumonitis.[7]
Diagnosis
[edit]A chest X-ray or CT is necessary to differentiate between pneumonitis and pneumonia of an infectious etiology. Some degree of pulmonary fibrosis may be evident in a CT which is indicative of chronic pulmonary inflammatory processes. Diagnosis of Pneumonitis is often difficult as it depends on a high degree of clinical suspicion when evaluating a patient with a recent onset of a possible interstitial lung disease. In addition, interpreting pathologic and radiographic test results remains a challenge to clinicians. Pneumonitis is often difficult to recognize and discern from other interstitial lung diseases.[7]
Diagnostic procedures currently available include:
- Evaluation of patient history and possible exposure to a known causative agent
- High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) consistent with pneumonitis
- Bronchoalveolar lavage with lymphocytosis
- Lung biopsy consistent with pneumonitis histopathology
Exposure to causative agents of pneumonitis in a specific environment can be confirmed through aero/microbiologic analysis to verify its presence. Subsequent testing of patient serum for evidence of serum specific IgG antibodies confirms patient exposure.[7]
Clinical tests include chest radiography or (HRCT) which may show centrilobular nodular and ground-glass opacities with air-trapping in the middle and upper lobes of the lungs. Fibrosis may also be evident. Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) findings coinciding with pneumonitis typically include a lymphocytosis with a low CD4:CD8 ratio.[7][13]
Reticular or linear patterns may be observed in diagnostic imaging.[7] Pneumonitis may cause subpleural honeycombing, changing the shape of the air spaces in an image, which may be used to identify the respiratory disease.[7] The interlobular septa may also thicken and indicate pneumonitis when viewed on a scan.[7]
Histological samples of lung tissue with pneumonitis include the presence of poorly formed granulomas or mononuclear cell infiltrates. The presence of bronchocentric lymphohistiocytic interstitial pneumonia with chronic bronchiolitis and non-necrotising granulomas coincides with pneumonitis.[13]
Since pneumonitis manifests in all areas of the lungs, imaging such as chest x-rays and Computerized tomography (CT) scans are useful diagnostic tools.[3] While pneumonia is a localized infection, pneumonitis is widespread.[3] A spirometer may also be used to measure pulmonary function.
During external examination, clubbing (swelling of fingertip tissue and increase in angle at the nail bed),[14] and basal crackles may be observed.
For hypersensitivity pneumonitis many diagnoses take place through the focus of blood test, chest x-rays, and depending on severity of infection doctors may recommend a bronchoscopy. Blood test are important to early detect for other causative substances that could eliminate possible causes of the hypersensitivity pneumonitis.[15]
Classification
[edit]Pneumonitis can be separated into several distinct categories based upon causative agent.
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (Extrinsic Allergenic Alveolitis) describes the inflammation of alveoli which occurs after inhalation of organic dusts (oxford). These particles can be proteins, bacteria, or mold spores and are usually specific to an occupation.[citation needed]
- Acute Interstitial Pneumonitis can result from many different irritants in the lungs and usually is resolved in under a month.[14]
- Chemical Pneumonitis is caused by toxic substances reaching the lower airways of the bronchial tree. This causes a chemical burn and severe inflammation. (oxford)
- Radiation Pneumonitis, also known as Radiation Induced Lung Injury, describes the initial damage done to the lung tissue by ionization radiation. Radiation, used to treat cancer, can cause pneumonitis when applied to the chest or full body.[16] Radiation pneumonitis occurs in approximately 30% of advanced lung cancer patients treated with radiation therapy.[16]
- Aspiration pneumonitis is caused by a chemical inhalation of harmful gastric contents which include causes such as:
Treatment
[edit]Typical treatment for pneumonitis includes conservative use of corticosteroids such as a short course of oral prednisone or methylprednisolone. Inhaled corticosteroids such as fluticasone or budesonide may also be effective for reducing inflammation and preventing re-inflammation on a chronic level by suppressing inflammatory processes that may be triggered by environmental exposures such as allergens. Severe cases of pneumonitis may require corticosteroids and oxygen therapy, as well as elimination of exposure to known irritants.[8]
Corticosteroid dose and treatment duration vary from case to case. However, a common regimen beginning at 0.5 mg/kg per day for a couple of days before tapering to a smaller dose for several months to a year, has been used successfully.[13]
Corticosteroids effectively reduce inflammation by switching off several genes activated during an inflammatory reaction.[18] The production of anti-inflammatory proteins, and the degeneration of mRNA encoding inflammatory proteins, can also be increased by a high concentration of corticosteroids.[18] These responses can help mitigate the inflammation seen in pneumonitis and reduce symptoms.[13]
Certain immune-modulating treatments may be appropriate for patients with chronic pneumonitis. Azathioprine and mycophenolate are two particular treatments that have been associated with an improvement of gas exchange. Patients with chronic pneumonitis also may be evaluated for lung transplantation.[13]
Images
[edit]-
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis with interstitial multinucleate giant cells
-
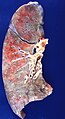
Human lung with radiation pneumonitis.
See also
[edit]- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis, also known as extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA)
- Acute Interstitial Pneumonitis
- Radiation Pneumonitis
- Chemical Pneumonitis
References
[edit]- ^ "pneumonitis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Stedman's medical dictionary (28th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2006. ISBN 978-0-7817-6450-6.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Pneumonitis - Symptoms and causes". mayoclinic.com. Archived from the original on 2013-05-17. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
- ^ a b "Pneumonitis. Medical information about Pneumonitis". www.patient.co.uk. 28 July 2020. Archived from the original on 15 March 2012. Retrieved 31 January 2008.
- ^ "pneumonia" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ a b c d e f Maxwell J (July 1938). "Pneumonitis". The Lancet. 232 (5996): 239–41. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)98250-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Miller R, Allen TC, Barrios RJ, Beasley MB, Burke L, Cagle PT, et al. (January 2018). "Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis A Perspective From Members of the Pulmonary Pathology Society". Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. 142 (1): 120–126. doi:10.5858/arpa.2017-0138-SA. PMID 28613913.
- ^ a b c d "Pneumonitis - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic". www.mayoclinic.org. Archived from the original on 2020-08-06. Retrieved 2020-03-26.
- ^ "Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis) : OSH Answers". Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. Government of Canada. 2020-03-26. Archived from the original on 2019-05-28. Retrieved 2020-03-26.
- ^ Sierra-Rodero, B; Cruz-Bermúdez, A; Nadal, E; Garitaonaindía, Y; Insa, A; Mosquera, J; Casal-Rubio, J; Dómine, M; Majem, M; Rodriguez-Abreu, D; Martinez-Marti, A; De Castro Carpeño, J; Cobo, M; López Vivanco, G; Del Barco, E; Bernabé Caro, R; Viñolas, N; Barneto Aranda, I; Viteri, S; Massuti, B; Laza-Briviesca, R; Casarrubios, M; García-Grande, A; Romero, A; Franco, F; Provencio, M (August 2021). "Clinical and molecular parameters associated to pneumonitis development in non-small-cell lung cancer patients receiving chemoimmunotherapy from NADIM trial". Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer. 9 (8): e002804. doi:10.1136/jitc-2021-002804. PMC 8395363. PMID 34446577.
- ^ "Occupational Health Guideline for Sodium Hydroxide" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 7, 2009.
- ^ "Mushroom Toxicity: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology". 6 January 2017. Archived from the original on 9 November 2019. Retrieved 15 February 2010 – via eMedicine.
- ^ a b c d e Vasakova M, Morell F, Walsh S, Leslie K, Raghu G (September 2017). "Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Perspectives in Diagnosis and Management". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 196 (6): 680–689. doi:10.1164/rccm.201611-2201PP. PMID 28598197. S2CID 40479842.
- ^ a b "Evaluation of the Pulmonary Patient - Pulmonary Disorders". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Archived from the original on 2020-07-30. Retrieved 2020-03-26.
- ^ "Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - Pulmonary Disorders". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Archived from the original on 2020-03-26. Retrieved 2020-03-26.
- ^ a b Keffer S, Guy CL, Weiss E (2020). "Fatal Radiation Pneumonitis: Literature Review and Case Series". Advances in Radiation Oncology. 5 (2): 238–249. doi:10.1016/j.adro.2019.08.010. PMC 7136627. PMID 32280824.
- ^ a b c d Marik PE (March 2001). "Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia". The New England Journal of Medicine. 344 (9): 665–71. doi:10.1056/NEJM200103013440908. PMID 11228282.
- ^ a b Barnes PJ (June 2006). "How corticosteroids control inflammation: Quintiles Prize Lecture 2005". British Journal of Pharmacology. 148 (3): 245–54. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706736. PMC 1751559. PMID 16604091.