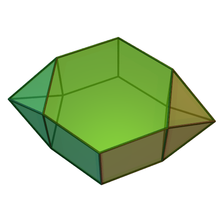
Parabiaugmented hexagonal prism
| Parabiaugmented hexagonal prism | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Johnson J54 - J55 - J56 |
| Faces | 2x4 triangles 4 squares 2 hexagons |
| Edges | 26 |
| Vertices | 14 |
| Vertex configuration | 4(42.6) 2(34) 8(32.4.6) |
| Symmetry group | D2h |
| Dual polyhedron | - |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |
In geometry, the parabiaugmented hexagonal prism is one of the Johnson solids (J55). As the name suggests, it can be constructed by doubly augmenting a hexagonal prism by attaching square pyramids (J1) to two of its nonadjacent, parallel (opposite) equatorial faces. Attaching the pyramids to nonadjacent, nonparallel equatorial faces yields a metabiaugmented hexagonal prism. (The solid obtained by attaching pyramids to adjacent equatorial faces is not convex, and thus not a Johnson solid.)
A Johnson solid is one of 92 strictly convex polyhedra that is composed of regular polygon faces but are not uniform polyhedra (that is, they are not Platonic solids, Archimedean solids, prisms, or antiprisms). They were named by Norman Johnson, who first listed these polyhedra in 1966.[1]
External links
- ^ Johnson, Norman W. (1966), "Convex polyhedra with regular faces", Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 18: 169–200, doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8, MR 0185507, Zbl 0132.14603.
