Longleaf pine
| Longleaf pine | |
|---|---|

| |
| Longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) forest | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Subgenus: | |
| Species: | P. palustris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pinus palustris | |
| |
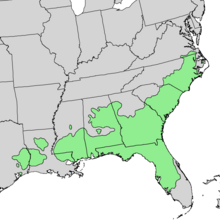
Pinus palustris, commonly known as the longleaf pine, is a pine native to the southeastern United States, found along the coastal plain from eastern Texas to southeast Virginia, extending into northern and central Florida.[2] It reaches a height of 30–35 m (98–115 ft) and a diameter of 0.7 m (28 in). In the past, they reportedly grew to 47 m (154 ft) with a diameter of 1.2 m (47 in).[clarification needed]
The bark is thick, reddish-brown, and scaly. The leaves are dark green and needle-like, and occur in bundles of three. They often are twisted and 20–45 cm (7.9–17.7 in) in length. It is one of the two southeastern U.S. pines with long needles, the other being slash pine.

The cones, both female seed cones (ovulate strobili) and male pollen cones (staminate strobili), are initiated during the growing season before buds emerge. Pollen cones begin forming in their buds in July, while seed conelets are formed during a relatively short period of time in August. Pollination occurs early the following spring, with the male cones 3–8 cm (1.2–3.1 in) long. The female (seed) cones mature in about twenty months from pollination; when mature they are yellow-brown in color, 15–25 cm (5.9–9.8 in) long, and 5–7 cm (2.0–2.8 in) broad, opening to 12 cm (4.7 in), and have a small, but sharp, downward-pointing spine on the middle of each scale. The seeds are 7–9 mm (0.28–0.35 in) long, with a 25–40 mm (0.98–1.57 in) wing.
Longleaf pine takes 100 to 150 years to become full size and may live to be 500 years old. When young, they grow a long taproot, which usually is 2–3 m (6.6–9.8 ft) long; by maturity they have a wide spreading lateral root system with several deep 'sinker' roots. It grows on well-drained, usually sandy soil, often in pure stands. In northern Alabama, it sometimes occurs on clay soil. The scientific name meaning, "of marshes," is a misunderstanding on the part of Philip Miller who described the species, after seeing longleaf pine forests with temporary winter flooding.
Longleaf pine also is known as being one of several species grouped as a southern yellow pine[3] or longleaf yellow pine, and in the past as pitch pine (a name dropped as it caused confusion with pitch pine, Pinus rigida).
Ecology

Longleaf pine is highly pyrophytic (resistant to wildfire). Periodic natural wildfire selects for this species by killing other trees, leading to open longleaf pine forests or savannas. New seedlings do not appear at all tree-like and resemble a dark green fountain of needles. This form is called the grass stage. During this stage, which lasts for 5–12 years, vertical growth is very slow, and the tree may take a number of years simply to grow ankle-high. After that it makes a growth spurt, especially if there is no tree canopy above it. In the grass stage, it is very resistant to grass fires, which burn off the ends of the needles, but the fire cannot penetrate the tightly-packed needle bases to reach the bud. While relatively immune to fire, at this stage, the plant is quite appealing to feral pigs, and the early settlers' habit of releasing swine into the woodlands to feed was greatly responsible for the decline of the species.
Longleaf pine forests are rich in biodiversity. They are well-documented for their high levels of plant diversity, in groups including sedges, grasses, carnivorous plants and orchids.[4][5] These forests also provide habitat for gopher tortoises, which, as keystone species, dig burrows that provide habitat for hundreds of other species of animals. The red-cockaded woodpecker is dependent on mature pine forests and is now endangered as a result of this decline. Longleaf pine seeds are large and nutritious, forming a significant food source for birds (notably the brown-headed nuthatch) and other wildlife. There are 9 salamander species and 26 frog species that are characteristic of pine savannas, along with 56 species of reptiles, 13 of which could be considered specialists on this habitat.[6]
The Red Hills Region of Florida and Georgia is home to some of the best preserved stands of longleaf pine. These forests have been burned regularly for many decades to encourage bobwhite quail habitat in private hunting plantations.
Uses

Vast forests of longleaf pine once were present along the southeastern Atlantic coast and Gulf Coast of North America, as part of the eastern savannas. These forests were the source of naval stores - resin, turpentine, and timber - needed by merchants and the navy for their ships. They have been cutover since for timber and usually replaced with faster-growing loblolly pine and slash pine, for agriculture, and for urban and suburban development. Due to this deforestation and over-harvesting, only about 3% of the original longleaf pine forest remains, and little new is planted. Longleaf pine is available, however, at many nurseries within its range; the southernmost known point of sale is in Lake Worth, Florida.
The yellow, resinous wood is used for lumber and pulp. Boards cut years ago from virgin timber were very wide, up to 1 m (3.3 ft), and a thriving salvage business obtains these boards from demolition projects to be reused as flooring in upscale homes.
The extremely long needles are popular for use in the ancient craft of coiled basket making.
The stumps and taproots of old trees become saturated with resin and will not rot. Farmers sometimes find old buried stumps in fields, even in some that were cleared a century ago, and these usually are dug up and sold as Fatwood, "fat lighter" or "lighter wood" which is in demand as kindling for fireplaces, wood stoves, and barbecue pits. In old growth pine the heartwood of the bole is often saturated in the same way. When boards are cut from the fat lighter wood, they are very heavy and will not rot, but buildings constructed of them are quite flammable and make extremely hot fires.
The longleaf pine is the official state tree of Alabama and North Carolina.[7][8] and the longleaf pine specifically is lauded in the official state toast.[9]
Native range, restoration, and protection
Before European settlement, longleaf pine forest dominated as much as 90,000,000 acres (360,000 km2) stretching from Virginia south to Florida and west to eastern Texas. Its range was defined by the frequent widespread fires that occurred throughout the southeast. In the late 19th century, these virgin timber stands were "among the most sought after timber trees in the country." This rich ecosystem now has been relegated to less than 5% of its pre-settlement range due to clear cutting practices:
As they stripped the woods of their trees, loggers left mounds of flammable debris that frequently fueled catastrophic fires, destroying both the remaining trees and seedlings. The exposed earth left behind by clear cutting operations was highly susceptible to erosion, and nutrients were washed from the already porous soils. This further destroyed the natural seeding process. At the peak of the timber cutting in the 1890s and the first decade of the new century, the longleaf pine forests of the Sandhills were providing millions of board feet of timber each year. The timber cutters gradually moved across the South; by the 1920s, most of the "limitless" virgin longleaf pine forests were gone.
In "pine barrens" most of the day. Low, level, sandy tracts; the pines wide apart; the sunny spaces between full of beautiful abounding grasses, liatris, long, wand-like solidago, saw palmettos, etc., covering the ground in garden style. Here I sauntered in delightful freedom, meeting none of the cat-clawed vines, or shrubs, of the alluvial bottoms. – John Muir
Efforts are being made to restore longleaf pine ecosystems within its natural range. Some groups such as the Longleaf Alliance are actively promoting research, education, and management of the longleaf pine.[10]
The USDA offers cost-sharing and technical assistance to private landowners for longleaf restoration through the NRCS Longleaf Pine Initiative. Similar programs are available through most state forestry agencies in the longleaf's native range. In August 2009, the Alabama Forestry Commission received 1.757 million dollars in stimulus money to restore longleaf pines in state forests.[11]
There are four large core areas within the range of the species that provide the opportunity to protect the biological diversity of the coastal plain, as well as to restore wilderness areas east of the Mississippi River.[12] Each of these four (Eglin Air Force Base: 187,000+ ha; Apalachicola National Forest: 228,000+ ha; Okefenokee-Osceola: 289,000+ ha; De Soto National Forest: 200,000+ ha) have nearby lands that offer the potential to expand the total protected territory for each area to well beyond 500,000 ha. These areas would provide the opportunity not only to restore forest stands, but to restore populations of native vertebrate animals threatened by landscape fragmentation.
Notable eccentric populations exist within the Uwharrie National Forest in the central Piedmont region of North Carolina. These have survived owing to relative inaccessibility and, in one instance, intentional protection in the 20th century by a private landowner (a property now owned and conserved by the Land Trust of Central North Carolina).

The United States Forest Service is conducting prescribed burning programs in the 258,864-acre Francis Marion National Forest, located outside of Charleston, South Carolina. They are hoping to increase the longleaf pine forest type to 44,700 acres (181 km2) by 2017 and 53,500 acres (217 km2) in the long term. In addition to Longleaf restoration, prescribed burning will enhance the endangered Red-cockaded Woodpeckers' preferred habitat of open, park-like stands, provide habitat for wildlife dependent on grass-shrub habitat, which is very limited, and reduce the risk of damaging wildfires.[13]
Since the 1960s, Longleaf restoration has been ongoing on almost 95,000 acres of state and federal land in the sandhills region of South Carolina, between the piedmont and coastal plain. The region is characterized by deep, infertile sands deposited by a prehistoric sea, with generally arid conditions. By the 1930s, most of the native longleaf had been logged, and the land was heavily eroded. Between 1935-1939, the federal government purchased large portions of this area from local landowners as a relief measure under the Resettlement Administration. These landowners were resettled on more fertile land elsewhere. Today, the South Carolina Sand Hills State Forest comprises approximately half of the acreage, and half is owned by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service as the adjacent Carolina Sandhills National Wildlife Refuge. At first, restoration of forest cover was the goal. Fire suppression was practiced until the 1960s, when prescribed fire was introduced on both the state forest[14] and the Sandhills NWR[15][16] as part of the restoration of the longleaf/wiregrass ecosystem.
Nokuse Plantation is a 53,000 acre private nature preserve located approximately 100 miles east of Pensacola, Florida. The preserve was established by M.C. Davis, a wealthy philanthropist who made his fortune buying and selling land and mineral rights, and who has spent $90 million purchasing land for the preserve, primarily from timber companies. One of its main goals is the restoration of longleaf pine forest, to which end he has had 8 million longleaf pine seedlings planted on the land.[17]
A 2009 study by the National Wildlife Federation says that longleaf pine forests will be particularly well adapted to environmental changes caused by climate disruption. [18]
See also
- Longleaf Pine Ecosystem
- Sonderegger Pine, a hybrid between loblolly and longleaf species
- Mountain Longleaf National Wildlife Refuge
Notes
- ^ Template:IUCN
- ^ "Longleaf Pine Range Map". The Longleaf Alliance. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Moore, Gerry; Kershner, Bruce; Craig Tufts; Daniel Mathews; Gil Nelson; Spellenberg, Richard; Thieret, John W.; Terry Purinton; Block, Andrew (2008). National Wildlife Federation Field Guide to Trees of North America. New York: Sterling. p. 75. ISBN 1-4027-3875-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Peet, R. K. and D. J Allard. 1993. Longleaf pine vegetation of the southern Atlantic and eastern Gulf coast regions: a preliminary classification. pp. 45–81. In S. M. Hermann (ed.) Proceedings of the Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference. No. 18. The Longleaf Pine Ecosystem: Ecology, Restoration, and Management. Florida: Tall Timbers Research Station.
- ^ Keddy, P.A., L. Smith, D.R. Campbell, M. Clark and G. Montz. 2006. Patterns of herbaceous plant diversity in southeastern Louisiana pine savannas. Applied Vegetation Science 9:17-26.
- ^ Means, D. Bruce. 2006. Vertebrate faunal diversity in longleaf pine savannas. Pages 155-213 in S. Jose, E. Jokela and D. Miller (eds.) Longleaf Pine Ecosystems: Ecology, Management and Restoration. Springer, New York. xii + 438 pp.
- ^ "Southern Longleaf Pine". Official Symbols and Emblems of Alabama. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- ^ http://www.ncleg.net/enactedlegislation/statutes/html/bysection/chapter_145/gs_145-3.html
- ^ North Carolina General Statutes § 149‑2 http://www.ncleg.net/enactedlegislation/statutes/html/bysection/chapter_149/gs_149-2.html
- ^ "Longleaf Pine Forests and Longleaf Alliance Home". Longleaf Alliance. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- ^ "Stimulus to fund repopulation of longleaf pines in Alabama". The Birmingham News. Retrieved 1 September 2009.
- ^ Keddy, P.A. 2009. Thinking big: A conservation vision for the Southeastern coastal plain of North America. Southeastern Naturalist 8: 213-226.
- ^ "Fiscal Year 2006 Monitoring and Evaluation Annual Report" (PDF). Francis Marion National Forest. United States Forest Service. 26 September 2007. Retrieved 16 June 2009.
- ^ http://www.state.sc.us/forest/refshill.htm.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ "Carolina Sandhills NWR History".
- ^ "Refuge to Begin Conducting Prescribed Burns in February" (PDF). United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 14 December 2011.
- ^ Block, Melissa (17 June 2015). "Gambler-Turned-Conservationist Devotes Fortune To Florida Nature Preserve". All Things Considered. NPR. Retrieved 18 June 2015.
- ^ "Restoring roots of Southeast: Environmental benefits, quality of wood touted". The (Charleston, SC) Post and Courier. 12 December 2009. Retrieved 12 December 2009.
References
- "A Toast" to North Carolina., January 1957, retrieved 4 April 2009
- Vanderbilt University, Department of Biological Sciences. "Bioimages - Pinus palustris". Bioimages. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- "Pinus palustris description". The Gymnosperm Database. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- Pinus palustris description, retrieved 4 April 2009
- "Pinus palustris in Flora of North America @ efloras.org". Flora of North America. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- Pinus palustris in Flora of North America @ efloras.org, retrieved 4 April 2009
- State tree, January 1963, retrieved 4 April 2009
- "Tall Timbers". Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- Outcalt, Kenneth W. (2000). "The Longleaf Pine Ecosystem of the South". Native Plants Journal. 1 (1).
- Ashe, William Willard (1897). The Forests, Forest Lands, and Forest Products of Eastern North Carolina. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- "North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service - Reforestation of North Carolina's Pines". 14 August 2007. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- "Longleaf pine/wiregrass ecosystem". Carolina Sandhills National Wildlife Refuge. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- Barnett, James P. (2014). Direct Seeding Southern Pines: History and Status of a Technique Developed for Restoring Cutover Forests. Asheville, NC: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Southern Research Station. Retrieved 27 July 2014.

