Portal:Germany/Selected article/2006
These articles have appeared on the Portal:Germany page in 2006. They are (or were at the time of listing) Featured Articles unless marked otherwise.

Ludwigsburg Palace, nicknamed the "Versailles of Swabia", is a 452-room palace complex of 18 buildings located in Ludwigsburg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Its total area, including the gardens, is 32 ha (79 acres) – the largest palatial estate in the country. The palace has four wings: the northern wing, the Alter Hauptbau, is the oldest and was used as a residence of the Duke of Württemberg; the east and west wings were used for court purposes and housing guests and courtiers; the southern wing, the Neuer Hauptbau, was built to house more court functions and was later used as a residence.
Eberhard Louis, Duke of Württemberg, appointed Philipp Joseph Jenisch to direct the work, and construction began in 1704. In 1707, Jenisch was replaced by Johann Friedrich Nette, who completed most of the palace and surrounding gardens. Nette died in 1714, and Donato Giuseppe Frisoni finished much of the palace façades. In the final year of construction, Eberhard Louis died, and the Neue Hauptbau's interiors were left incomplete. Charles Eugene's court architect, Philippe de La Guêpière, completed and refurbished parts of the New Hauptbau in the Rococo style, especially the palace theatre. Charles Eugene abandoned the palace for Stuttgart in 1775. Duke Frederick II, later King Frederick I, began using Ludwigsburg as his summer residence in the last years of Charles Eugene's reign. Frederick and his wife Charlotte, Princess Royal, resided at Ludwigsburg and employed Nikolaus Friedrich von Thouret to renovate the palace in the Neoclassical style. Thouret converted much of Ludwigsburg's interiors over the reign of Frederick and the later life of Charlotte. As a result of each architect's work, Ludwigsburg is a combination of Baroque, Rococo, Neoclassical, and Empire style architecture. (Full article...)
- This article was the Selected article from June 2005 to early February 2006. It was not a Featured article.

Adelheid Luise "Adele" Spitzeder ([ˈaːdl̩haɪt ʔaˈdeːlə ˈʃpɪtˌtseːdɐ]; 9 February 1832 – 27 or 28 October 1895), also known by her stage name Adele Vio, was a German actress, folk singer, and con artist. Initially a promising young actress, Spitzeder became a well-known private banker in 19th-century Munich when her theatrical success dwindled. Running what was possibly the first recorded Ponzi scheme, she offered large returns on investments by continually using the money of new investors to pay back the previous ones. At the height of her success, contemporary sources considered her the wealthiest woman in Bavaria.
Opening her bank in 1869, Spitzeder managed to fend off attempts to discredit her for a few years before authorities were able to bring her to trial in 1872. Because Ponzi schemes were not yet illegal, she was convicted instead of bad accounting and mishandling customers' money and sentenced to three years in prison. Her bank was closed and 32,000 people lost 38 million gulden, the equivalent of almost 400 million euros in 2017 money, causing a wave of suicides. Her personal fortune in art and cash was stripped from her. (Full article...)
- This article was not a Featured article.

Riesling is a white grape variety which originates in the Rhine region of Germany. Riesling is an aromatic grape variety displaying flowery, almost perfumed, aromas as well as high acidity. It is used to make dry, semi-sweet, sweet and sparkling white wines. Riesling wines are usually varietally pure and are seldom oaked. As of 2004, Riesling was estimated to be the world's 20th most grown variety at 48,700 hectares (120,000 acres) (with an increasing trend), but in terms of importance for quality wines, it is usually included in the "top three" white wine varieties together with Chardonnay and Sauvignon Blanc. Riesling is a variety which is highly "terroir-expressive", meaning that the character of Riesling wines is clearly influenced by the wine's place of origin.
In 2006, Riesling was the most grown variety in Germany with 20.8% and 21,197 hectares (52,380 acres), and in the French region of Alsace with 21.9% and 3,350 hectares (8,300 acres). There are also significant plantings of Riesling in Austria, Luxembourg, northern Italy, Australia, New Zealand, United States, Canada, South Africa, China and Ukraine. In the countries where it is cultivated, Riesling is most commonly grown in colder regions and locations. More ...

Johannes Kepler (/ˈkɛplər/; German: [joˈhanəs ˈkɛplɐ, -nɛs -] ⓘ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books Astronomia nova, Harmonice Mundi, and Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae, influencing among others Isaac Newton, providing one of the foundations for his theory of universal gravitation. The variety and impact of his work made Kepler one of the founders and fathers of modern astronomy, the scientific method, natural and modern science. He has been described as the "father of science fiction" for his novel Somnium.
Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Later he became an assistant to the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague, and eventually the imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II and his two successors Matthias and Ferdinand II. He also taught mathematics in Linz, and was an adviser to General Wallenstein. Additionally, he did fundamental work in the field of optics, being named the father of modern optics, in particular for his Astronomiae pars optica. He also invented an improved version of the refracting telescope, the Keplerian telescope, which became the foundation of the modern refracting telescope, while also improving on the telescope design by Galileo Galilei, who mentioned Kepler's discoveries in his work. (Full article...)

Johann Peter Hebel (10 May 1760 – 22 September 1826) was a German short story writer, dialectal poet, Lutheran theologian and pedagogue, most famous for a collection of Alemannic lyric poems (Allemannische Gedichte) and one of German tales (Schatzkästlein des rheinischen Hausfreundes – "Treasure Chest of Rhenish Tales").
Born in Basel, Hebel entered primary school in 1766 and joined a Latin school three years later; he visited the schools in Basel during summer and in Hausen and Schopfheim respectively in the nearby Wiesental during winter. After the death of his mother in 1773, he remained at school, graduating with the help of friends from the Gymnasium illustre of Karlsruhe in 1778 and going on to study theology. He became a home tutor, an assistant preacher, an assistant teacher, a subdeacon and, in 1798, a professor and court deacon.
Hebel was interested in botany, natural history and other subjects. His literary work began with Allemannische Gedichte, which is perhaps the most popular work written in Alemannic. He had success with his calendar stories in the Badischer Landkalender, and later with Rheinländischer Hausfreund (Rhenish Family Treasury), but a dispute between Catholics forced him to resign as editor of the calendar. In his last years he devoted himself increasingly to religion, becoming a prelate in 1819, but his wish to become a parish priest was never fulfilled. His last works were biblical stories for young readers, which served as textbooks until 1855. Hebel died 1826 in Schwetzingen. Goethe, Tolstoy, Gottfried Keller, Hermann Hesse, Martin Heidegger and other writers have praised his works. (Full article...)

Albert Einstein (March 14, 1879 – April 18, 1955) was a theoretical physicist widely regarded as the most important scientist of the 20th century. He developed the special and general theories of relativity and made significant contributions to quantum mechanics, statistical mechanics, and cosmology. He was awarded the 1921 Nobel Prize for Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect in 1905 (his "wonderful year") and "for his services to Theoretical Physics".
After British solar eclipse expeditions in 1919 confirmed that light rays from distant stars were deflected by the gravity of the Sun in the amount he had predicted in his theory of relativity, Einstein became world-famous, an unusual achievement for a scientist. In his later years, his fame perhaps exceeded that of any other scientist in history. In popular culture, his name has become synonymous with great intelligence and genius. More...

Emanuel Lasker (German pronunciation: [eˈmaːnuɛl ˈlaskɐ] ⓘ; December 24, 1868 – January 11, 1941) was a German chess player, mathematician, and philosopher. He was the second World Chess Champion, holding the title for 27 years, from 1894 to 1921, the longest reign of any officially recognised World Chess Champion winning 6 World Chess Championships. In his prime, Lasker was one of the most dominant champions, and he is still generally regarded as one of the strongest players in history.
His contemporaries used to say that Lasker used a "psychological" approach to the game, and even that he sometimes deliberately played inferior moves to confuse opponents. Recent analysis, however, indicates that he was ahead of his time and used a more flexible approach than his contemporaries, which mystified many of them. Lasker knew contemporary analyses of openings well but disagreed with many of them. He published chess magazines and five chess books, but later players and commentators found it difficult to draw lessons from his methods.
Lasker made contributions to the development of other games. He was a first-class contract bridge player and wrote about bridge, Go, and his own invention, Lasca. His books about games presented a problem that is still considered notable in the mathematical analysis of card games. Lasker was a research mathematician who was known for his contributions to commutative algebra, which included proving the primary decomposition of the ideals of polynomial rings. His philosophical works and a drama that he co-wrote, however, received little attention. (Full article...)

Johann George Adam Forster, also known as Georg Forster (German pronunciation: [ˈɡeːɔʁk ˈfɔʁstɐ], 27 November 1754 – 10 January 1794), was a German geographer, naturalist, ethnologist, travel writer, journalist and revolutionary. At an early age, he accompanied his father, Johann Reinhold Forster, on several scientific expeditions, including James Cook's second voyage to the Pacific. His report of that journey, A Voyage Round the World, contributed significantly to the ethnology of the people of Polynesia and remains a respected work. As a result of the report, Forster, who was admitted to the Royal Society at the early age of twenty-two, came to be considered one of the founders of modern scientific travel literature.
After returning to continental Europe, Forster turned toward academia. He taught natural history at the Collegium Carolinum in the Ottoneum, Kassel (1778–84), and later at the Academy of Vilna (Vilnius University) (1784–87). In 1788, he became head librarian at the University of Mainz. Most of his scientific work during this time consisted of essays on botany and ethnology, but he also prefaced and translated many books about travel and exploration, including a German translation of Cook's diaries.
Forster was a central figure of the Enlightenment in Germany, and corresponded with most of its adherents, including his close friend Georg Christoph Lichtenberg. His ideas, travelogues and personality influenced Alexander von Humboldt, one of the great scientists of the 19th century who hailed Forster as the founder of both comparative ethnology (Völkerkunde) and regional geography (Länderkunde). When the French took control of Mainz in 1792, Forster played a leading role in the Mainz Republic, the earliest republican state in Germany. During July 1793 and while he was in Paris as a delegate of the young Mainz Republic, Prussian and Austrian coalition forces regained control of the city and Forster was declared an outlaw. Unable to return to Germany and separated from his friends and family, he died in Paris of illness in early 1794, not yet 40. (Full article...)

SMS Lothringen was the last of five pre-dreadnought battleships of the Braunschweig class, built for the German Kaiserliche Marine (Imperial Navy). She was laid down in December 1902, was launched in May 1904, and was commissioned in May 1906. She was named for Lothringen (now Lorraine), a province of the German Empire from 1871 to 1918. The ship was armed with a battery of four 28 cm (11 in) guns and had a top speed of 18 knots (33 km/h; 21 mph). Like all other pre-dreadnoughts built around the turn of the century, Lothringen was quickly made obsolete by the launching of the revolutionary HMS Dreadnought in December 1906; as a result, her career as a front-line battleship was cut short.
Lothringen's peacetime career centered on squadron and fleet exercises and training cruises with II Battle Squadron. Scheduled to be withdrawn from service in July 1914 and replaced by newer dreadnought battleships, the outbreak of World War I that month prevented her retirement. She spent the first two years of the war primarily serving as a guard ship in the German Bight. She and the rest of II Squadron joined the dreadnoughts of the High Seas Fleet to support the raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool, and Whitby in December 1914. In poor condition by 1916, she was withdrawn from fleet service in February. She thereafter patrolled the Danish straits until she was replaced by the battleship Hannover in September 1917. She spent the rest of the war as a disarmed training ship.
After the war, Lothringen was retained by the re-formed Reichsmarine and converted into a depot ship for F-type minesweepers from 1919 to 1920. After the task of clearing the wartime minefields in the North Sea was completed, she was placed in reserve in March 1920. The ship remained inactive for the next decade and was stricken from the naval register in March 1931 and sold to ship breakers later that year. (Full article...)
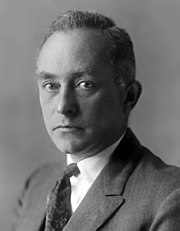
Max Born (German: [ˈmaks ˈbɔʁn] ⓘ; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German-British theoretical physicist who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 1930s. Born was awarded the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his "fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function".
Born entered the University of Göttingen in 1904, where he met the three renowned mathematicians Felix Klein, David Hilbert, and Hermann Minkowski. He wrote his PhD thesis on the subject of the stability of elastic wires and tapes, winning the university's Philosophy Faculty Prize. In 1905, he began researching special relativity with Minkowski, and subsequently wrote his habilitation thesis on the Thomson model of the atom. A chance meeting with Fritz Haber in Berlin in 1918 led to discussion of how an ionic compound is formed when a metal reacts with a halogen, which is today known as the Born–Haber cycle.
In World War I he was originally placed as a radio operator, but his specialist knowledge led to his being moved to research duties on sound ranging. In 1921 Born returned to Göttingen, where he arranged another chair for his long-time friend and colleague James Franck. Under Born, Göttingen became one of the world's foremost centres for physics. In 1925 Born and Werner Heisenberg formulated the matrix mechanics representation of quantum mechanics. The following year, he formulated the now-standard interpretation of the probability density function for ψ*ψ in the Schrödinger equation, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1954. His influence extended far beyond his own research. Max Delbrück, Siegfried Flügge, Friedrich Hund, Pascual Jordan, Maria Goeppert-Mayer, Lothar Wolfgang Nordheim, Robert Oppenheimer, and Victor Weisskopf all received their PhD degrees under Born at Göttingen, and his assistants included Enrico Fermi, Werner Heisenberg, Gerhard Herzberg, Friedrich Hund, Wolfgang Pauli, Léon Rosenfeld, Edward Teller, and Eugene Wigner.
In January 1933, the Nazi Party came to power in Germany, and Born, who was Jewish, was suspended from his professorship at the University of Göttingen. He emigrated to the United Kingdom, where he took a job at St John's College, Cambridge, and wrote a popular science book, The Restless Universe, as well as Atomic Physics, which soon became a standard textbook. In October 1936, he became the Tait Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Edinburgh, where, working with German-born assistants E. Walter Kellermann and Klaus Fuchs, he continued his research into physics. Born became a naturalised British subject on 31 August 1939, one day before World War II broke out in Europe. He remained in Edinburgh until 1952. He retired to Bad Pyrmont, in West Germany, and died in a hospital in Göttingen on 5 January 1970. (Full article...)

Max Weber (April 21, 1864 – June 14, 1920) was a German political economist and sociologist who is considered one of the founders of the modern study of sociology and public administration. He began his career at the University of Berlin, and later worked at Freiburg University, University of Heidelberg, University of Vienna and University of Munich. He was influential in contemporary German politics, being one of Germany's negotiators at the Treaty of Versailles and the member of the commission charged with drafting the Weimar Constitution.
His major works deal with rationalisation in sociology of religion and government, but he also contributed much in the field of economics. His most famous work is his essay The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism, which began his work in the sociology of religion. More...

The I.G. Farben Building – also known as the Poelzig Building and the Abrams Building, formerly informally called The Pentagon of Europe – is a building complex in Frankfurt, Germany, which currently serves as the main structure of the Westend Campus of the University of Frankfurt. Construction began in 1928 and was complete in 1930 as the corporate headquarters of the I.G. Farben conglomerate, then the world's largest chemical company and the world's fourth-largest company overall.
The building's original design in the modernist New Objectivity style was the subject of a competition which was eventually won by the architect Hans Poelzig. On its completion, the complex was the largest office building in Europe and remained so until the 1950s. The I.G. Farben Building's six square wings retain a modern, spare elegance, despite its mammoth size. It is also notable for its paternoster elevators.
The building was the headquarters for production administration of dyes, pharmaceutical drugs, magnesium, lubricating oil, explosives, and methanol, and for research projects relating to the development of synthetic oil and rubber during World War II. Notably I.G. Farben scientists discovered the first antibiotic,[dubious – discuss] fundamentally reformed medical research and "opened a new era in medicine." After World War II, the IG Farben Building served as the headquarters for the Supreme Allied Command and from 1949 to 1952 the High Commissioner for Germany (HICOG). William L. Shirer called it the "building from where the Americans ruled the western part of Germany" in the aftermath of World War II. Notably Dwight D. Eisenhower had his office in the building. It became the principal location for implementing the Marshall Plan, which supported the post-war reconstruction of Europe. The 1948 Frankfurt Documents, which led to the creation of a West German state allied with the western powers, were signed in the building. The I.G. Farben Building served as the headquarters for the US Army's V Corps and the Northern Area Command (NACOM) until 1995. It was also the headquarters of the CIA in Germany. During the early Cold War, it was referred to by US authorities as the Headquarters Building, United States Army Europe (USAREUR); the US Army renamed the building the General Creighton W. Abrams Building in 1975. It was informally referred to as "The Pentagon of Europe."
In 1995, the US Army transferred the IG Farben Building to the German government, and it was purchased by the state of Hesse on behalf of the University of Frankfurt. Renamed the Poelzig Building in honour of its architect, the building underwent a restoration and was opened as part of the university in 2001. It is the central building of the Westend Campus of the university, which also includes over a dozen other buildings built after 2001. (Full article...)
