Posterior auricular muscle
| Posterior auricular muscle | |
|---|---|
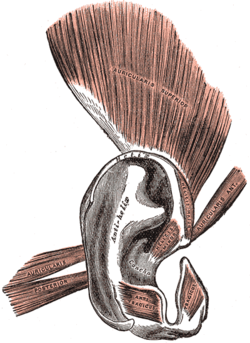 The muscles of the auricula | |
 Auricula in context. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | mastoid process of temporal bone |
| Insertion | posterior part of auricle of outer ear |
| Artery | posterior auricular artery |
| Vein | posterior auricular vein |
| Nerve | posterior auricular nerve of facial nerve (VII) |
| Actions | pulls ear backward |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus auricularis posterior |
| TA98 | A04.1.03.022 |
| TA2 | 2091 |
| FMA | 46857 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The posterior auricular muscle is a muscle behind the auricle of the outer ear. It arises from the mastoid part of the temporal bone, and inserts into the lower part of the cranial surface of the auricle of the outer ear. It draws the auricle backwards, usually a very slight effect.
Structure
The posterior auricular muscle is found behind the auricle of the outer ear.[1] It consists of two or three fleshy fasciculi. These arise from the mastoid part of the temporal bone by short aponeurotic fibers.[1] They insert into the lower part of the cranial surface of the auricle of the outer ear.[1]
The posterior auricular muscle is supplied by branches of the posterior auricular artery, which continues deep to the muscle.[2] It is drained by the posterior auricular vein that accompanies the artery.[2]
Nerve supply
The posterior auricular muscle is supplied by the posterior auricular nerve, a branch of the facial nerve (VII).[2][3]
Function
The posterior auricular nerve draws the auricle of the outer ear backwards.[2] This effect is usually very slight, although some people can wiggle their ears due to a more significant muscle movement.[2]
Postauricular reflex
The postauricular reflex is a vestigial muscle response in humans that acts to pull the ear upward and backward.[4] Research suggests neural circuits for auricle orienting have survived in a vestigial state for over 25 million years. It is often assumed the reflex is a vestigial Preyer reflex (also known as the pinna reflex).[5][6]
Clinical significance
If the posterior auricular muscle inserts into an unusual part of the auricle of the outer ear, this can cause protruding ears.[1]
See also
References
 This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1035 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1035 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d Yotsuyanagi, Takatoshi; Yamauchi, Makoto; Yamashita, Ken; Sugai, Asuka; Gonda, Ayako; Kitada, Ayaka; Saito, Tamotsu; Urushidate, Satoshi (July 2015). "Abnormality of Auricular Muscles in Congenital Auricular Deformities:". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 136 (1): 78e–88e. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000001383. ISSN 0032-1052.
- ^ a b c d e Niamtu, Joseph (2018). "8 - Cosmetic Otoplasty and Related Ear Surgery". Cosmetic Facial Surgery (2nd ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. pp. 473–532. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-39393-5.00008-X. ISBN 978-0-323-39402-4. OCLC 976037123.
- ^ Barral, Jean-Pierre; Croibier, Alain (2009). "25 - Ear". Manual Therapy for the Cranial Nerves. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone / Elsevier. pp. 227–238. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-3100-7.50028-8. ISBN 978-0-7020-3736-8. OCLC 460904284.
- ^ Benning, Stephen D. (2011-03-01). "Postauricular and superior auricular reflex modulation during emotional pictures and sounds". Psychophysiology. 48 (3): 410–414. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01071.x. ISSN 1469-8986. PMC 2962877. PMID 20636290.
- ^ Hackley, Steven A. (2015-10-01). "Evidence for a vestigial pinna-orienting system in humans". Psychophysiology. 52 (10): 1263–1270. doi:10.1111/psyp.12501. ISSN 1469-8986. PMID 26211937.
- ^ "ZFIN Behavior Ontology: pinna reflex". zfin.org. Retrieved 2020-01-05.
