Giant cuttlefish
| Giant cuttlefish | |
|---|---|

| |
| Sepia apama from Whyalla, South Australia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Subgenus: | |
| Species: | S. apama
|
| Binomial name | |
| Sepia apama Gray, 1849
| |
| |
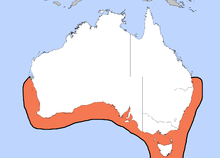
| Distribution of Sepia apama | |
| Synonyms | |
Sepia apama, also known as the giant cuttlefish and Australian giant cuttlefish,[2] is the world's largest cuttlefish species, growing to 50 cm in mantle length and over 10.5 kg (23 lb) in weight.[3] Using cells known as chromatophores, the cuttlefish can put on spectacular displays, changing color in an instant.
S. apama is native to the southern coast of Australia, from Brisbane in Queensland to Shark Bay in Western Australia. It occurs on rocky reefs, seagrass beds, and sand and mud seafloor to a depth of 100 m.[4]
Life cycle and reproduction
Sepia apama live from two to three years. Breeding takes place with the onset of the southern winter. Males abandon their normal cryptic coloring and set out to dazzle the females by adopting rapidly changing bright colours and striking patterns. Females are polyandrous, and collaborative research indicates the tendency for females to reproduce using male genetic material deposited in spermatangia more favorably than in sperm receptacles directly. Females then attach their eggs to the underside of rocks in caves or crevises where they will hatch within three to five months. Sepia apama are semelparous and death follows shortly after a single mating cycle and laying of eggs that will spawn the next generation.[5] Sepia apama have poor anaerobic capability compared to most aquatic invertebrates and a lack of food leads to catabolism. Stomach content analysis indicates fasting during the breeding season and as Sepia apama can catabolise no more than 50% of their body weight they slowly lose physical condition as the season progresses and eventually die. Throughout their range, Sepia apama breed in pairs or small groups, laying eggs in suitable caves or rock crevises. Loose spawning aggregations can form but rarely exceed 10 animals in any one location,[6] with one known exception: hundreds of thousands aggregate along rockey reefs between Whyalla and Point Lowly in the Upper Spencer Gulf. While surveys suggest that juveniles leave these spawning grounds after hatching, nothing is known of their subsequent movement or lifestyle strategies as a juvenile. Adult Sepia apama return to the aggregation site the following winter, or delay their return by an additional year.[citation needed]
Physiology and biochemistry

Genetic studies have shown that there is little if any interbreeding between Sepia apama populations. While there is some genetic divergence, the various populations are not considered taxonomically distinct and are commonly referred to by their location, e.g. Sepia apama upper Spencer Gulf population.[5] The upper Spencer Gulf population is unique in that a permanent salinity gradient in the Spencer Gulf may physiologically exclude other populations from the zone occupied by the upper Spencer Gulf population.[5] Research suggests that the upper Spencer Gulf population may in fact be a separate species as it does show some hallmarks, such as genetic separation, differences in morphology and different patterns of sexual dimorphism to adjacent populations.[6][7]
Sepia apama is a neritic demersal species. They are carnivorous, opportunistic and voracious predators who feed predominantly on crustaceans and fish.[6] Using neurally controlled cells known as chromatophore organs (red to yellow), iridophores (iridescent: spans the entire visible spectrum from blue to near-IR) and leucophores (white), the cuttlefish can put on spectacular displays, changing colour and patterns in a fraction of a second. Located in three layers under the skin, leucophores make up the bottom layer, with chromatophores the outermost. By selective blocking, the three layers work together to produce polarised patterns. Unlike those in most animals, cuttlefish iridophores are physiologically active; they can change their reflectivity and the degree of polarization can also be controlled. Cuttlefish are colourblind, however the photoreceptors of cuttlefish eyes are arranged in a way which gives them the ability to see the linear polarization of light. While the mantis shrimp is the only known creature to have true polarization vision, it is believed that cephalopods may also.[8] Because the optic lobes of cuttlefish are larger than any other region of the brain and their skin produces polarized reflective patterns, it has been postulated that they may communicate through this visual system.[9] By raising elaborate papillae on their skin, S. apama can change the shape and the texture of their skin to imitate rock, sand or seaweed.[10]
An energetics study found that Sepia apama are primarily diurnal and have a small home range (90–550 metres) over short recording periods while travelling large distances to breed. They are able to channel most of their energy directly into growth because they spend 95% of the day resting, suggesting bioenergetics more like that of an octopus than a squid. Very little time is spent foraging (3.7% during the day and 2.1% during the night), most of their time is spent resting and hiding in crevices from predators. The exception to this behavioral routine is the mass spawning aggregation, where cuttlefish are far more active during the days or weeks that they spend there.[11][12]
Role in ecosystem
The Australian giant cuttlefish is eaten by Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins, which have been observed (in South Australia's Spencer Gulf) to have developed a technique for removing the ink and cuttlebone from a cuttlefish before eating it.[13] They are also eaten by New Zealand fur seals.[citation needed]
Upper Spencer Gulf population
Discovered by divers in the late 1990s, the upper Spencer Gulf population is the world's only known mass cuttlefish spawning aggregation with hundreds of thousands of Sepia apama congregating on sub-tidal reefs around Point Lowly near Whyalla between May and August. While outside of the breeding season, the sex ratio is 1 to 1, Spencer Gulf males outnumber females by up to 11 to 1 in the spawning aggregation. It is unclear if this is due to fewer females taking part or to males breeding for a longer period of time than females. With densities of one cuttlefish per square metre, covering approximately 61 hectares (150 acres), the sheer number of Sepia apama makes this breeding aggregation unique in the world. As the cuttlefish are oblivious to divers while spawning, they are now a major regional tourist attraction for divers from around the world.[6] Professor Roger Hanlon of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution has called the breeding aggregation "the premier marine attraction on the planet."[7]
The Sepia apama upper Spencer Gulf population displays two alternative life cycles in both sexes (growth pattern polymorphism). The first involves rapid growth with maturity reached in seven to eight months with small adults returning to spawn in the first year. The second involves slow growth with maturity reached in two years with large adults returning to spawn in the second year.[5] The upper Spencer Gulf population displays reproductive behaviours unique to this population, possibly as a result of the high spawning densities. Large males defend females and egg laying sites while small males, 'sneakers'[14] mimic female colouring and form in order to gain access to the females being protected by the dominant males which are extremely territorial. Male genetic material is deposited in sperm receptacles directly. The females, who potentially lay hundreds of eggs, extracts one egg at a time and fertilises it by passing it over the sperm receptacle before attaching it to the underside of a rock at depths of 2 metres (6.6 ft) to 5 metres (16 ft).[6]
Prior to the mid-1990s, the population was fished for snapper bait with annual catches of around four tonnes (approx 4,000 cuttlefish). During the 1995 and 1996 spawning seasons, commercial fishing of the spawning grounds harvested around 200 tonnes annually. Over exploitation was recognised after 245 tonnes was harvested in 1997, leading to 50% of the grounds being closed to commercial fishing in 1998. Despite half of the grounds being closed, commercial fishers took 109 tonnes in 1998 (approximately half of the estimated biomass) before dropping to 3.7 tonnes in 1999. The catch data for 2000 to 2005 has not been released for confidentiality reasons.[15] Surveys indicated that the cuttlefish biomass remained stable from 1998 to 2001. A further survey in 2005 revealed a 34% decrease in biomass since 2001 that was attributed to natural variability and illegal fishing during the peak spawning period.[15] The closure was subsequently expanded to the entire spawning grounds and anecdotal observations suggested increased numbers in 2006 and 2007, however, a new survey in 2008 found the biomass had decreased a further 17%.[5][6]
Catch data for the South Australian cuttlefish fishery is reported in annual reports of the Marine Scalefish Fishery, published by SARDI. 2014 data is graphed below. From its establishment in 1987 to the financial year ending June 1992, the fishery caught less than 3 tonnes per annum.[16]
| Financial Year | Tonnes caught |
|---|---|
| 1992-93 | |
| 1993-94 | |
| 1994-95 | |
| 1995-96 | |
| 1996-97 | |
| 1997-98 | |
| 1998-99 | |
| 1999-00 | |
| 2000-01 | |
| 2001-02 | |
| 2002-03 | |
| 2003-04 | |
| 2004-05 | |
| 2005-06 | |
| 2006-07 | |
| 2007-08 | |
| 2008-09 | |
| 2009-10 | |
| 2010-11 | |
| 2011-12 | |
| 2012-13 | |
| 2013-14 |
In 2011, it was estimated that only 33% of the 2010 population had returned to breed, less than 80,000 cuttlefish. Beginning in May, the cuttlefish leave deep water and migrate along coastal reefs to reach their spawning grounds. Local fishermen claim that a small "finger of land" near Point Lowly extends outside the exclusion zone and that commercial fishers have been targeting the area, intercepting the Sepia apama before they can reach the spawning grounds. Being semelparous breeders, ecologist Bronwyn Gillanders believed the cuttlefish were in danger, stating that it is hard to determine whether this is a natural phenomenon or something else and that the cause requires more research.[17]
In 2012, the number of cuttlefish that returned to the spawning ground again dropped dramatically with numbers as low as 6,000 estimated. A cross-government Cuttlefish Working Group was established and has recommended investigating broader ecological factors.[citation needed] Tour guide Tony Bramley, who had been taking divers to view the spawning grounds since they were discovered stated "It's heartbreaking, when you look at what's left...[once] there were so many animals you couldn't land on the bottom, you had to push them aside."[18] The Conservation Council of SA, which believes the population to be a separate species, has warned that the Spencer Gulf cuttlefish face extinction within two or three years if nothing is done to protect them. The state government working group had recommended an immediate ban on fishing for the cuttlefish, however, this was rejected by State Cabinet on 3 September with Fisheries Minister Gail Gago stating; "There is no strong evidence to suggest that fishing is impacting on the giant cuttlefish, therefore, further closures would be ineffective."[7]
On 28 March 2013, the State Government introduced a temporary ban on fishing for cuttlefish in the northern Spencer Gulf for the 2013 breeding season. Fisheries Minister Gago announced that research into the reasons behind the 90% decline in the cuttlefish population had ruled out commercial fishing as a cause but was otherwise inconclusive and that further areas of Spencer Gulf would be closed in 2014.[19][20] The ban has been extended, and will remain in place until 15 February 2017. The closed area is defined as all Spencer Gulf waters north of Wallaroo and Arno Bay.[21]
In 2014, the cuttlefish population showed first signs of potential recovery, following 15 years of recorded decline.[citation needed] Numbers increased again in 2015,[22] but as of early 2015 have not returned to pre-fishing levels.
| Year | Population estimate |
|---|---|
| 1999 | |
| 2000 | |
| 2001 | |
| 2002 | |
| 2003 | |
| 2004 | |
| 2005 | |
| 2006 | |
| 2007 | |
| 2008 | |
| 2009 | |
| 2010 | |
| 2011 | |
| 2012 | |
| 2013 | |
| 2014 | |
| 2015 |
- data sourced from SARDI, 2015. Figure '0' is used to represent years in which surveys did not occur, and no estimation was made.
Effect of local industrialisation
In 1984, before the spawning grounds were discovered, Santos built a hydrocarbon processing plant at adjoining Port Bonython. There is some concern over the possible impact of the plant on the cuttlefish population and there have been two major spills at the plant.[23][24] Santos denies that the recent spill spread off-site, but the SA EPA said hydrocarbons had migrated through the rock strata beyond the plant and the barrier trench built by Santos. Santos now provides funding for cuttlefish research.[25]
BHP Billiton has plans to build a desalination plant at Point Lowly to supply fresh water to Roxby Downs copper and uranium mine. The plant, located within 200 metres (660 ft) of the breeding grounds, would release around 120 megalitres (32,000,000 US gal) of brine (46–60 ppt) into the area each day. As cuttlefish embryos die off as salinity levels rise (optimal range 28–38 ppt, 100% mortality at 50 ppt), there has been considerable public opposition to the proposed plant because of the expected environmental impact.[25][26][27]
Due to its proximity to the ore deposits of the Middleback Ranges, several mining companies have indicated they want to build petrochemical and diesel refining facilities at Port Bonython, adjacent to Point Lowly. A second wharf for the loading of iron ore, and possibly copper concentrates and uranium, is also planned. A community action group called the Cuttlefish Coast Coalition was formed in opposition to these proposed developments.[25]
As a result of the above threats, in 2010 an application was made to list that population of Sepia apama in the list of threatened species. On February 2, 2011, the Threatened Species Scientific Committee ruled the species was not eligible for listing as the affected population was not taxonomically distinct from the rest of Sepia apama for the purposes of the Act.[27]
Industrial nutrient pollution sources exist to the west of the cuttlefish breeding reef at the Whyalla Steelworks, which produced ammonia as a byproduct of its coking process for steelmaking. North of the cuttlefish aggregation, seacage farming of yellowtail kingfish occurred commercially prior to 2011. Fish farming also introduces nutrients to the water in the forms of uneaten feed and fish excrement.
In popular culture
In May 2009, D'Faces of Youth Arts and Snuff Puppets produced a live theatre performance for Come Out Festival. It featured several large cuttlefish puppets and appeared in Adelaide's Victoria Square, at the Adelaide Airport and at a Whyalla performance. There was some controversy surrounding the performances after a participant in the project was openly critical of the plan to build a desalination plant at Point Lowly.[28] The major sponsor of Come Out Festival in 2009 was the BHP Billiton Youth Fund, the same company which proposes to construct the desalination plant. The overarching theme of the festival that year was 'Colliding Worlds'.[29] BHP Billiton has not sponsored the Come Out Festival since the 2009 event.

During the Adelaide Fringe Festival in March 2012, the RiAus presented Sepia, an original work by Welsh playwright, Emily Steel.[30] Set in Whyalla, the play told the story of the fictitious character Neil, the proprietor of a caravan park who was struggling to come to terms with the cuttlefish decline whilst trying to keep his family together. The play also featured at the Melbourne Fringe Festival.[31] Presenting partner RiAus is sponsored by the oil and gas company Santos. Santos was responsible for hydrocarbon groundwater contamination at Port Bonython, adjacent to the cuttlefish breeding grounds, first discovered in 2008.
In 2014, the Adelaide Fringe Festival launched Stobie the Disco Cuttlefish, a 13 m long electrified cuttlefish puppet, equipped with strobing, coloured lighting and a sound system. Stobie the Disco Cuttlefish first appeared during the Adelaide Fringe Opening Parade, then performed with a troupe of dancers each Saturday night during the festival.[32] The soundtrack to the performance included samples from The Beegees hit 'Stayin' Alive'[33] and the entire theme song from the movie Fame.
In 2016, underwater photographer Scott Portelli's image Cuttlefish aggregation won the national first prize (Australia) in the 2015 Sony World Photography Awards — the world’s biggest photography competition.[22]
The mass aggregation of Sepia apama at Point Lowly has inspired the development of a retro computer game called Cuttle Scuttle which is scheduled for release in 2016.[34]
See also
References
- ^ Barratt, I. & Allcock, L. 2012. Sepia apama. In: IUCN 2012. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Downloaded on 27 October 2012.
- ^ "Giant Cuttlefish - Sepia apama". Australian Museum. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- ^ Reid, A., P. Jereb, & C.F.E. Roper 2005. Family Sepiidae. In: P. Jereb & C.F.E. Roper, eds. Cephalopods of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of species known to date. Volume 1. Chambered nautiluses and sepioids (Nautilidae, Sepiidae, Sepiolidae, Sepiadariidae, Idiosepiidae and Spirulidae). FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes. No. 4, Vol. 1. Rome, FAO. pp. 57–152.
- ^ Norman, M.D. 2000. Cephalopods: A World Guide. ConchBooks.
- ^ a b c d e Amendment to the list of Threatened Population under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC Act). Threatened Species Scientific Committee.
- ^ a b c d e f Natural History of the Giant Australian Cuttlefish BHP Billiton
- ^ a b c Clare Peddie, Heather Kennett The cuttle scuttle The Advertiser September 29, 2012 Pg 67
- ^ Silvery fish reflect polarised light; they reflect the same amount of light in the same direction as the light they are viewed against, making them almost invisible in water. If the polarisation is reduced, the fish become easily visible. Cuttlefish will ignore fish with reduced polarisation and preferentially attack fish emitting polarised light.[1]
- ^ Mäthger; et al. (April 21, 2009). "Do cephalopods communicate using polarized light reflections from their skin?" (PDF). The Journal of Experimental Biology 212, 2133-2140. Retrieved 4 November 2011.
- ^ Alison King The Colourful World of Cephalopods - Cephalopod body patterning II. The Cephalopod Page.
- ^ Hanlon, R.T. 2008. Australian Giant Cuttlefish - Physiology and Biochemistry. Encyclopedia of Life.
- ^ Aitken, J.P.; O'Dor, R.K.; Jackson, G.D. (2005). "The secret life of the giant Australian cuttlefish Sepia apama (Cephalopoda): Behaviour and energetics in nature revealed through radio acoustic positioning and telemetry (RAPT)". Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 320: 77–91. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2004.12.040.
- ^ Catch cuttlefish, drain off the ink, then fillet. Serves five (dolphins): Scientists stunned by mammals' elaborate culinary preparations
- ^ Life. Extraordinary Animals, Extreme Behaviour by BBC Books, Martha Holmes & Michael Gunton, 2009 ISBN 978 1846076428, pg 28.
- ^ a b MA Steer and KC Hall Estimated Abundance and Biomass of the Unique Spawning Aggregation of the Giant Australian Cuttlefish (Sepia apama) in Northern Spencer Gulf, South Australia. PIRSA October 2005
- ^ Fowler, A. J.; McGarvey, R.; Steer, M. A.; Feenstra, J. E. (2014). The South Australian Marine Scalefish Fishery Status Report - Analysis of Fishery Statistics for 2013/14 (PDF). Adelaide, South Australia: SARDI. p. 42.
- ^ Mystery of the Missing Cuttlefish. The Advertiser, July 24, 2011. p. 7.
- ^ Drastic loss in giant colony. The Advertiser, September 25, 2012. p. 24.
- ^ "Cuttlefish update" (PDF). Primary Industries and Regions SA. Primary Industries and Regions SA. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- ^ AAP (27 March 2013). "Giant cuttlefish decline prompts catch ban parts of South Australia's Spencer Gulf". The Advertiser. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- ^ "Fishing closures". pir.sa.gov.au. Department of Primary Industries and Regions, South Australia. Retrieved 2016-03-16.
- ^ a b Broadstock, Amelia (2016-03-15). "Wildlife photographer captures amazing photo of breeding SA giant cuttlefish". The Advertiser. Retrieved 2016-03-16.
- ^ http://www.amsa.gov.au/marine_environment_protection/major_oil_spills_in_australia/Era/index.asp
- ^ http://www.abc.net.au/news/2010-03-22/epa-fears-bigger-santos-oil-spill/374516
- ^ a b c Cuttlefish chaos at Whyalla. Archived from Dive Pacific Issue No. 116, Feb/Mar 2010.
- ^ Desalination and South Australia's Gulfs ecosystems. Fishers For Conservation Inc.
- ^ a b Conservation Assessment. Advice to the Minister for Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities from the Threatened Species Scientific Committee (the Committee) on Amendment to the list of Threatened Population under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC Act) February 2, 2011.
- ^ McDonald, Patrick "Fun with a serious message as Come Out'09 launched" The Advertiser, South Australia (2009-05-17). Retrieved 2014-01-22.
- ^ 2009.pdf Come Out Festival 2009 Program Come Out Festival, South Australia (2009). Accessed 2014-01-22.
- ^ Fuss, Eloise "Cuttlefish controversy takes centre stage" ABC North & West SA, South Australia (2012-02-17). Retrieved 2014-02-20.
- ^ Sepiatheplay.com Accessed 2014-01-21.
- ^ Keen, Suzie "Record line-up for 2014 Adelaide Fringe" InDaily (2013-11-29)
- ^ Disco Cuttlefish - Adelaide Fringe Festival (2014). Accessed 2014-02-20.
- ^ "Cuttle Scuttle" Facebook.com. Accessed 2014-06-13.
- Kassahn, K.S.; Donnellan, S.C.; Fowler, A.J.; Hall, K.C.; Adams, M.; Shaw, P.W. (2003). "Molecular and morphological analyses of the cuttlefish Sepia apama indicate a complex population structure". Marine Biology. 143 (5): 947–962. doi:10.1007/s00227-003-1141-5.
External links
- BBC: Giant cuttlefish
- "CephBase: Giant cuttlefish". Archived from the original on 2005-08-17.
- Video of Sepia apama at YouTube



