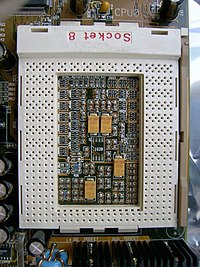
Socket 8
 | |
| Type | ZIF |
|---|---|
| Chip form factors | CPGA |
| Contacts | 387 |
| FSB protocol | AGTL |
| FSB frequency | 60–66MHz |
| Voltage range | 3.1 or 3.3V |
| Processors | Pentium Pro, Pentium II OverDrive |
| Predecessor | Socket 7 |
| Successor | Slot 2 |
This article is part of the CPU socket series | |
The Socket 8 CPU socket was used exclusively with the Intel Pentium Pro and Pentium II Overdrive computer processors. Intel discontinued Socket 8 in favor of Slot 1 with the introduction of the Pentium II and Slot 2 with the release of the Pentium II Xeon in 1999.
Technical specifications

Socket 8 has a unique rectangular socket with 387 pins. It supports a FSB speeds ranging from 60 to 66 MHz, a voltage from 3.1 or 3.3V, and support for the Pentium Pro and the Pentium II OverDrive CPUs. Socket 8 also has a unique pin arrangement pattern. One part of the socket has pins in a PGA grid, while the other part uses a SPGA grid.[1]
See also
References
- ^ "Intel Socket 8 Specification". pcguide.com. Retrieved 2009-04-21.
