Spinal disc herniation
| Spinal disc herniation | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Neurosurgery |
A Spinal disc herniation (prolapsus disci intervertebralis) is a medical condition affecting the spine in which a tear in the outer, fibrous ring (annulus fibrosus) of an intervertebral disc (discus intervertebralis) allows the soft, central portion (nucleus pulposus) to bulge out beyond the damaged outer rings. Disc herniation is usually due to age related degeneration of the annulus fibrosus, although trauma, lifting injuries, or straining have been implicated. Tears are almost always postero-lateral in nature owing to the presence of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the spinal canal.[1] This tear in the disc ring may result in the release of inflammatory chemical mediators which may directly cause severe pain, even in the absence of nerve root compression.
Disc herniations are normally a further development of a previously existing disc "protrusion", a condition in which the outermost layers of the annulus fibrosus are still intact, but can bulge when the disc is under pressure. In contrast to a herniation, none of the nucleus pulposus escapes beyond the outer layers.
Most minor herniations heal within several weeks. Anti-inflammatory treatments for pain associated with disc herniation, protrusion, bulge, or disc tear are generally effective. Severe herniations may not heal of their own accord and may require surgical intervention.
The condition is widely referred to as a slipped disc, but this term is not medically accurate as the spinal discs are firmly attached between the vertebrae and cannot "slip".
Terminology


Some of the terms commonly used to describe the condition include herniated disc, prolapsed disc, ruptured disc and slipped disc. Other phenomena that are closely related include disc protrusion, pinched nerves, sciatica, disc disease, disc degeneration, degenerative disc disease, and black disc.
The popular term slipped disc is a misnomer, as the intervertebral discs are tightly sandwiched between two vertebrae to which they are attached, and cannot actually "slip", or even get out of place. The disc is actually grown together with the adjacent vertebrae and can be squeezed, stretched and twisted, all in small degrees. It can also be torn, ripped, herniated, and degenerated, but it cannot "slip".[2] Some authors consider that the term "slipped disc" is harmful, as it leads to an incorrect idea of what has occurred and thus of the likely outcome.[3][4] However, during growth, one vertebral body can slip relative to an adjacent vertebral body. This congenital deformity is called spondylolisthesis.[5]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location of the herniation and the types of soft tissue that become involved. They can range from little or no pain if the disc is the only tissue injured, to severe and unrelenting neck or lower back pain that will radiate into the regions served by affected nerve roots that are irritated or impinged by the herniated material. Often, herniated discs are not diagnosed immediately, as the patients come with undefined pains in the thighs, knees, or feet. Other symptoms may include sensory changes such as numbness, tingling, muscular weakness, paralysis, paresthesia, and affection of reflexes. If the herniated disc is in the lumbar region the patient may also experience sciatica due to irritation of one of the nerve roots of the sciatic nerve. Unlike a pulsating pain or pain that comes and goes, which can be caused by muscle spasm, pain from a herniated disc is usually continuous or at least is continuous in a specific position of the body.
It is possible to have a herniated disc without any pain or noticeable symptoms, depending on its location. If the extruded nucleus pulposus material doesn't press on soft tissues or nerves, it may not cause any symptoms. A small-sample study examining the cervical spine in symptom-free volunteers has found focal disc protrusions in 50% of participants, which suggests that a considerable part of the population can have focal herniated discs in their cervical region that do not cause noticeable symptoms.[6][7]
Typically, symptoms are experienced only on one side of the body. If the prolapse is very large and presses on the spinal cord or the cauda equina in the lumbar region, both sides of the body may be affected, often with serious consequences. Compression of the cauda equina can cause permanent nerve damage or paralysis. The nerve damage can result in loss of bowel and bladder control as well as sexual dysfunction. This disorder is called cauda equina syndrome.
Cause
Disc herniations can result from general wear and tear, such as when performing jobs that require constant sitting and squatting.[citation needed] However, herniations often result from jobs that require lifting.[citation needed] Minor back pain and chronic back tiredness are indicators of general wear and tear that make one susceptible to herniation on the occurrence of a traumatic event, such as bending to pick up a pencil or falling.[citation needed] When the spine is straight, such as in standing or lying down, internal pressure is equalized on all parts of the discs. While sitting or bending to lift, internal pressure on a disc can move from 17 psi (lying down) to over 300 psi (lifting with a rounded back). [citation needed]
Herniation of the contents of the disc into the spinal canal often occurs when the anterior side (stomach side) of the disc is compressed while sitting or bending forward, and the contents (nucleus pulposus) get pressed against the tightly stretched and thinned membrane (annulus fibrosis) on the posterior side (back side) of the disc. The combination of membrane thinning from stretching and increased internal pressure (200 to 300 psi) results in the rupture of the confining membrane. The jelly-like contents of the disc then move into the spinal canal, pressing against the spinal nerves, which may produce intense and potentially disabling pain and other symptoms.[citation needed]
There is also a strong genetic component. Mutation in genes coding for proteins involved in the regulation of the extracellular matrix, such as MMP2 and THBS2, has been demonstrated to contribute to lumbar disc herniation.[8]
Location
The majority of spinal disc herniation cases occur in lumbar region (95% in L4-L5 or L5-S1).[9] The second most common site is the cervical region (C5-C6, C6-C7). The thoracic region accounts for only 0.15% to 4.0% of cases.
Herniations usually occur posterolaterally, where the annulus fibrosis is relatively thin and is not reinforced by the posterior or anterior longitudinal ligament.[9] In the cervical spinal cord, a symptomatic posterolateral herniation between two vertebrae will impinge on the nerve which exits the spinal canal between those two vertebrae on that side.[9] So for example, a right posterolateral herniation of the disc between vertebrae C5 and C6 will impinge on the right C6 spinal nerve. The rest of the spinal cord, however, is oriented differently, so a symptomatic posterolateral herniation between two vertebrae will actually impinge on the nerve exiting at the next intervertebral foramen down.[9] So for example, a herniation of the disc between the L5 and S1 vertebrae will impinge on the S1 spinal nerve, which exits between the S1 and S2 vertebrae.
Cervical
Cervical disc herniations occur in the neck, most often between the fifth & sixth (C5/6) and the sixth and seventh (C6/7) cervical vertebral bodies. Symptoms can affect the back of the skull, the neck, shoulder girdle, scapula,[10] shoulder, arm, and hand. The nerves of the cervical plexus and brachial plexus can be affected.[11]
Lumbar
Lumbar disc herniations occur in the lower back, most often between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebral bodies or between the fifth and the sacrum. Symptoms can affect the lower back, buttocks, thigh, anal/genital region (via the Perineal nerve), and may radiate into the foot and/or toe. The sciatic nerve is the most commonly affected nerve, causing symptoms of sciatica. The femoral nerve can also be affected[12] and cause the patient to experience a numb, tingling feeling throughout one or both legs and even feet or even a burning feeling in the hips and legs.
Pathophysiology
There is now recognition of the importance of “chemical radiculitis” in the generation of back pain.[13] A primary focus of surgery is to remove “pressure” or reduce mechanical compression on a neural element: either the spinal cord, or a nerve root. But it is increasingly recognized that back pain, rather than being solely due to compression, may also be due to chemical inflammation.[13][14][15][16] There is evidence that points to a specific inflammatory mediator of this pain.[17][18] This inflammatory molecule, called tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF), is released not only by the herniated disc, but also in cases of disc tear (annular tear), by facet joints, and in spinal stenosis.[13][19][20][21] In addition to causing pain and inflammation, TNF may also contribute to disc degeneration.[22]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by a practitioner based on the history, symptoms, and physical examination. At some point in the evaluation, tests may be performed to confirm or rule out other causes of symptoms such as spondylolisthesis, degeneration, tumors, metastases and space-occupying lesions, as well as to evaluate the efficacy of potential treatment options.
Physical examination
The Straight leg raise may be positive, as this finding has low specificity; however, it has high sensitivity. Thus the finding of a negative SLR sign is important in helping to "rule out" the possibility of a lower lumbar disc herniation. A variation is to lift the leg while the patient is sitting.[23] However, this reduces the sensitivity of the test.[24]
Imaging
- X-ray: Although traditional plain X-rays are limited in their ability to image soft tissues such as discs, muscles, and nerves, they are still used to confirm or exclude other possibilities such as tumors, infections, fractures, etc. In spite of these limitations, X-ray can still play a relatively inexpensive role in confirming the suspicion of the presence of a herniated disc. If a suspicion is thus strengthened, other methods may be used to provide final confirmation.
- Computed tomography scan (CT or CAT scan): A diagnostic image created after a computer reads x-rays. It can show the shape and size of the spinal canal, its contents, and the structures around it, including soft tissues. However, visual confirmation of a disc herniation can be difficult with a CT.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): A diagnostic test that produces three-dimensional images of body structures using powerful magnets and computer technology. It can show the spinal cord, nerve roots, and surrounding areas, as well as enlargement, degeneration, and tumors. It shows soft tissues even better than CAT scans. An MRI performed with a high magnetic field strength usually provides the most conclusive evidence for diagnosis of a disc herniation. T2-weighted images allow for clear visualization of protruded disc material in the spinal canal.
- Myelogram: An x-ray of the spinal canal following injection of a contrast material into the surrounding cerebrospinal fluid spaces. By revealing displacement of the contrast material, it can show the presence of structures that can cause pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, such as herniated discs, tumors, or bone spurs. Because it involves the injection of foreign substances, MRI scans are now preferred for most patients. Myelograms still provide excellent outlines of space-occupying lesions, especially when combined with CT scanning (CT myelography).
- Electromyogram and Nerve conduction studies (EMG/NCS): These tests measure the electrical impulse along nerve roots, peripheral nerves, and muscle tissue. This will indicate whether there is ongoing nerve damage, if the nerves are in a state of healing from a past injury, or whether there is another site of nerve compression. EMG/NCS studies are typically used to pinpoint the sources of nerve dysfunction distal to the spine.
- The presence and severity of myelopathy can be evaluated by means of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), a neurophysiological method that allows the measurement of the time required for a neural impulse to cross the pyramidal tracts, starting from the cerebral cortex and ending at the anterior horn cells of the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spinal cord. This measurement is called Central Conduction Time (CCT). TMS can aid physicians to:
- determine whether myelopathy exists
- identify the level of the spinal cord where myelopathy is located. This is especially useful in cases where more that two lesions may be responsible for the clinical symptoms and signs, such as in patients with two or more cervical disc hernias[25]
- follow-up the progression of myelopathy in time, for example before and after cervical spine surgery
- TMS can also help in the differential diagnosis of different causes of pyramidal tract damage.[26]
-
Narrowed space between L5 and S1 vertebrae, indicating probable prolapsed intervertebral disc - a classic picture.
-
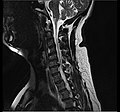
MRI scan of cervical disc herniation between fifth and sixth cervical vertebral bodies. Note that herniation between sixth and seventh cervical vertebral bodies is most common.
-
MRI scan of cervical disc herniation between sixth and seventh cervical vertebral bodies.
-
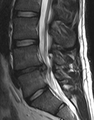
MRI scan of large herniation (on the right) of the disc between the L4-L5 vertebrae.
-
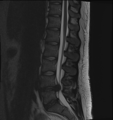
MRI Scan of lumbar disc herniation between fourth and fifth lumbar vertebral bodies.
-
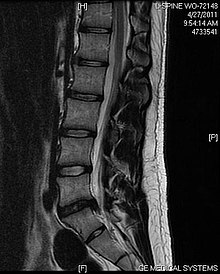
A rather severe herniation of the L4-L5 disc.
Differential diagnosis
- Mechanical pain
- Discogenic pain
- Myofascial pain
- Spondylosis/spondylolisthesis
- Spinal stenosis
- Abscess
- Hematoma
- Discitis/osteomyelitis
- Mass lesion/malignancy
- Myocardial infarction
- Aortic dissection
Treatment
In the majority of cases, spinal disc herniation doesn't require surgery, and a study on sciatica, which can be caused by spinal disc herniation, found that "after 12 weeks, 73% of patients showed reasonable to major improvement without surgery."[27] The study, however, did not determine the number of individuals in the group that had sciatica caused by disc herniation.
Initial treatment usually consists of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain medication (NSAIDs), but the long-term use of NSAIDs for patients with persistent back pain is complicated by their possible cardiovascular and gastrointestinal toxicity.[28] An alternative often employed is the injection of cortisone into the spine adjacent to the suspected pain generator, a technique known as “epidural steroid injection”.[29] Epidural steroid injections "may result in some improvement in radicular lumbosacral pain when assessed between 2 and 6 weeks following the injection, compared to control treatments."[30] Specifically epidural steroids given via the transforaminal route in the peri radicular distribution result in significant improvements in 55 percent of patients with benefits lasting for one year or longer in half of those who respond [31] The probability of response depends on the extent of neural compression of the nerve root as defined by the preservation of epidural fat (on T1 weighted MRI sequences) and CSF on T2 weighted images and the presence of nerve root distortion and efface meant. Greater nerve root compression correlated with lower success rates with transforaminal injection of steroids. [32] Complications resulting from poor technique are rare.[33]
Ancillary approaches, such as rehabilitation, physical therapy, anti-depressants, and, in particular, graduated exercise programs, may all be useful adjuncts to anti-inflammatory approaches.[28]
Lumbar
Non-surgical methods of treatment are usually attempted first, leaving surgery as a last resort. Pain medications are often prescribed as the first attempt to alleviate the acute pain and allow the patient to begin exercising and stretching. There are a variety of other non-surgical methods used in attempts to relieve the condition after it has occurred, often in combination with pain killers. They are either considered indicated, contraindicated, relatively contraindicated, or inconclusive based on the safety profile of their risk-benefit ratio and on whether they may or may not help:
Indicated
- Patient education on proper body mechanics[34]
- Physical therapy, to address mechanical factors, and may include modalities to temporarily relieve pain (i.e. traction, electrical stimulation, massage)[34]
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)[34]
- Oral steroids (e.g. prednisone or methylprednisolone)[34]
- Epidural cortisone injection[34]
- Intravenous sedation, analgesia-assisted traction therapy (IVSAAT)
- Weight control[34]
- Tobacco cessation
- Lumbosacral back support[34]
- Spinal manipulation: Moderate quality evidence suggests that spinal manipulation is more effective than placebo for the treatment of acute (less than 3 months duration) lumbar disk herniation and acute sciatica.[35][36] The same study also found "low to very low" evidence for its usefulness in treating chronic lumbar symptoms (more than 3 months) and "The quality of evidence for ... cervical spine–related extremity symptoms of any duration is low or very low". A 2006 review of published research stated that spinal manipulation is likely to be safe when used by appropriately-trained practitioners,"[37] and research currently suggests that spinal manipulation is safe for the treatment of disk-related pain.[38]
Contraindicated
- Spinal manipulation: According to the WHO, in their guidelines on chiropractic practice, spinal manipulation is contraindicated for disc herniations when there are progressive neurological deficits. An example of this would be cauda equina syndrome.[39]
Inconclusive
- Non-surgical spinal decompression: A 2007 review of published research on this treatment method found shortcomings in most published studies and concluded that there was only "very limited evidence in the scientific literature to support the effectiveness of non-surgical spinal decompression therapy."[40] Its use and marketing have been very controversial.[41]
Surgical
Surgery is generally considered only as a last resort, or if a patient has a significant neurological deficit.[42] The presence of cauda equina syndrome (in which there is incontinence, weakness and genital numbness) is considered a medical emergency requiring immediate attention and possibly surgical decompression.
Regarding the role of surgery for failed medical therapy in patients without a significant neurological deficit, a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials by the Cochrane Collaboration concluded that "limited evidence is now available to support some aspects of surgical practice". More recent randomized controlled trials refine indications for surgery as follows:
- The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT)
- Patients studied "intervertebral disk herniation and persistent symptoms despite some nonoperative treatment for at least 6 weeks...radicular pain (below the knee for lower lumbar herniations, into the anterior thigh for upper lumbar herniations) and evidence of nerve-root irritation with a positive nerve-root tension sign (straight leg raise–positive between 30° and 70° or positive femoral tension sign) or a corresponding neurologic deficit (asymmetrical depressed reflex, decreased sensation in a dermatomal distribution, or weakness in a myotomal distribution)
- Conclusions. "Patients in both the surgery and the nonoperative treatment groups improved substantially over a 2-year period. Because of the large numbers of patients who crossed over in both directions, conclusions about the superiority or equivalence of the treatments are not warranted based on the intent-to-treat analysis"[43][44]
- The Hague Spine Intervention Prognostic Study Group[45]
- Patients studied "had a radiologically confirmed disk herniation...incapacitating lumbosacral radicular syndrome that had lasted for 6 to 12 weeks...Patients presenting with cauda equina syndrome, muscle paralysis, or insufficient strength to move against gravity were excluded."
- Conclusions. "The 1-year outcomes were similar for patients assigned to early surgery and those assigned to conservative treatment with eventual surgery if needed, but the rates of pain relief and of perceived recovery were faster for those assigned to early surgery."
Surgical options
- Chemonucleolysis - dissolves the protruding disc[46]
- IDET (a minimally invasive surgery for disc pain)
- Discectomy/Microdiscectomy - to relieve nerve compression
- Tessys method - a transforaminal endoscopic method to remove herniated discs
- Laminectomy - to relieve spinal stenosis or nerve compression
- Hemilaminectomy - to relieve spinal stenosis or nerve compression
- Lumbar fusion (lumbar fusion is only indicated for recurrent lumbar disc herniations, not primary herniations)
- Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (for cervical disc herniation)
- Disc arthroplasty (experimental for cases of cervical disc herniation)
- Dynamic stabilization
- Artificial disc replacement, a relatively new form of surgery in the U.S. but has been in use in Europe for decades, primarily used to treat low back pain from a degenerated disc.
- Nucleoplasty[47]
Surgical goals include relief of nerve compression, allowing the nerve to recover, as well as the relief of associated back pain and restoration of normal function.
Complications
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of a herniated disc varies greatly upon a patient’s condition. Major factors taken into consideration are the patient’s pain threshold and severity of injury. Degree of injury ranges from some minor discomfort to immense pain that causes movement restrictions *.[48] Possible sciatica symptoms are also taken into account when discussing a patient’s discomfort and should always be considered for possible MRI investigation.
Electrostimulation
A module of rehabilitation is electrostimulation *[49] which is commonly used in the physical therapy field. Electrostimulation therapy includes placement of electrode pads proximal to the strained or weakened erector spinae surrounding the herniated disc.[50]
Laser Light Therapy
Laser light therapy is a light utilizing module with an instrument that emits the therapeutic light directly onto the injured area.


Ultrasound Therapy
Ultrasound*[49] is similar to laser therapy in its direct application to damaged tissues but utilizes vibrations in a crystal-containing handheld unit.
Hot/Cold Therapy
A general form of therapy is the use of ice packs and heat packs which are usually wrapped in a towel and applied directly.
Weightlifting
Weightlifting has been used in conjunction with the aforementioned therapeutic modalities. Gasiorowski’s research proves that patients who qualify for surgical procedures can alternatively select weightlifting to avoid risks of surgery. Weightlifting involves the use of multigym machines, free-weights, and barbells. As a part of this type of therapy, plyometric exercises were implemented to help correct any imbalances in the patient’s gait that resulted from disc herniation *.[48]
Epidemiology

Disc herniation can occur in any disc in the spine, but the two most common forms are lumbar disc herniation and cervical disc herniation. The former is the most common, causing lower back pain (lumbago) and often leg pain as well, in which case it is commonly referred to as sciatica.
Lumbar disc herniation occurs 15 times more often than cervical (neck) disc herniation, and it is one of the most common causes of lower back pain. The cervical discs are affected 8% of the time and the upper-to-mid-back (thoracic) discs only 1 - 2% of the time.[51]
The following locations have no discs and are therefore exempt from the risk of disc herniation: the upper two cervical intervertebral spaces, the sacrum, and the coccyx.
Most disc herniations occur when a person is in their thirties or forties when the nucleus pulposus is still a gelatin-like substance. With age the nucleus pulposus changes ("dries out") and the risk of herniation is greatly reduced. After age 50 or 60, osteoarthritic degeneration (spondylosis) or spinal stenosis are more likely causes of low back pain or leg pain.
- 4.8% males and 2.5% females older than 35 experience sciatica during their lifetime.
- Of all individuals, 60% to 80% experience back pain during their lifetime.
- In 14%, pain lasts more than 2 weeks.
- Generally, males have a slightly higher incidence than females.
Prevention
Because there are various causes for back injuries, prevention must be comprehensive . Back injuries are predominant in manual labor so the majority low back pain prevention methods have been applied primarily toward biomechanics[52] Prevention must come from multiple sources such as education, proper body mechanics, and physical fitness.
Education
Education should emphasize not lifting beyond ones capabilities and giving the body a rest after strenuous effort. Over time, poor posture can cause the IVD to tear or become damaged. Striving to maintain proper posture and alignment will aid in preventing disc degradation.[53]
Exercise
Exercises that are used to enhance back strength may also be used to prevent back injuries. Back exercises include the prone press-ups, transverse abdominus bracing, and floor bridges. Abdominal bracing protects against joint and disc injury. If pain is present in the back, it can mean that the stabilization muscles of the back are weak and a person needs to train the trunk musculature. Another preventative measure is to not work oneself past fatigue. Signs of fatigue include shaking, poor coordination, muscle burning and loss of the transverse abdominal brace. Individuals who engage in power lifting place their bodies under heavy stress. Barbells are common tools used in strength training. The usage of lumbarsacral support belts may restrict movement at the spine and support the back during lifting.[54]
Research
Future treatments may include stem cell therapy. Doctors Victor Y. L. Leung, Danny Chan and Kenneth M. C. Cheung have reported in the European Spine Journal that "substantial progress has been made in the field of stem cell regeneration of the intervertebral disc. Autogenic mesenchymal stem cells in animal models can arrest intervertebral disc degeneration or even partially regenerate it and the effect is suggested to be dependent on the severity of the degeneration."[55]
References
- ^ Gerald L. Burke. "Backache: From Occiput to Coccyx". MacDonald Publishing. Retrieved 2013-02-14.
- ^ December 19, 2011. "Slipped discs: "they do not actually 'slip'..."". Emedicinehealth.com. Retrieved 2011-12-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Prolapsed disc". Spine-inc.com. Retrieved 2011-12-19.
- ^ Ehealthmd.com FAQ: "...the entire disc does not 'slip' out of place."
- ^ Gerald L. Burke. "Backache: From Occiput to Coccyx". MacDonald Publishing. Retrieved 2008-03-14.
- ^ Robert E Windsor (2006). "Frequency of asymptomatic cervical disc protrusions". Cervical Disc Injuries. eMedicine. Retrieved 2008-02-27.
- ^ Ernst CW, Stadnik TW, Peeters E, Breucq C, Osteaux MJ (2005). "Prevalence of annular tears and disc herniations on MR images of the cervical spine in symptom free volunteers". Eur J Radiol. 55 (3): 409–14. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.11.003. PMID 16129249.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Yuichiro Hirose; et al. (2008). "A Functional Polymorphism in THBS2 that Affects Alternative Splicing and MMP Binding Is Associated with Lumbar-Disc Herniation" (PDF). American Journal of Human Genetics. 82 (5): 1122–1129. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.03.013. PMC 2427305. PMID 18455130.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d Moore, Keith L. Moore, Anne M.R. Agur ; in collaboration with and with content provided by Arthur F. Dalley II ; with the expertise of medical illustrator Valerie Oxorn and the developmental assistance of Marion E. (2007). Essential clinical anatomy (3rd ed. ed.). Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 286. ISBN 0-7817-6274-X.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Neck and Shoulder Blade Pain".
- ^ Cervical herniation at eMedicine
- ^ Lumbar herniation at eMedicine
- ^ a b c Peng B, Wu W, Li Z, Guo J, Wang X (2007). "Chemical radiculitis". Pain. 127 (1–2): 11–6. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.06.034. PMID 16963186.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Marshall LL, Trethewie ER (1973). "Chemical irritation of nerve-root in disc prolapse". Lancet. 2 (7824): 320. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(73)90818-0. PMID 4124797.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ McCarron RF, Wimpee MW, Hudkins PG, Laros GS (1987). "The inflammatory effect of nucleus pulposus. A possible element in the pathogenesis of low-back pain". Spine. 12 (8): 760–4. doi:10.1097/00007632-198710000-00009. PMID 2961088.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Takahashi H, Suguro T, Okazima Y, Motegi M, Okada Y, Kakiuchi T (1996). "Inflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine". Spine. 21 (2): 218–24. doi:10.1097/00007632-199601150-00011. PMID 8720407.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Igarashi T, Kikuchi S, Shubayev V, Myers RR (2000). "2000 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies: Exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha mimics nucleus pulposus-induced neuropathology. Molecular, histologic, and behavioral comparisons in rats". Spine. 25 (23): 2975–80. doi:10.1097/00007632-200012010-00003. PMID 11145807.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sommer C, Schäfers M (2004). "Mechanisms of neuropathic pain: the role of cytokines". Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms. 1 (4): 441–8. doi:10.1016/j.ddmec.2004.11.018.
- ^ Igarashi A, Kikuchi S, Konno S, Olmarker K (2004). "Inflammatory cytokines released from the facet joint tissue in degenerative lumbar spinal disorders". Spine. 29 (19): 2091–5. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000141265.55411.30. PMID 15454697.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sakuma Y, Ohtori S, Miyagi M; et al. (2007). "Up-regulation of p55 TNF alpha-receptor in dorsal root ganglia neurons following lumbar facet joint injury in rats". Eur Spine J. 16 (8): 1273–8. doi:10.1007/s00586-007-0365-3. PMC 2200776. PMID 17468886.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Sekiguchi M, Kikuchi S, Myers RR (2004). "Experimental spinal stenosis: relationship between degree of cauda equina compression, neuropathology, and pain". Spine. 29 (10): 1105–11. doi:10.1097/00007632-200405150-00011. PMID 15131438.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Séguin CA, Pilliar RM, Roughley PJ, Kandel RA (2005). "Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates matrix production and catabolism in nucleus pulposus tissue". Spine. 30 (17): 1940–8. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000176188.40263.f9. PMID 16135983.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Waddell G, McCulloch JA, Kummel E, Venner RM (1980). "Nonorganic physical signs in low-back pain". Spine. 5 (2): 117–25. doi:10.1097/00007632-198003000-00005. PMID 6446157.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rabin A, Gerszten PC, Karausky P, Bunker CH, Potter DM, Welch WC (2007). "The sensitivity of the seated straight-leg raise test compared with the supine straight-leg raise test in patients presenting with magnetic resonance imaging evidence of lumbar nerve root compression". Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 88 (7): 840–3. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.04.016. PMID 17601462.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Deftereos SN; et al. (2009). "Localisation of cervical spinal cord compression by TMS and MRI". Funct Neurol. 24 (2): 99–105. PMID 19775538.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Chen R, Cros D, Curra A; et al. (2008). "The clinical diagnostic utility of transcranial magnetic stimulation: report of an IFCN committee". Clin Neurophysiol. 119 (3): 504–32. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2007.10.014. PMID 18063409.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Vroomen PC, de Krom MC, Knottnerus JA (2002). "Predicting the outcome of sciatica at short-term follow-up". Br J Gen Pract. 52 (475): 119–23. PMC 1314232. PMID 11887877.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Carragee EJ (2005). "Clinical practice. Persistent low back pain". N Engl J Med. 352 (18): 1891–8. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp042054. PMID 15872204.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Fredman B, Nun MB, Zohar E; et al. (1999). "Epidural steroids for treating "failed back surgery syndrome": is fluoroscopy really necessary?". Anesth Analg. 88 (2): 367–72. doi:10.1097/00000539-199902000-00027. PMID 9972758.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Landau WM, Nelson DA, Armon C, Argoff CE, Samuels J, Backonja MM (2007). "Assessment: use of epidural steroid injections to treat radicular lumbosacral pain: report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology. 69 (6): 614, author reply 614–5. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000278878.51713.c8. PMID 17679685.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Template:Ghahreman et al, Pain Medicine 2010; 11: 1149-68.
- ^ Template:Ghahreman et al. Predictors of response to transforaminal injection of steroids, Pain Medicine 2011;12
- ^ Abbasi A, Malhotra G, Malanga G, Elovic EP, Kahn S (2007). "Complications of interlaminar cervical epidural steroid injections: a review of the literature". Spine. 32 (19): 2144–51. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318145a360. PMID 17762818.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g "Rush University Medical Center". Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ Leininger B, Bronfort G, Evans R, Reiter T (2011). "Spinal manipulation or mobilization for radiculopathy: a systematic review". Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 22 (1): 105–25. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2010.11.002. PMID 21292148.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hahne AJ, Ford JJ, McMeeken JM (2010). "Conservative management of lumbar disc herniation with associated radiculopathy: a systematic review". Spine. 35 (11): E488–504. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181cc3f56. PMID 20421859.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Snelling, N (2006). "Spinal manipulation in patients with disc herniation: A critical review of risk and benefit". International Journal of Osteopathic Medicine. 9 (3): 77–84. doi:10.1016/j.ijosm.2006.08.001.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|author-name-separator=(help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help) - ^ Oliphant, D (2004). "Safety of Spinal Manipulation in the Treatment of Lumbar Disk Herniations: A Systematic Review and Risk Assessment". Journal of manipulative and physiological therapeutics. 27 (3): 197–210. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2003.12.023.
- ^ WHO guidelines on basic training and safety in chiropractic. "2.1 Absolute contraindications to spinal manipulative therapy", p. 21. WHO
- ^ Daniel, Dwain M (2007). "Non-surgical spinal decompression therapy: does the scientific literature support efficacy claims made in the advertising media?". Chiropractic and Osteopathy. 15 (1): 7. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-15-7. PMC 1887522. PMID 17511872.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|author-name-separator=(help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Be Wary of Spinal Decompression Therapy with VAX-D or Similar Devices, Stephen Barrett
- ^ Stern, Scott D. (2006). "Back Pain". In Janet Foltin, Harriet Lebowitz, Karen Davis (ed.). Symptom to Diagnosis: An Evidence-Based Guide. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. pp. 67–81. ISBN 0-07-146389-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Weinstein JN, Tosteson TD, Lurie JD; et al. (2006). "Surgical vs Nonoperative Treatment for Lumbar Disk Herniation: The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT): A Randomized Trial". JAMA. 296 (20): 2441–50. doi:10.1001/jama.296.20.2441. PMC 2553805. PMID 17119140.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD; et al. (2006). "Surgical vs Nonoperative Treatment for Lumbar Disk Herniation: The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) Observational Cohort". JAMA. 296 (20): 2451–9. doi:10.1001/jama.296.20.2451. PMC 2562254. PMID 17119141.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Peul WC, van Houwelingen HC, van den Hout WB; et al. (2007). "Surgery versus prolonged conservative treatment for sciatica". N Engl J Med. 356 (22): 2245–56. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa064039. PMID 17538084.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Minimally invasive procedures to treat herniated disk". Mayoclinic.com. 2010-12-18. Retrieved 2011-12-19.
- ^ Li J, Yan DL, Zhang ZH (2008). "Percutaneous cervical nucleoplasty in the treatment of cervical disc herniation". Eur Spine J. 17 (12): 1664–96. doi:10.1007/s00586-008-0786-7. PMC 2587670. PMID 18830638.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Gąsiorowski, A. (2012). "The role of weight training in treating farmers with lumbar discopathy". Ann Agric Environ Med. 19 (4): 817–20. PMID 23311814.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Feine, JS.; Lund, JP. (1997). "An assessment of the efficacy of physical therapy and physical modalities for the control of chronic musculoskeletal pain". Pain. 71 (1): 5–23. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(96)03287-3. PMID 9200169.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Floyd, R. T. (2009). Manual of structural kinesiolgy. (17 ed.). New York, NY: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
- ^ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia: Herniated nucleus pulposus Frequency
- ^ Jacobs WC, Arts MP, van Tulder MW; et al. (2012). "Surgical techniques for sciatica due to herniated disc, a systematic review". Eur Spine J. 21 (11): 2232–51. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2422-9. PMC 3481105. PMID 22814567.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Marrone, Lisa (2008). Overcoming Back and Neck Pain. Harvest House. p. 37.
- ^ Marrone, Lisa (2008). Overcoming Back and Neck Pain. Harvest House. p. 31.
- ^ Leung VY, Chan D, Cheung KM (2006). "Regeneration of intervertebral disc by mesenchymal stem cells: potentials, limitations, and future direction". Eur Spine J. 15 Suppl 3 (Suppl 3): S406–13. doi:10.1007/s00586-006-0183-z. PMC 2335386. PMID 16845553.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)